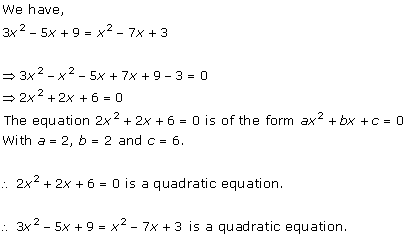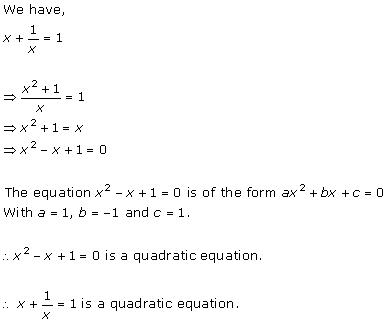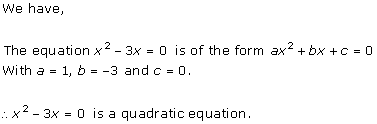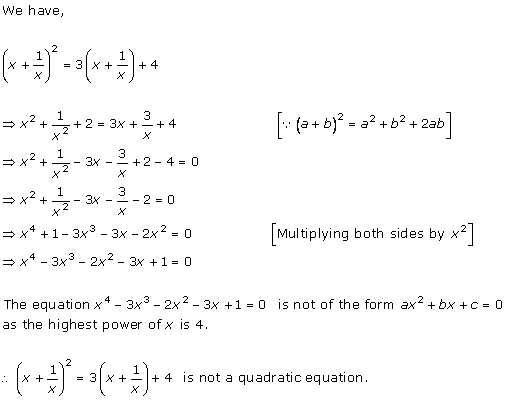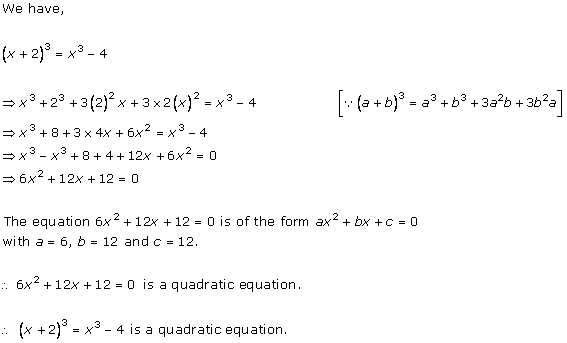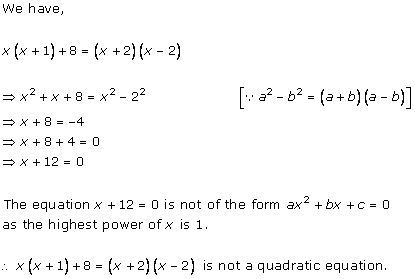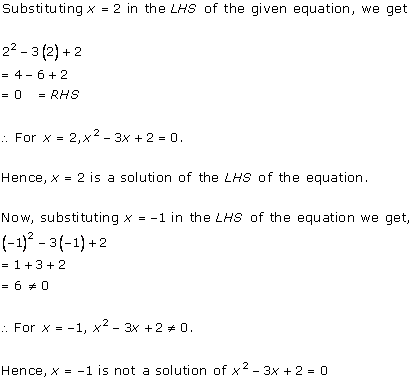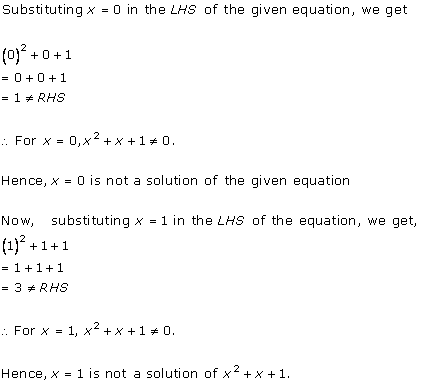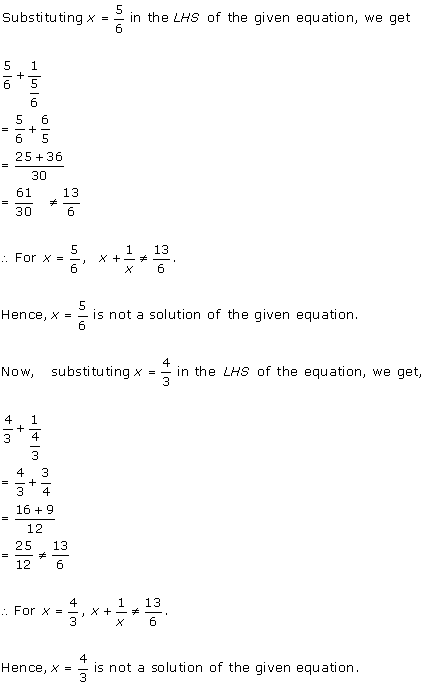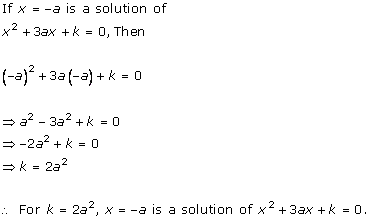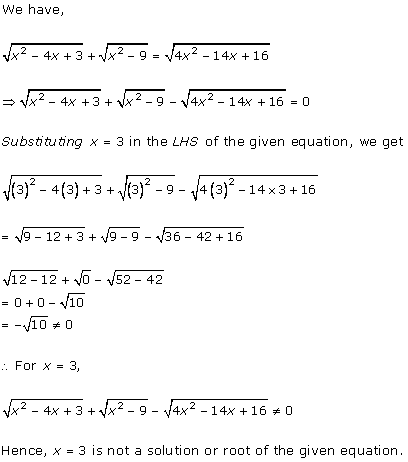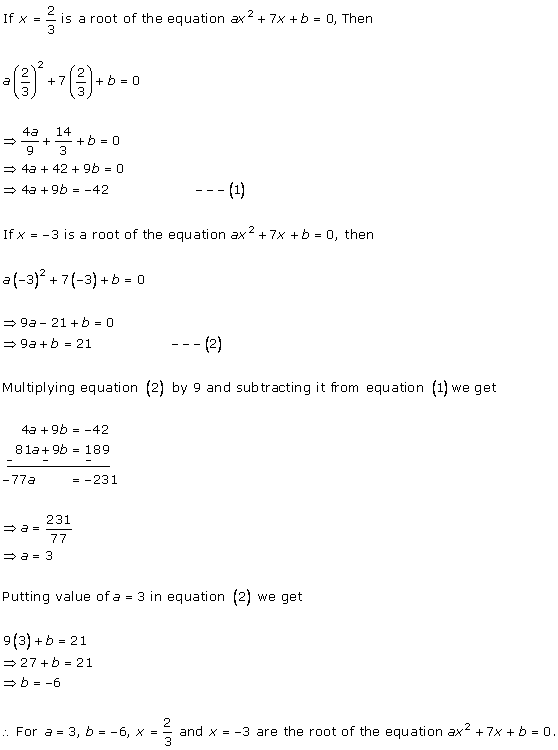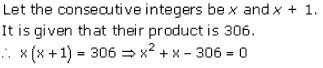