Class 10 SELINA Solutions Physics Chapter 4 - Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces Exercise Ex. 4A
Solution 1
The change in the direction of the path of light, when it passes from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, is called refraction of light.
Solution 2
Diagram showing the refraction of light from Air to glass
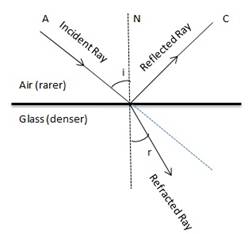
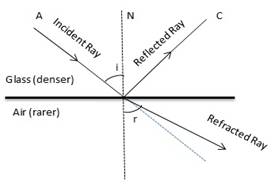
Diagram showing the refraction of light from Glass to Air
Solution 3
The ray of light which is incident normally on a plane glass slab passes undeviated. That is such a ray suffers no bending at the surface because here the angle of incidence is ![]() . Thus if angle of incidence
. Thus if angle of incidence![]() , then the angle of refraction
, then the angle of refraction![]() . And the angle of deviation of the ray will also be
. And the angle of deviation of the ray will also be ![]() .
.
Solution 4
Yes it will. When the medium changes, the speed of light changes.
Solution 5
The refraction of light (or change in the direction of path of light in other medium) occurs because light travels with different speeds in different media. When a ray of light passes from one medium to another, its direction (except for![]() ) changes because of change in its speed.
) changes because of change in its speed.
Solution 6
Air is a rarer medium while water is denser than air with refractive index of 1.33. Therefore when light ray will travel from air to water it will bend towards the normal.
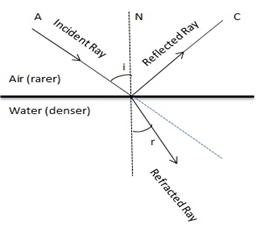
Solution 7
Speed, intensity and wavelength
Solution 8
The Snell's laws of refraction are:
1.The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
2.The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant for the pair of the given media.
![]()
where ![]() is known as the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium.
is known as the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium.
Solution 9
The refractive index of second medium with respect to first medium is defined as the ratio of the sine of angle of incidence in the first medium to the sine of the angle of refraction in the second medium.
Refractive index of a medium is always greater than 1 (it cannot be less than 1) because the speed of light in any medium is always less than that in vacuum.
Solution 10
(a) Speed of light depends on medium not on wavelength hence speed will be same for both.
(b) Denser medium has a higher refractive index and therefore the speed of light in such medium is lower in comparison to the speed of light in a medium which has a lower refractive index.
Solution 11
Refractive index of water,![]()
Refractive index of air, ![]()
Refractive index of glass,![]()
This implies that![]()
The speed of light decreases when it enters from a rarer medium to denser medium and increases when it enters from a denser medium to rarer medium.
Therefore, the speed of light increases when light ray passes from water to air and the speed of light decreases when light ray passes from water to glass.
Solution 12
When the speed increases it means that the refractive index of the medium is less than that of water.
When the speed decreases it means that the refractive index of the medium is greater than that of water.
Solution 13
The refractive index of glass is 1.5 for white light means white light travels in air 1.5 times faster than in glass.
Solution 14
(a) The relation between speed of light in air c and in glass v is given by
![]()
(b) The wavelength of light in glass (![]() )
)
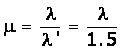
Solution 15
The refractive index will be different. The speed of blue light in glass is less than that of red light and refractive index of glass is
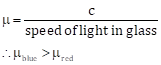
Solution 16(a)
(i) The least for red colour and (ii) the most for violet colour.
Solution 16(b)
Red colour travels the fastest as its wavelength is the highest.
Solution 17
The two factors on which the refractive index of a medium depends are:
1) Nature of a medium i.e. its optical density (e.g. ![]() =1.5,
=1.5, ![]() =1.33) - Smaller the speed of light in a medium relative to air, higher is the refractive index of that medium.
=1.33) - Smaller the speed of light in a medium relative to air, higher is the refractive index of that medium.
2) Physical condition such as temperature - with increase in temperature, the speed of light in medium increases, so the refractive index of medium decreases.
Solution 18
Refractive index of a medium decreases with increase in wavelength of light.
Refractive index of a medium for violet light (least wavelength) is greater than that for red light (greatest wavelength).
Solution 19
Refractive index of a medium decreases with the increase in temperature.