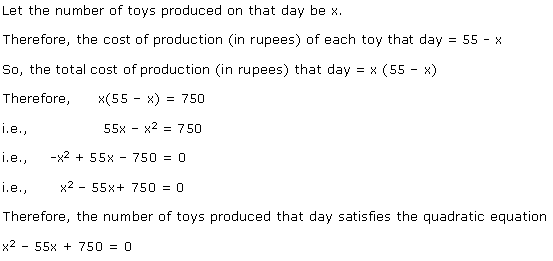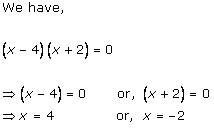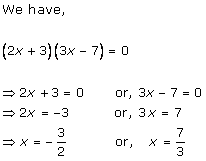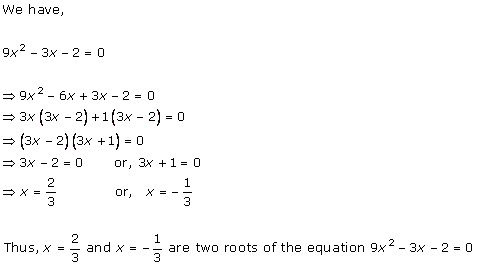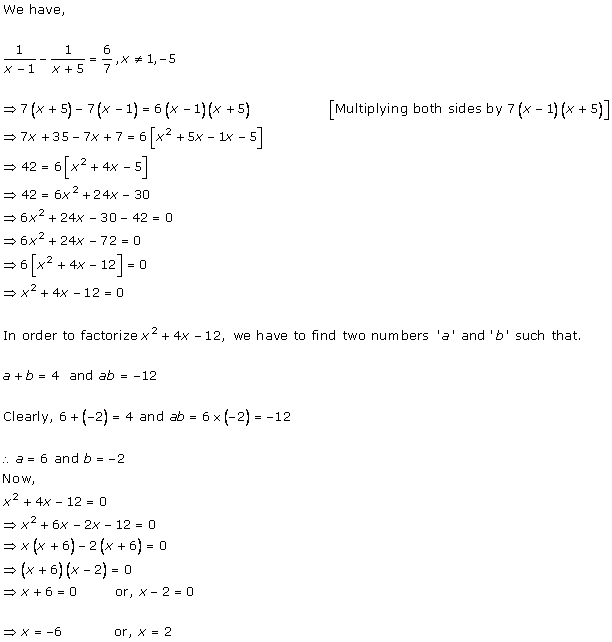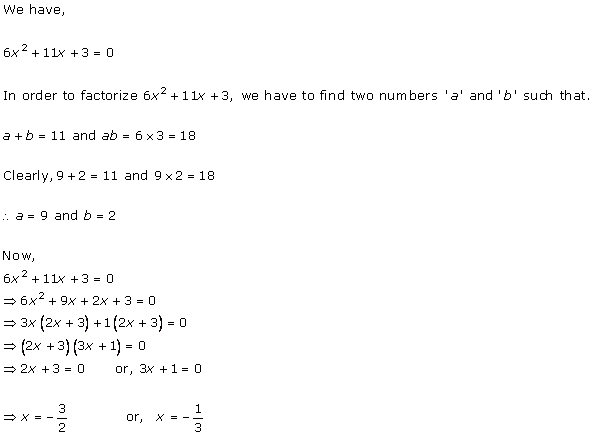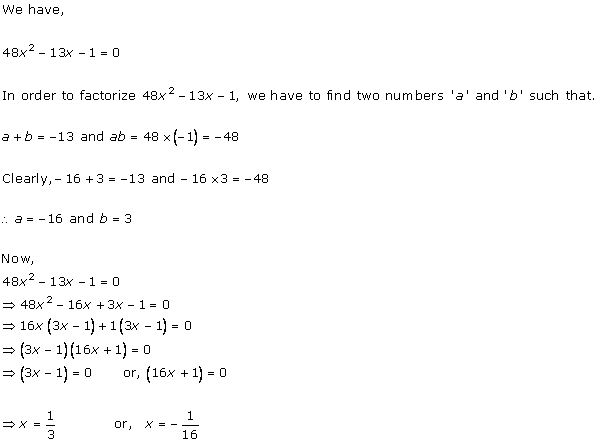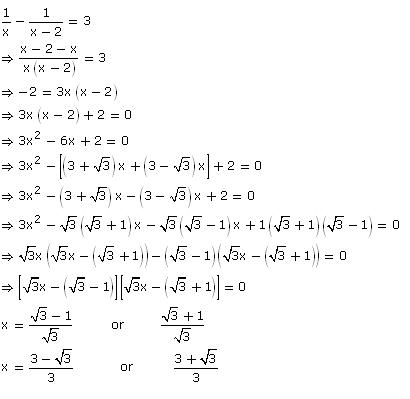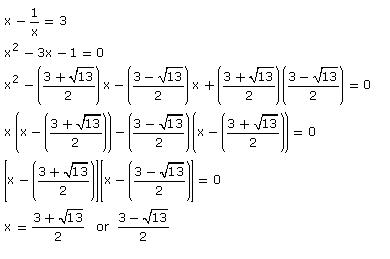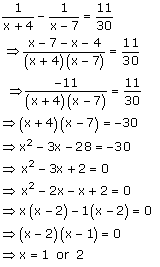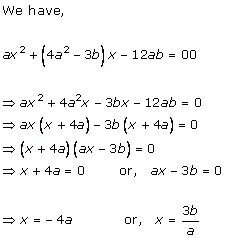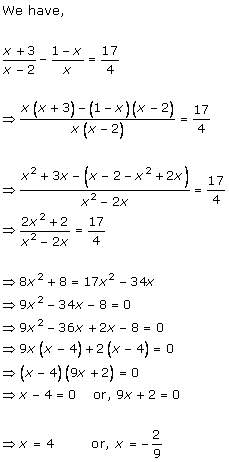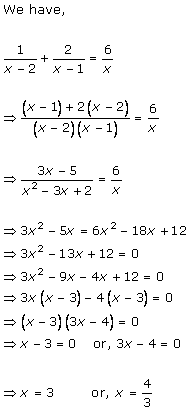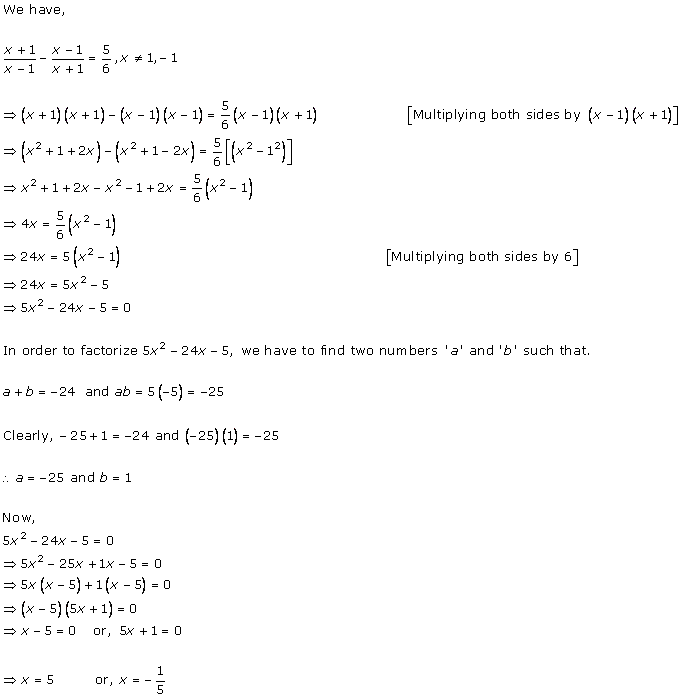