With increase in temperature, the speed of light in that medium increases; thus, the refractive index (= velocity of light in vacuum/velocity of light in medium) decreases.
Solution 20
(i) The glass piece is not seen when the refractive index of liquid becomes equal to the refractive index of glass.
(ii) Light of a single colour is used because the refractive index of a medium (glass or liquid) is different for the light of different colours.
Solution 21
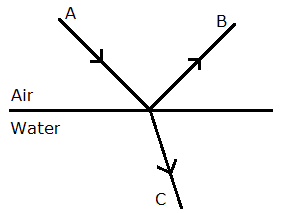
- The angles of incidence and refraction are related to each other by Snell's law relation sin i/sin r = μw.
Solution 22
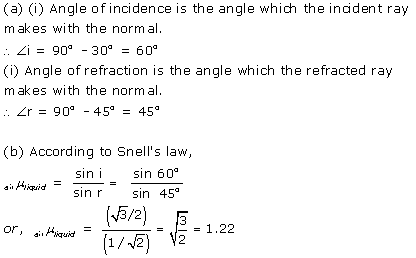
Solution 23
Refractive index of glass with respect to water![]() is given by
is given by
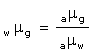
Solution 24
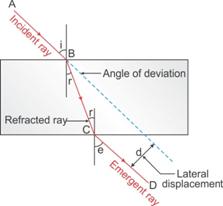
The perpendicular distance between the path of emergent ray and the direction of the incident ray is called the lateral displacement.
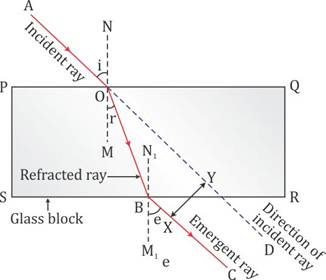
In the figure above, XY is the perpendicular distance or the lateral displacement.
Solution 25
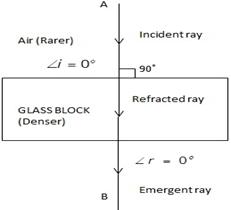
Case (i) when angle of incidence is 0o.
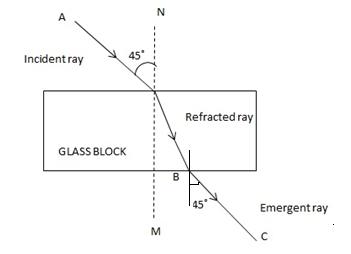
Case (ii) When angle of incidence is 45o.
Solution 26
(a)The complete path of incident ray in glass block is drawn in figure below.
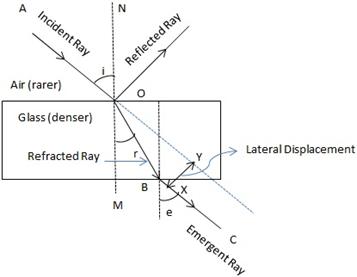
(b)Angle of incidence (i) and angle of refraction (r) are marked in part (a).
Refractive index (![]() ) of glass is related to the angles as
) of glass is related to the angles as
![]()
(c)Angle of emergence (e) is marked in part (a)
The two angles are related to each other by the relation
![]()
(d)Incident ray and emergent ray are parallel to each other.
(e)Lateral displacement is indicated in the figure by XY.
Solution 27
(a) Refractive index of the liquid =
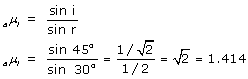
(b)
(c)
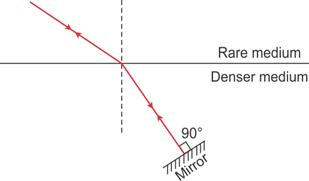
Here the 'Principle of Reversibility' is used.
Solution 28
When a ray of light from lighted candle fall on the surface of a thick plane glass mirror, a small part of light (nearly 4%) is reflected forming first image which is faint virtual image, while a large part of light (nearly 96%) is refracted inside the glass. This ray is now strongly reflected back by the silvered surface inside the glass. This ray is then partially refracted in air and this refracted ray forms another virtual image. This image is the brightest image because it is due to the light suffering a strong reflection at the silver surface.
Solution 29
(a) When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, its speed decreases
(b) When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, its speed increases
(c) The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2. The refractive index of air with respect to glass will be 2/3
Solution 1 (MCQ)
(b) bends towards the normal.