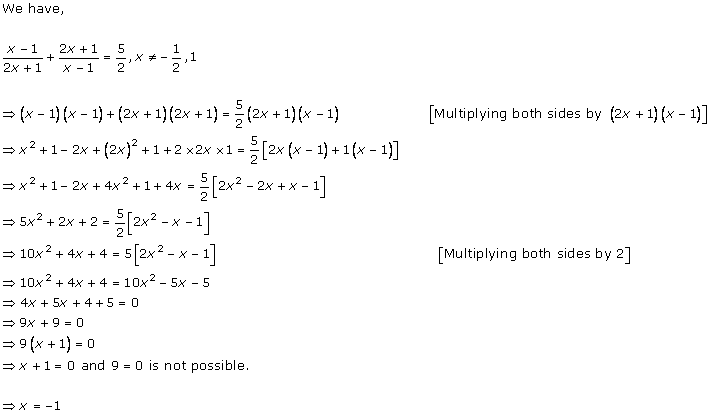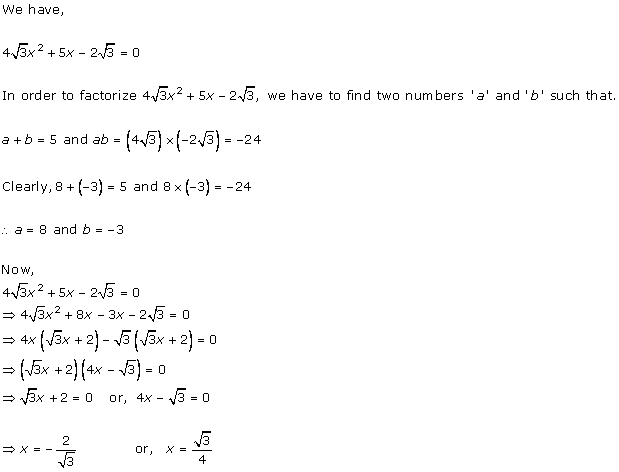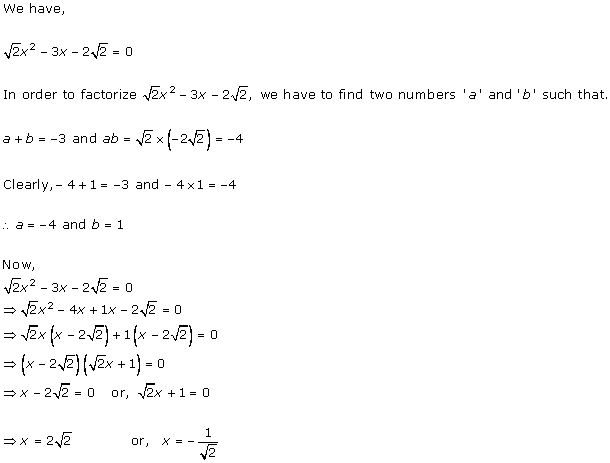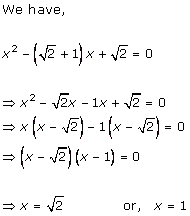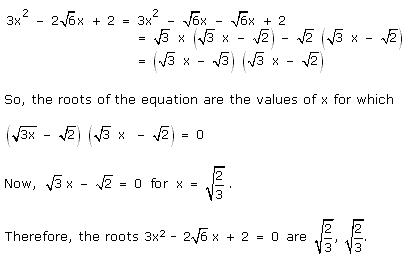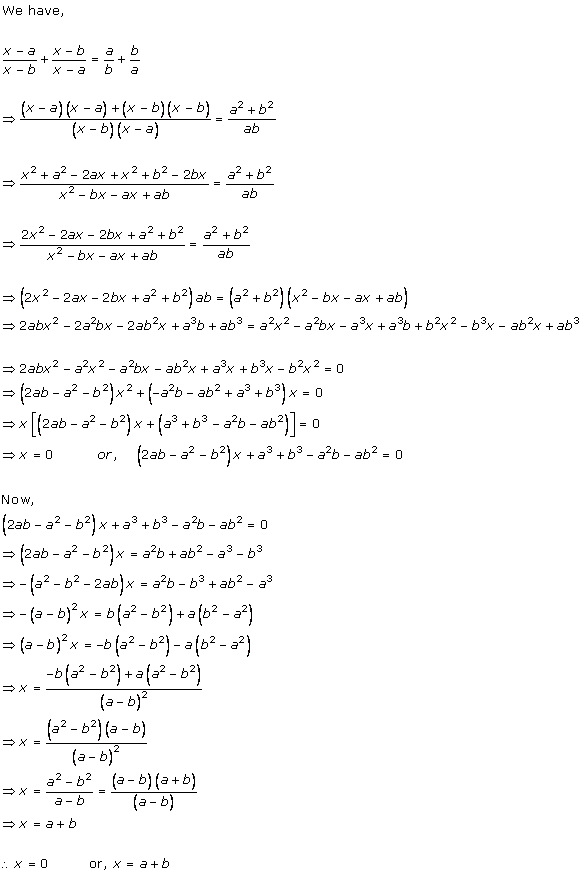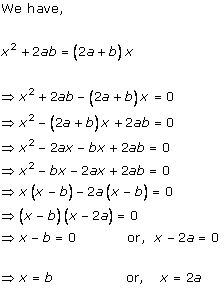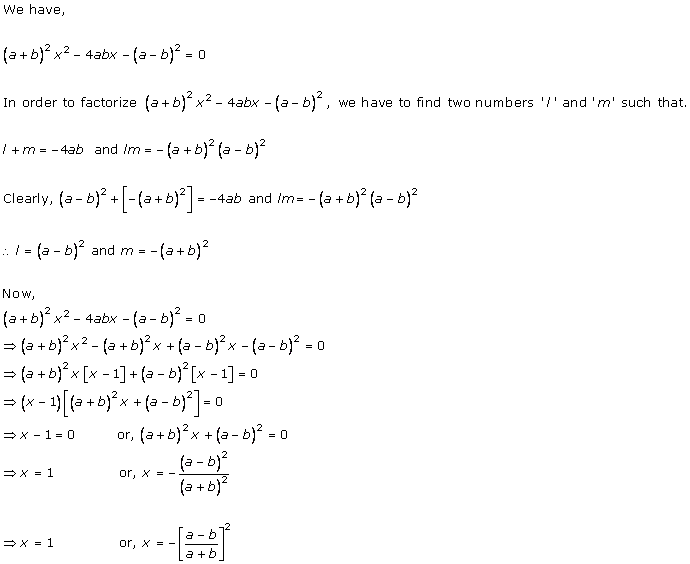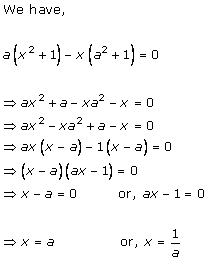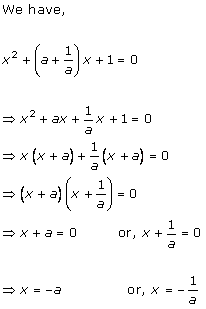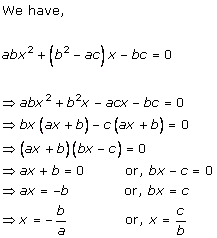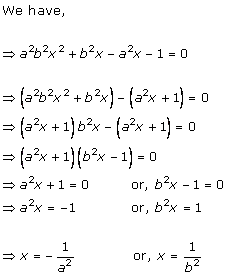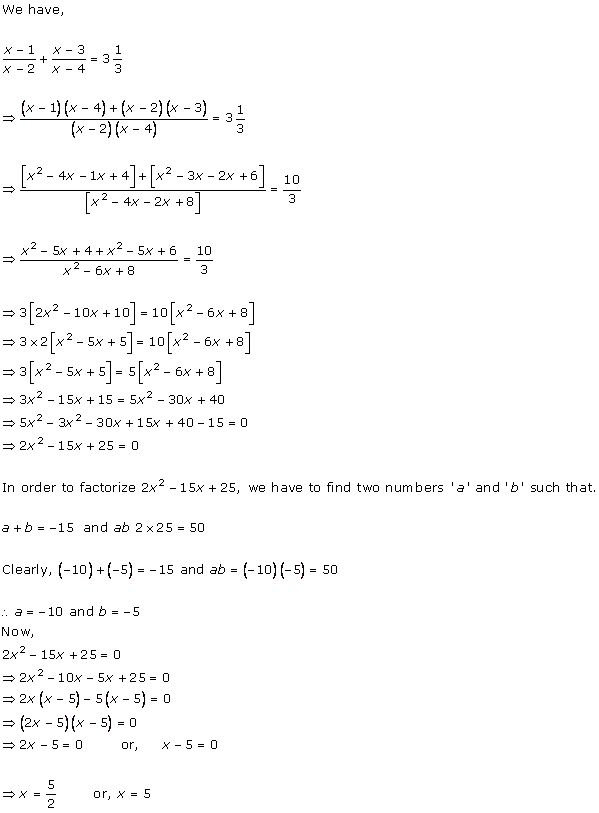