Reason: As the speed of light decreases in the denser medium, it bends towards the normal.
Solution 2 (MCQ)
(a) 0°
Reason: A ray of light which is incident normally (i.e. at angle of incidence = 0°) on the surface separating the two media, passes undeviated.
Solution 3 (MCQ)
(c) Diamond
Reason: As the speed of light in diamond is the least, diamond has the highest refractive index.
Solution 1 (Num)

Solution 2 (Num)

Solution 3 (Num)
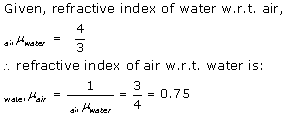
Solution 4 (Num)
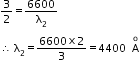
Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces Exercise Ex. 4B
Solution 1
A prism is a transparent refracting medium bounded by five plane surfaces inclined at some angle.
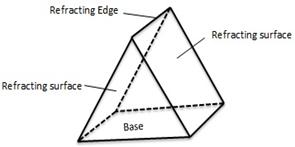
Solution 2
(a)
(b) For the prism, the emergent ray is not parallel to the incident ray but for the glass block it is parallel. This is because, in a prism, refraction takes place at two inclined surfaces while in a glass block refraction takes place at two parallel surfaces.
Solution 3
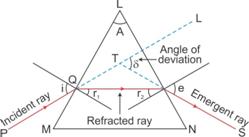
The angle between the direction of incident ray and the emergent ray, is called the angle of deviation.
Solution 4
Angle of deviation is the angle which the emergent ray makes with the direction of incident ray.
Solution 5
In a prism the ray of light suffers refraction at two faces. The prism produces a deviation at the first surface and another deviation at the second surface. Thus a prism produces a deviation in the path of light.
The value of the angle of deviation (or the deviation produced by a prism) depends on the following four factors:
(a)the angle of incidence (i),
(b)the material of prism(i.e., on refractive index ![]() ),
),
(c)the angle of prism (A),
(d)The colour or wavelength (![]() ) of light used.
) of light used.
Solution 6(a)
As the angle of incidence increases, the angle of deviation decreases first and reaches to a minimum value (![]() ) for a certain angle of incidence. By further increasing the angle of incidence, the angle of deviation is found to increase.
) for a certain angle of incidence. By further increasing the angle of incidence, the angle of deviation is found to increase.
Variation of angle of deviation (![]() ) with angle of incidence(i):
) with angle of incidence(i):
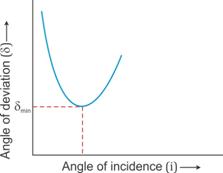
Solution 6(b)
For a given prism and given colour of light, angle of minimum deviation is unique since only one horizontal line can be drawn parallel to the i-axis at the lowest point of i-δ curve.
Solution 7
False.
With the increase in the angle of incidence, the deviation produced by a prism first decreases and then increases.
A given prism deviates the violet light most and the red light least.
Solution 8
(i) For a given angle of incidence, the prism with a higher refractive index produces a greater deviation than a prism with a lower refractive index.
(ii) The refractive index of a medium is different for light of different colours. It increases with decrease in wavelength. Thus, the refractive index of the material of prism is maximum for violet and least for red light. Hence, the prism deviates violet light the most and red light the least, i.e., δviolet > δred.
Solution 9
Changes in the angle of deviation as we increase
(i) The wavelength of incident light
As we increase the wavelength, angle of deviation decreases.
(ii) The refracting angle of the prism
The angle of deviation increases with the increase in the angle of prism.
Solution 10
The relation between the angle of incident (i), angle of emergence (e), angle of prism (A) and angle of deviation (![]() ) for a ray of light passing through an equilateral prism is
) for a ray of light passing through an equilateral prism is
![]()
Solution 11
(i) i2 = i1
(ii) Angle of deviation is minimum
Explanation: In minimum deviation position, the refracted ray inside the prism travels parallel to it if the prism is equilateral and the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence.
Solution 12
In case of an equilateral prism, when the prism is in the position of minimum deviation![]() , the angle of incidence i1 is equal to the angle of emergence i2.
, the angle of incidence i1 is equal to the angle of emergence i2.
![]()
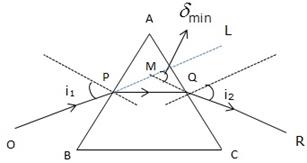
Solution 13
(i) As the ray is suffering minimum deviation in an equilateral glass prism so
![]()
![]()
(ii) If the angle of incidence is changed to
(a) 30o, the angle of deviation will be more than 36o.
(b) 60o, the angle of deviation will be more than 36o.
Solution 14
(i) Violet colour will deviate the most and (ii) Red colour will deviate the least.
Solution 15
B made of flint glass. Because it has higher refractive index.
Solution 16
The angle of deviation (![]() ) increases with the increase in the angle of prism (A).
) increases with the increase in the angle of prism (A).
Solution 17
Let two rays OA and OL from a source O are incident on the prism. They are refracted along AB and LM from first face of the prism. These two rays again refract from the second face of the prism emerge out along BC and MN respectively such that they appear to come from I.
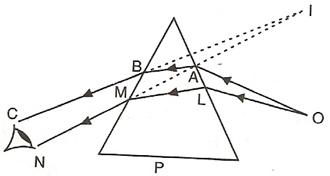
Thus, observer sees the object O raised to the position I.
Solution 18
(a)If the incident ray normal to prism then angle of incidence is 0o.
(b)In this case the angle of refraction from the first face r1= 0o.
(c)As the prism is equilateral so A=60o and r1=0o. So at the second face of the prism, the angle of incidence will be 60o.
(d)No the light will not suffer minimum deviation.
Solution 19
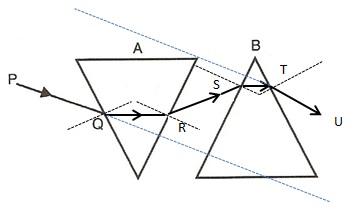
Solution 1 (MCQ)
(c) Bends at both the surfaces of prism towards its base.
Solution 2 (MCQ)
(d) Size of prism
The deviation produced by the prism does not depend on the size of prism.
Solution 1 (Num)

Solution 2 (Num)

Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces Exercise Ex. 4C
Solution 1
Relation
of refractive index ![]() with real and
apparent depths
with real and
apparent depths
![]()
Solution 2
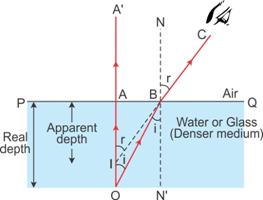
Consider a ray of light incident normally along OA. It passes straight along OAA'. Consider another ray from O (the object) incident at an angle i along OB. This ray gets refracted and passes along BC. On producing this ray BC backwards, it appears to come from the point I, and hence, AI represents the apparent depth, which is less than the real depth AO.

Since the point B is very close to point A, i.e. the object is viewed from a point vertically above the object,
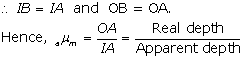
Solution 3
The depth of the tank appears to be lesser than its real depth. This happens due to the refraction of light from a denser medium (water) to a rarer medium.
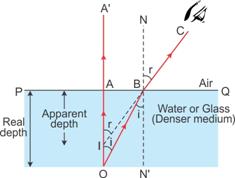
Solution 4
'Refraction of light' is responsible for this property.
When light coming from denser medium enters rarer medium, it is bent away from the normal.
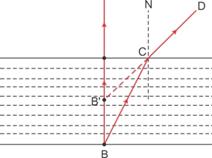
Let any object B is at the bottom of a pond. Consider a light ray BC from the object that moves from water to air. After refraction from the water surface, the ray moves away from the normal N along the path CD. The produce of CD appears from the point B' and a virtual image of the object at B appears at B'.
![]()
Solution 5
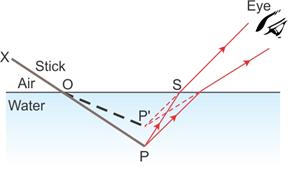
A stick partially immersed in water in a glass container appears bent or raised as shown in figure above. This happens because the rays appear to come from P' (which is the virtual image of the tip P of the stick) due to refraction from denser medium (water) to rarer medium (air) at the surface separating two media.
Solution 6
The plant will look taller than its actual height.