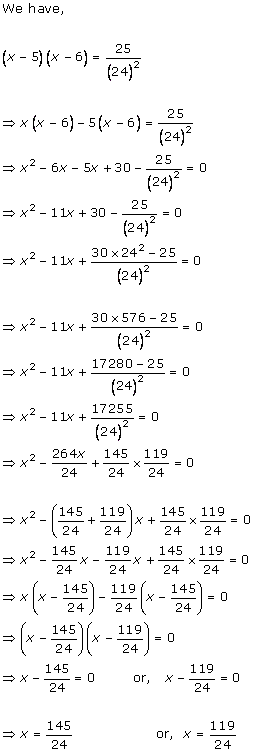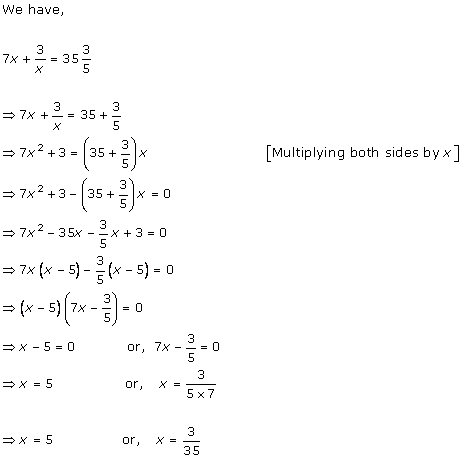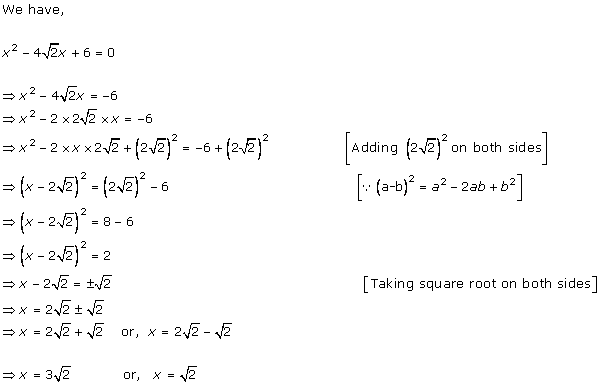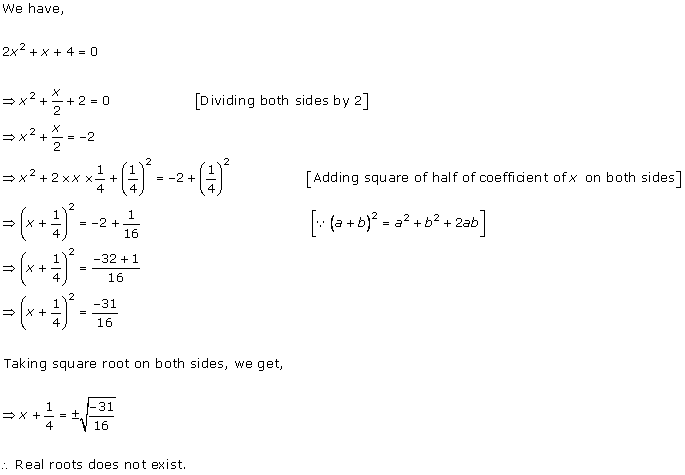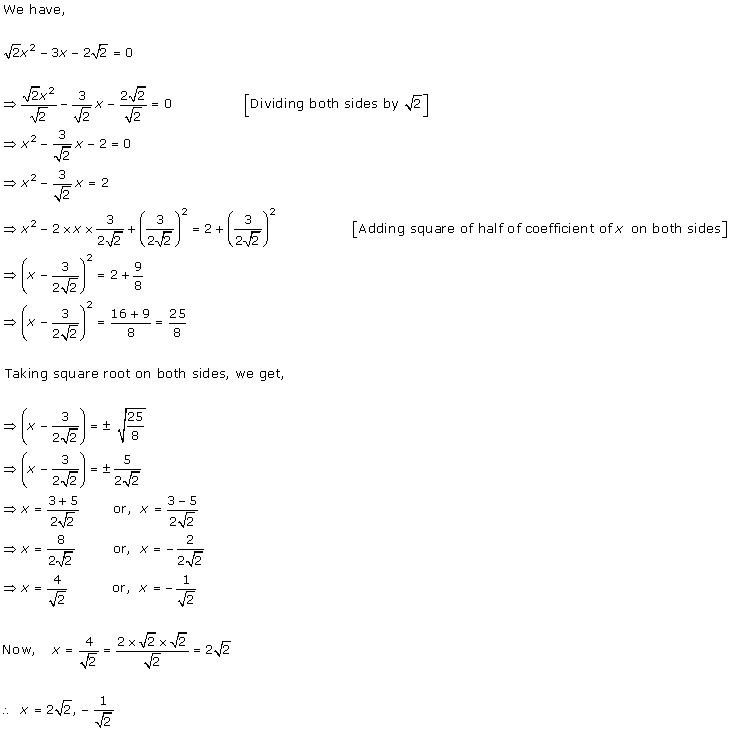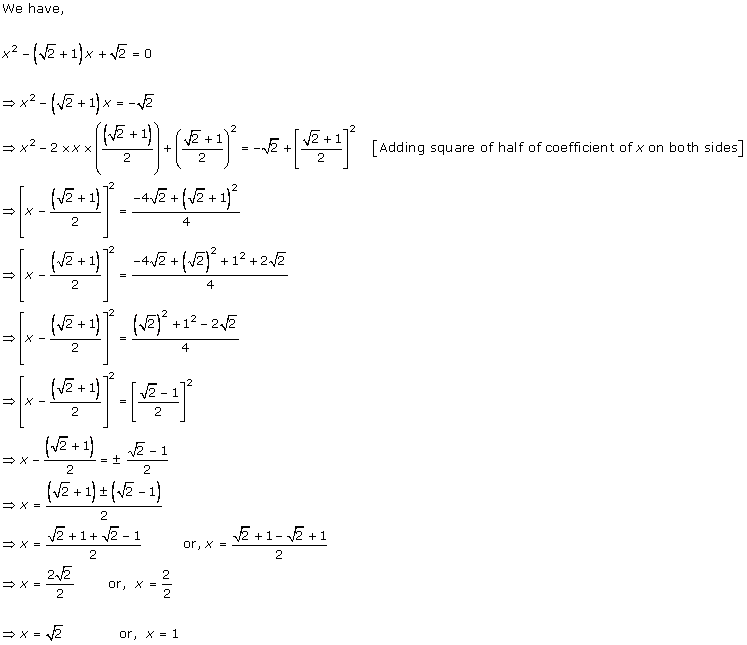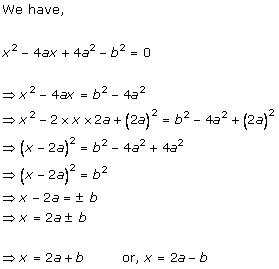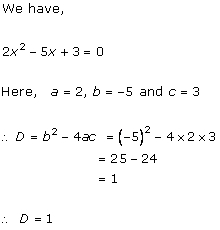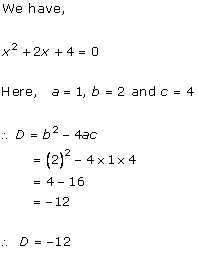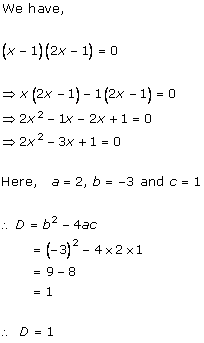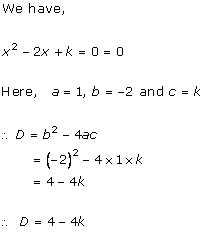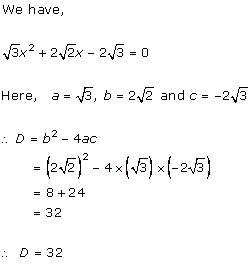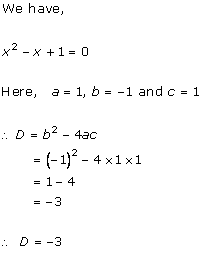