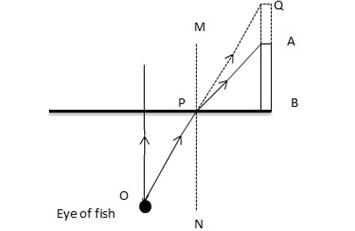
Let the fish is looking from the point O. As the ray OP emerges out from water to air, it will bend away from the normal MN because air is a rarer medium in comparison of water. But if we extend ray OP then it will meet at Q due to which the plant AB will look taller than its actual height.
Solution 7
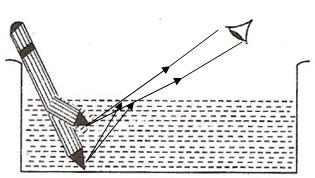
(i)Part of the pencil which is immersed in water will look short and raised up.
(ii)The phenomena which is responsible for the above observation is refraction of light.
(iii)The required figure is
Solution 8
The factors on which the magnitude of shift depends are:
(a)The refractive index of the medium,
(b)The thickness of the denser medium and
(c)The colour (or wavelength) of incident light.
The shift increase with the increase in the refractive index of medium. It also increases with the increase in thickness of denser medium but the shift decreases with the increases in the wavelength of light used.
Solution 1 (MCQ)
(a) Refraction of light
Hint: When a ray of light travels from denser to rarer medium, it moves away from the normal.
Solution 2 (MCQ)
(b) violet light.
Hint: The shift is maximum for violet light because the refractive index of glass is the most for the violet light.
Solution 1 (Num)
Given that,
Apparent depth = 3 m
refraction index of water, μw = 4/3
Now,
Real depth = μw × apparent depth
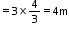
Solution 2 (Num)
Refractive index of the water, μw = 4/3
Real depth at which the coin is placed = 16 cm
Shift in the image =?
Now,
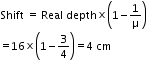
Solution 3 (Num)
Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces Exercise Ex. 4D
Solution 1
Critical angle: The angle of incidence in the denser medium corresponding to which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium is 90o is called the critical angle.
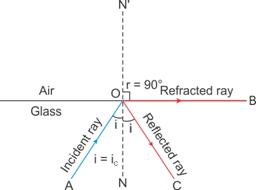
Solution 2
The critical angle is related to the refractive index of a medium by the relation
![]()
Solution 3
(a) The critical angle for glass-air surface is
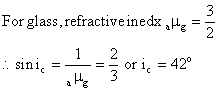
(b) The critical angle for water-air surface is

Solution 4
The critical angle for diamond is 24°. This implies that at an incident angle of 24° within the diamond the angle of refraction in the air will be 90°. And if incident angle will be more than this angle then the ray will suffer total internal reflection without any refraction.
Solution 5
When a ray is incident from a denser medium to a rarer medium at angle equal to critical angle (![]() ), the angle of refraction becomes 90°.
), the angle of refraction becomes 90°.
Solution 6
The factors which affect the critical angle are:
(i)The colour (or wavelength) of light, and
(ii)The temperature
(i)Effect of colour of light: The critical angle for a pair of media is less for the violet light and more for the red light. Thus critical angle increases with increase in wavelength of light.
(ii)Effect of temperature: The critical angle increases with increase in temperature because on increasing the temperature of medium, its refractive index decreases.
Solution 7
As the wavelength decreases (or increases) refractive index becomes more (or less) and critical angle becomes less (or more).
(i)For red light the critical angle will be more than 45° and
(ii)For blue light the critical angle will be less than 45°.
Solution 8
The critical angle of red light is higher that of green light.
Solution 9
(a)Total internal reflection: It is the phenomenon when a ray of light travelling in a denser medium, is incident at the surface of a rarer medium such that the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle for the pair of media, the ray is totally reflected back into the denser medium.
(b)The two necessary conditions for total internal reflection are:
i.The light must travel from a denser medium to a rarer medium.
ii.The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle for the pair of media.
(c)When incidence angle is more than critical angle i.e., in case of total internal reflection.
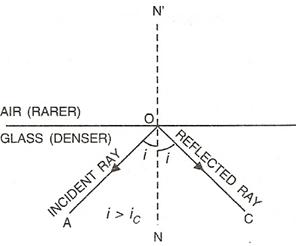
Solution 10
(a)Total internal reflection occurs when a ray of light passes from a denser medium to a rarer medium.
(b)Critical angle is the angle of incidence in denser medium for which the angle of refraction in rarer medium is 90°.
Solution 11
True
Solution 12
(a)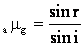
(b)If refractive angle,![]() , the corresponding angle of incidence, i will be equal to critical angle.
, the corresponding angle of incidence, i will be equal to critical angle.
(c)If the angle of incidenceexceeds the value of i obtained in part (b) (i.e., critical angle), total internal reflection will occur.
Solution 13
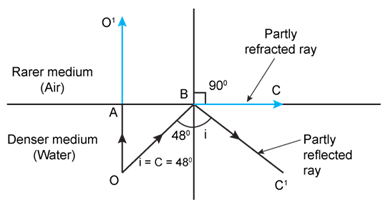
The necessary conditions for the total internal reflection to occur are
(i) Light must travel from a denser medium to a rarer medium.
(ii) The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle.
In this case, the angle of incidence![]() .
.
Solution 14
(a)
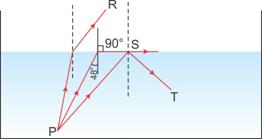
(b) Rays A and B exhibit the phenomenon of 'refraction of light'.
Rays C exhibits the phenomenon of 'total internal reflection'.
Solution 15
(a) Critical angle
Hint: The angle of incidence in the denser medium for which the angle of refraction in rarer medium is 90o is called the critical angle.
(b) 90o
(c) Total internal reflection.
Hint: When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, the phenomenon of total internal reflection occurs due to which the ray of light is not refracted but is reflected back in the same medium.
(d) For the ray PR, the angle of incidence is less than the critical angle (i.e. ![]() ); hence, at the interface of two media as per the laws of reflection, ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction.
); hence, at the interface of two media as per the laws of reflection, ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction.
(e)
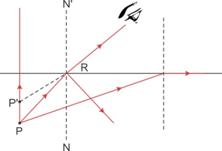
Solution 16
(a)
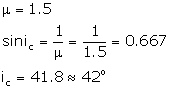
(b)
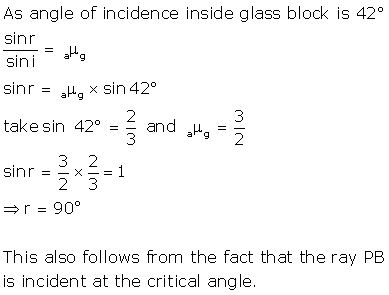
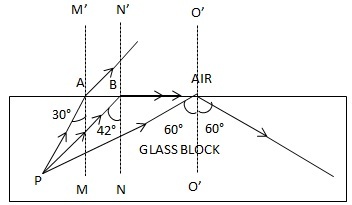
Solution 17
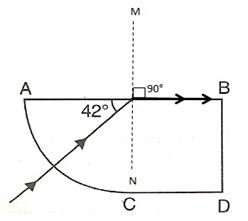
The angle of refraction will be 90° because the ray is incident on the glass at its critical angle.
Solution 18
A prism having an angle of 90° between its two refracting surfaces and the other two angles each equal to 45°, is called a total reflecting prism. The light incident normally on any of its faces, suffers total internal reflection inside the prism.
Due to this behavior, a total reflecting prism is used to produce following three actions:
(a)To deviate a ray of light through 90°,
(b)To deviate a ray of light through 180°, and
(c)To erect the inverted image without producing deviation in its path.
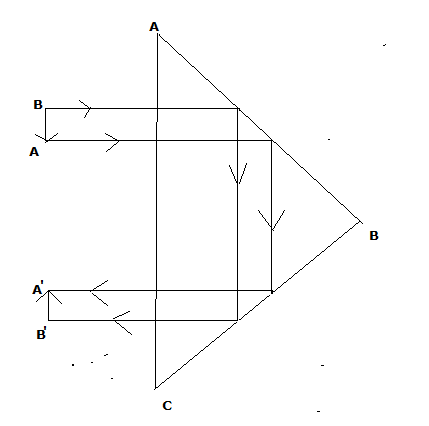
It is an erecting prism which is used to erect the inverted image without producing deviation in its path.