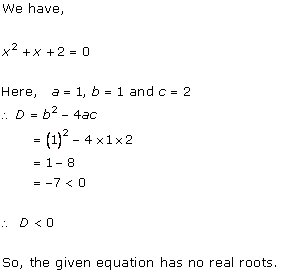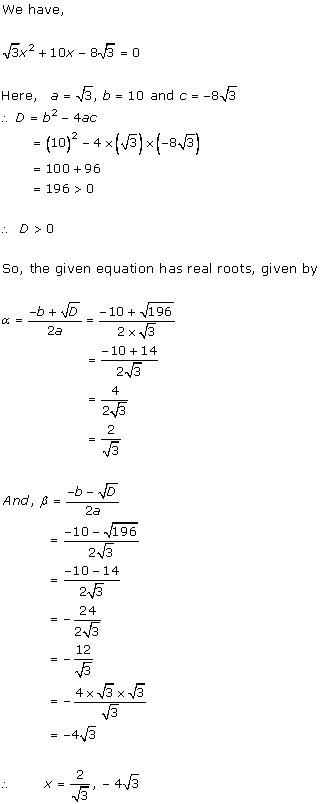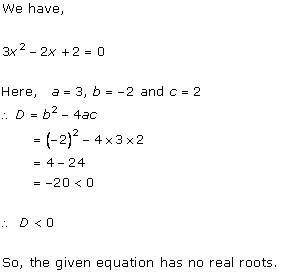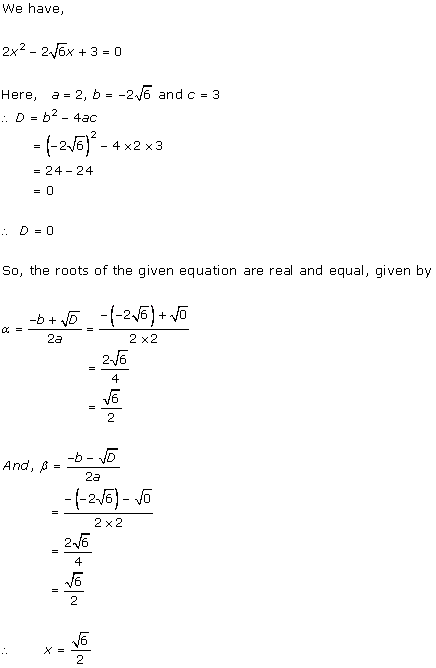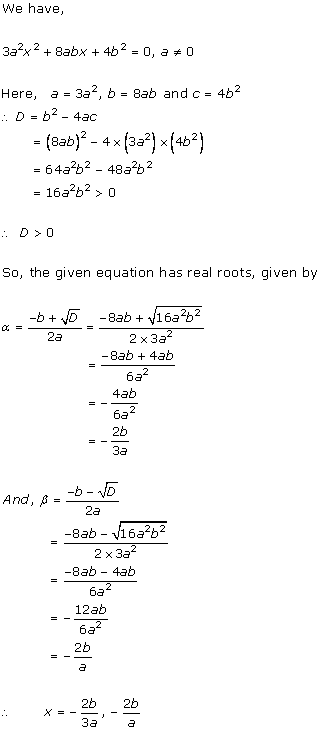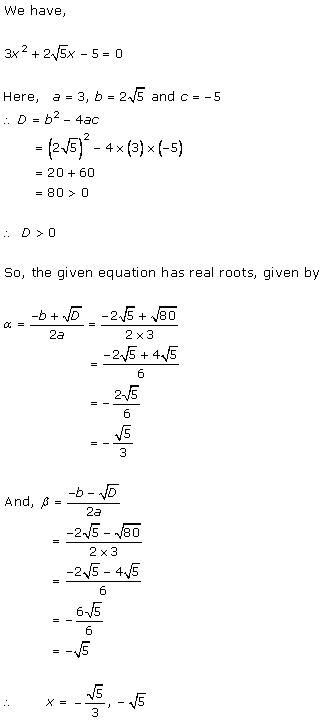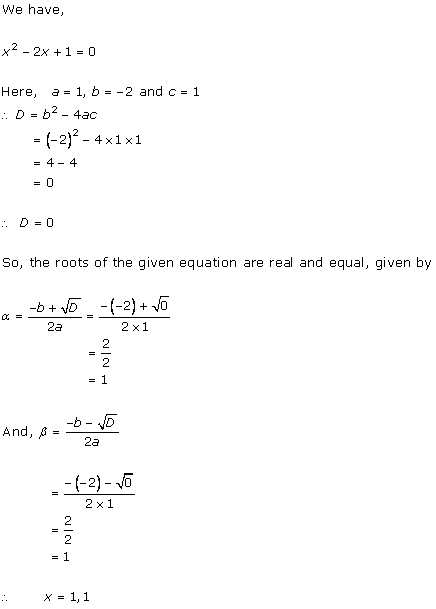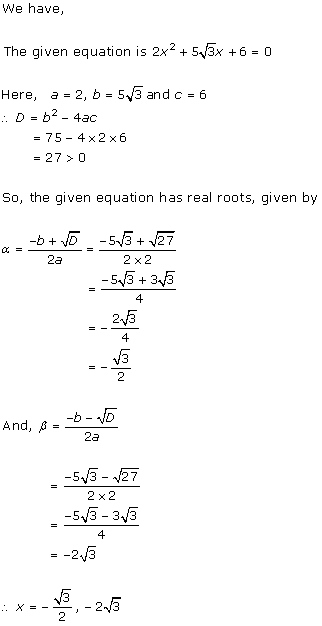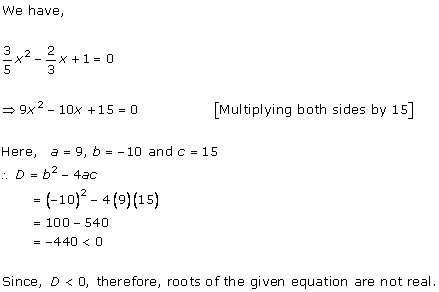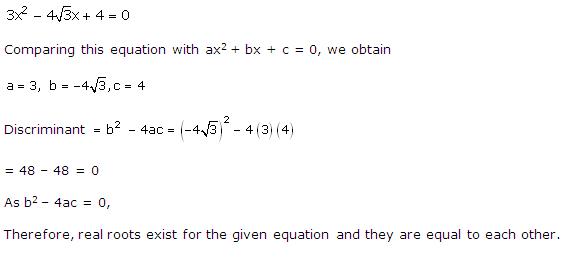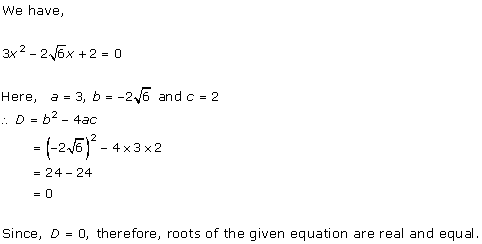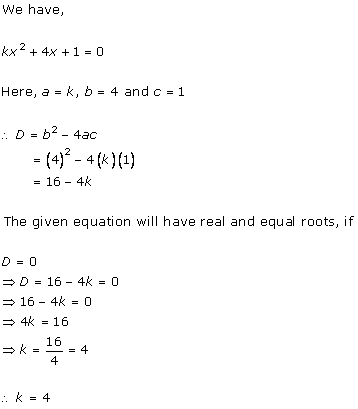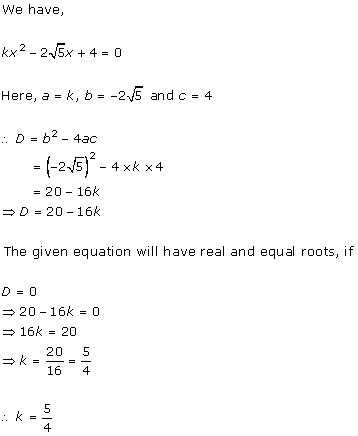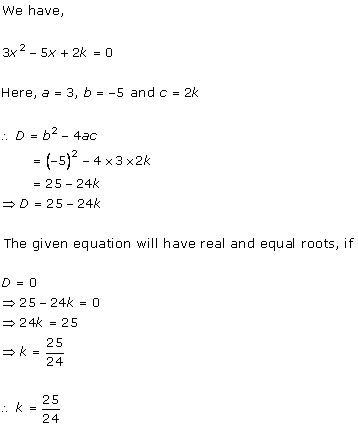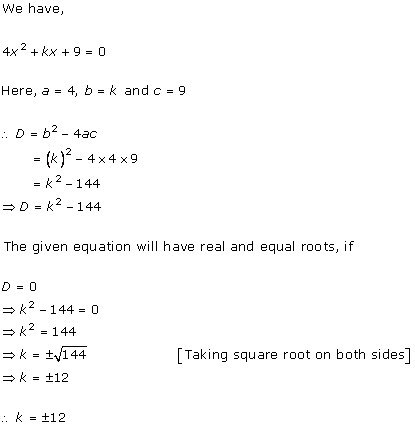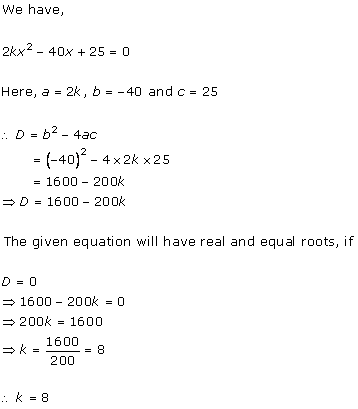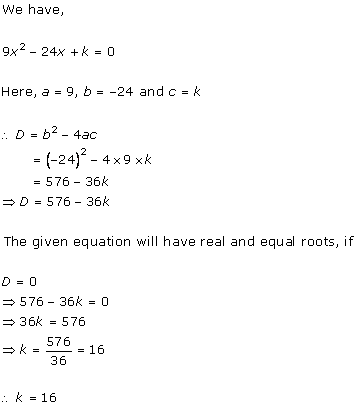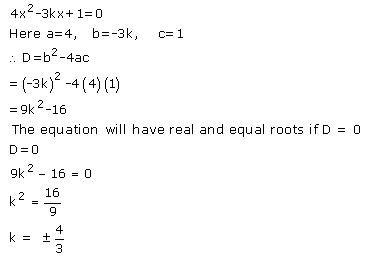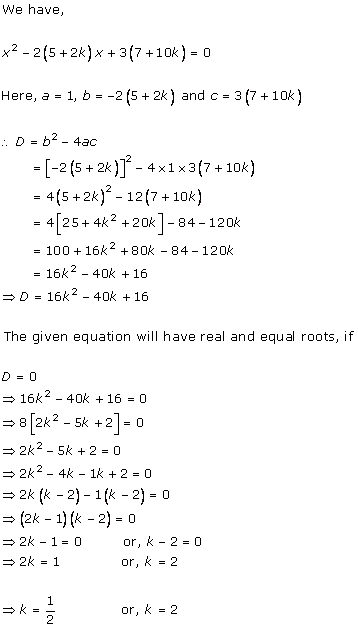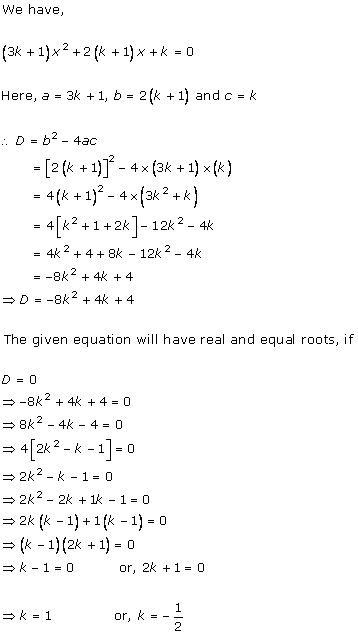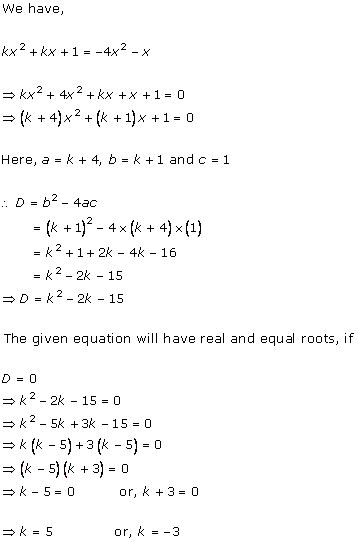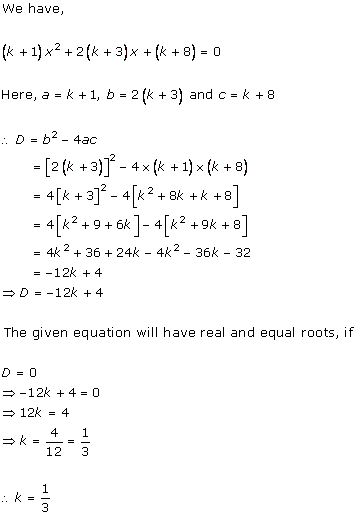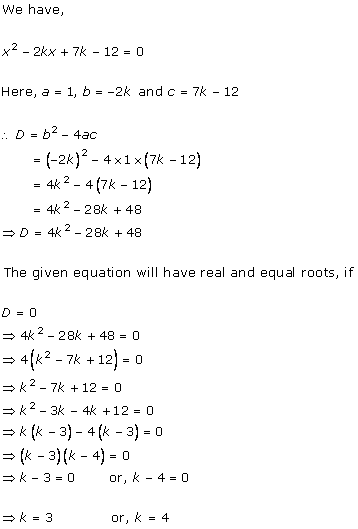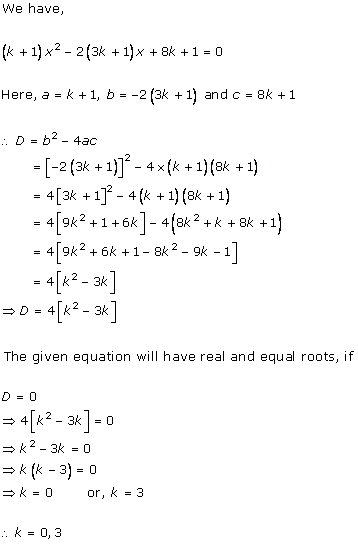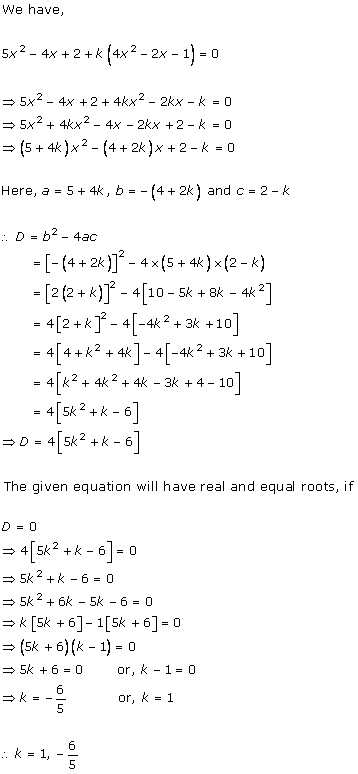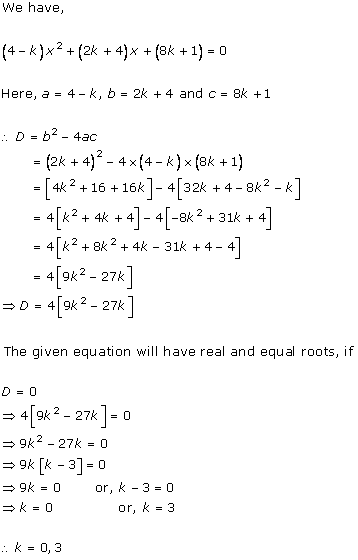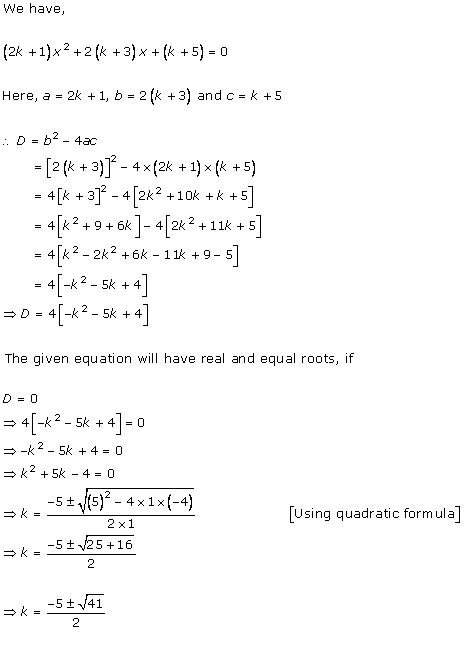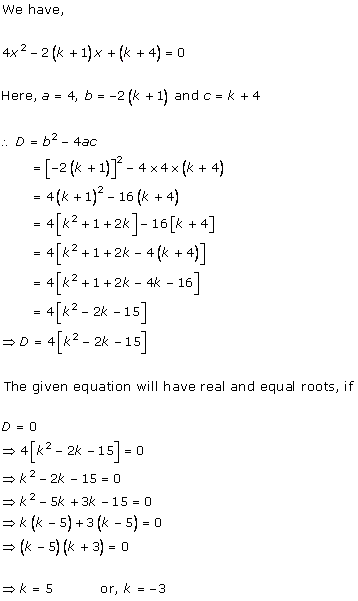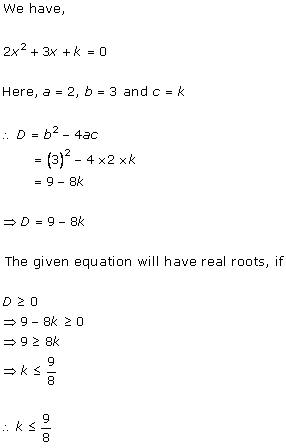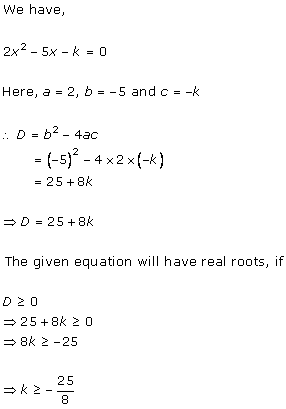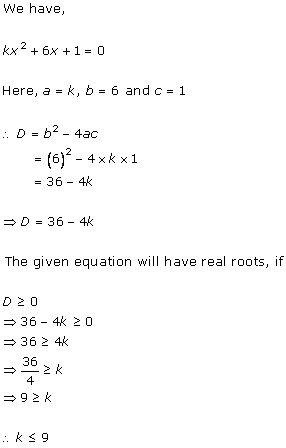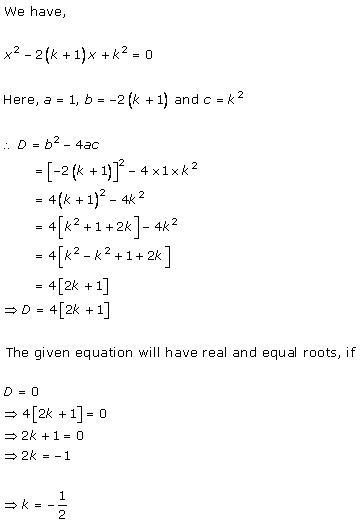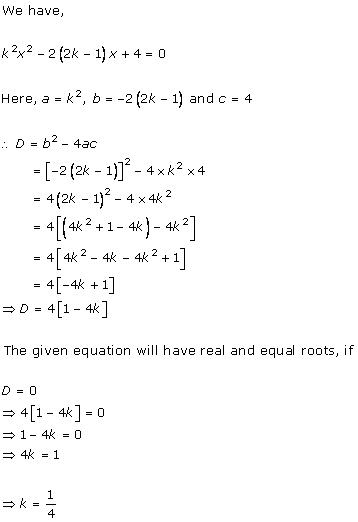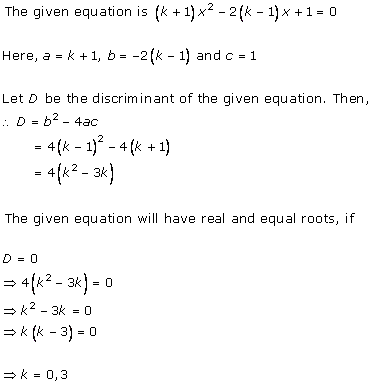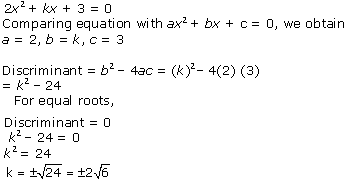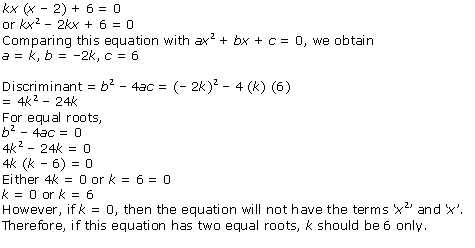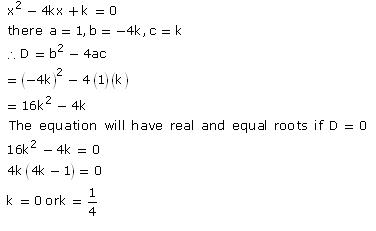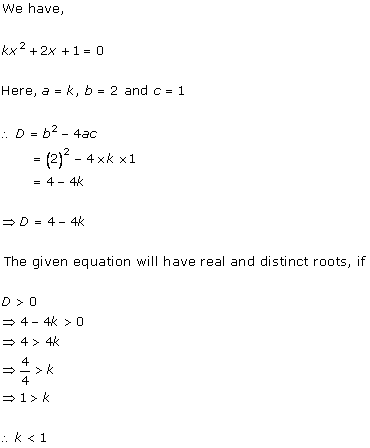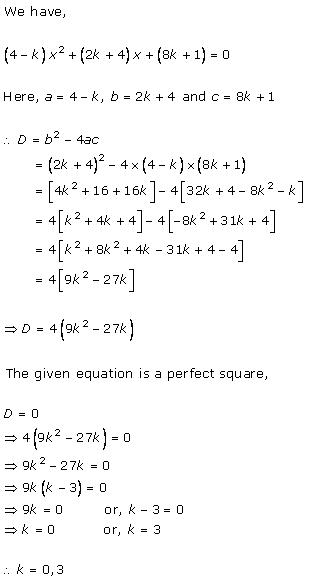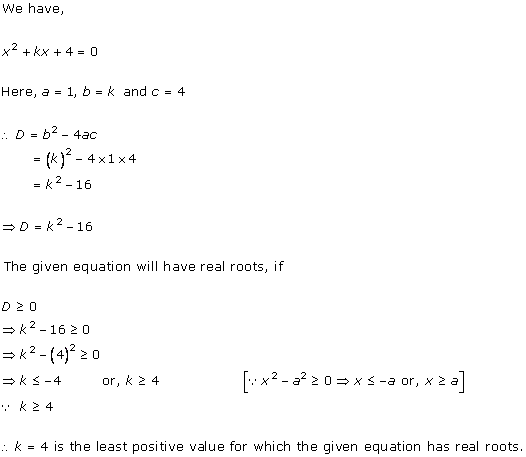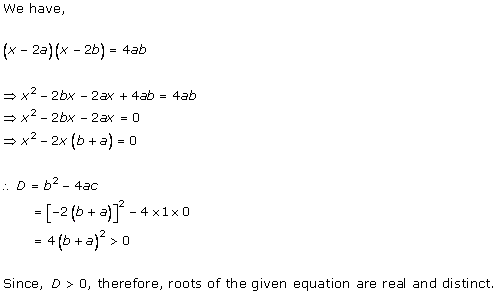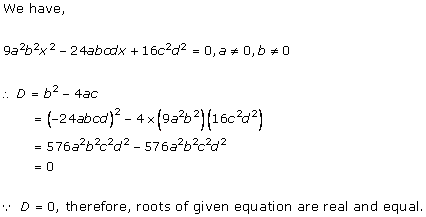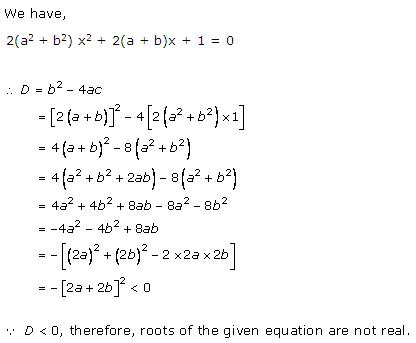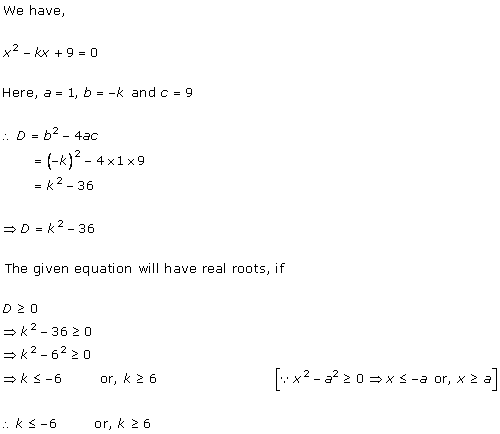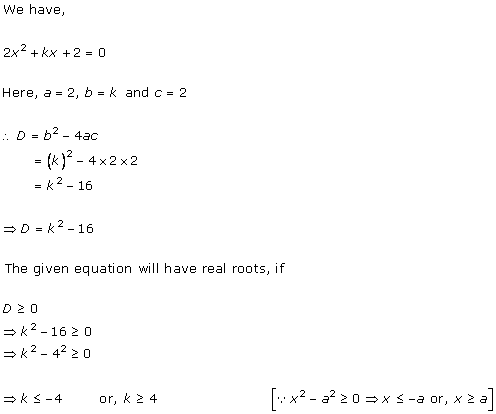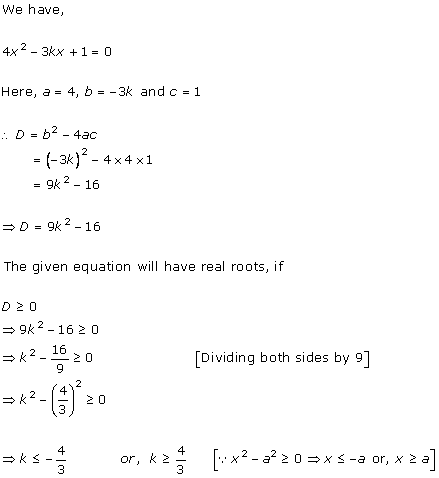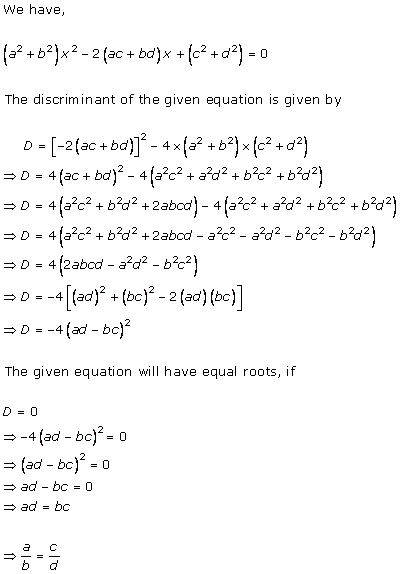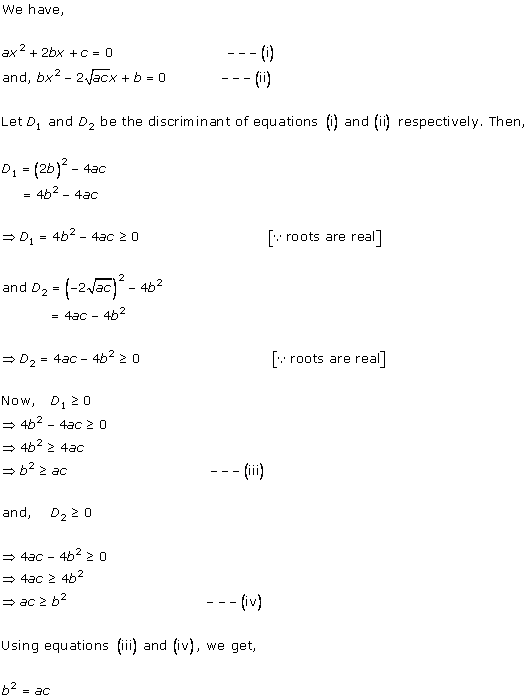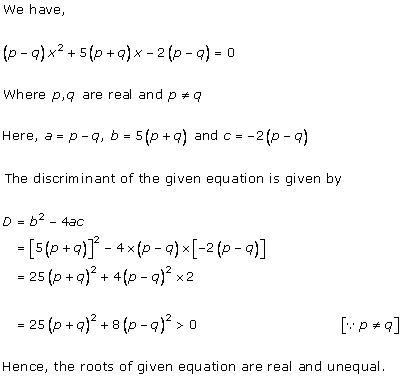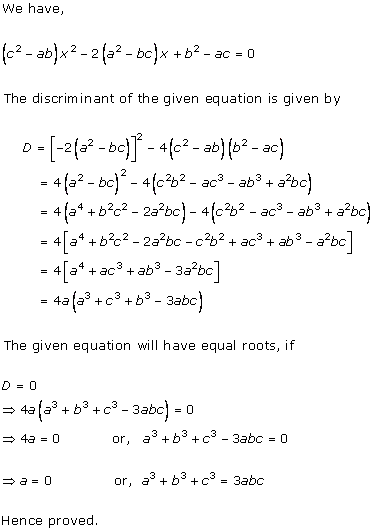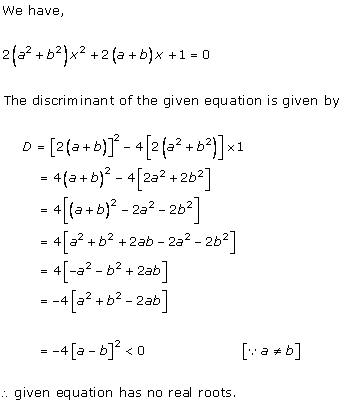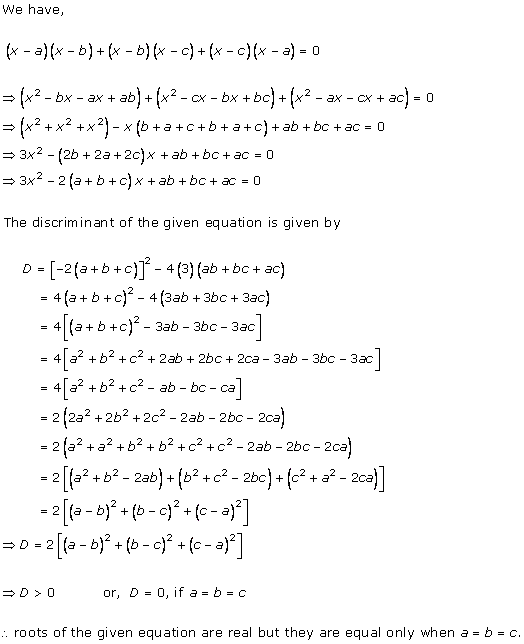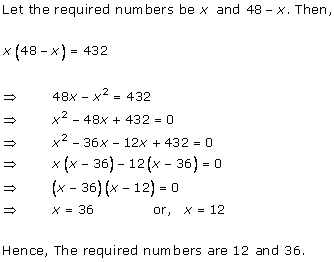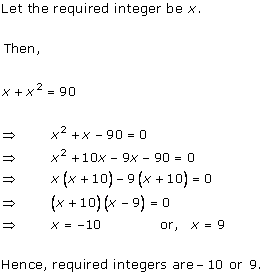