Solution 19
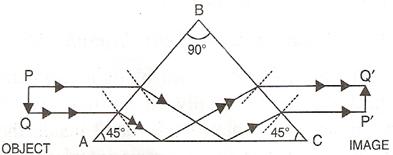
9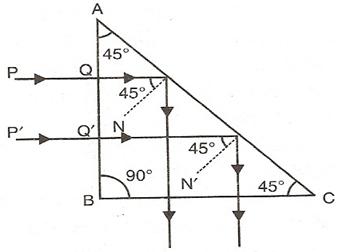
As shown in diagram, a beam of light is incident on face AB of the prism normally so it passes undeviated and strikes the face AC where it makes an angle of 45° with the normal to AC. Because here the incident angle is more than critical angle so rays suffer total internal reflection and reflect at angle of 45°. The beam then strikes face BC, where it is incident normally and so passes undeviated. As a result the incident beam gets deviated through 90°.
Such a prism is used in periscope.
Solution 20
(a)The angle of incidence at the face AC is 45° and angle of incidence at the face BC is 0°.
(b)The ray suffers total internal reflection at the face AC.
Solution 21
Solution 22
(a)
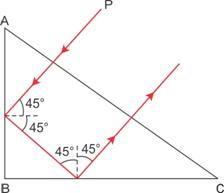
(b) Angle of deviation = 180o
(c) Prism binocular
Solution 23
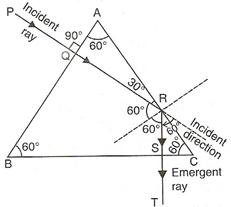
(a)At the face AB,![]() and at the face AC,
and at the face AC,![]() .
.
(b)At the face AB – refraction,
At the face AB – total internal reflection,
At the face BC – refraction.
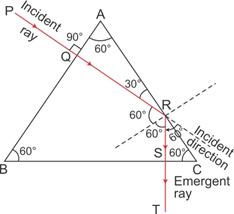
Solution 24
Incidence (on the boundary BC) is 60° which is more than its critical angle (42°). Thus this incident light ray (QR) does not enter into the next medium, instead it undergoes total internal reflection. When this reflected light ray (RS) reaches the side AC, its angle of incidence is 0°. Again, it does not undergo any refraction, which causes the angle of emergence to become 0°.
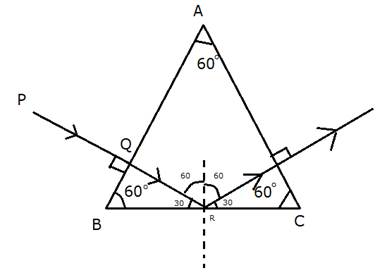
Solution 25
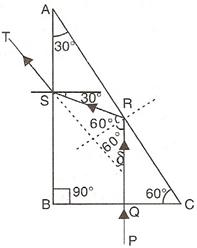
Solution 26
A total reflecting prism can be used to turn a ray of light by 180°. The following diagram can make it further clear.
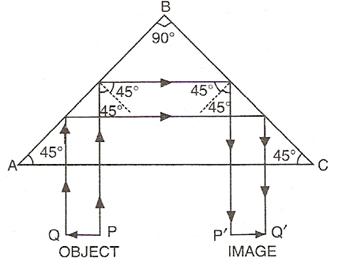
This action of prism is used in binocular.
Solution 27
When total internal reflection occurs from a prism, the entire incident light (100%) is reflected back into the denser medium. Whereas in ordinary reflection from a plane mirror, some light is refracted and absorbed so the reflection is partial.
Solution 28
A total reflecting prism gives us an image much brighter than that obtained by using a plane mirror.
Solution 29
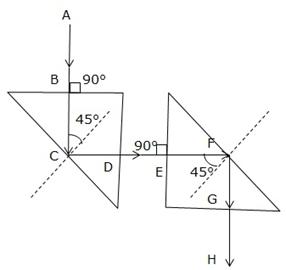
Solution 30
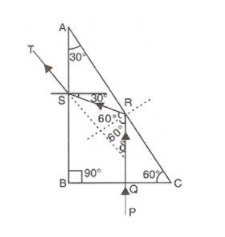
Solution 31
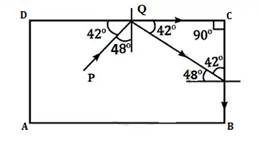
Solution 1 (MCQ)
(c) 42°
Solution 2 (MCQ)
(d) 90°
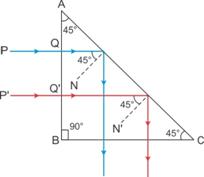
Solution 3 (MCQ)
(b) 60°
Hint: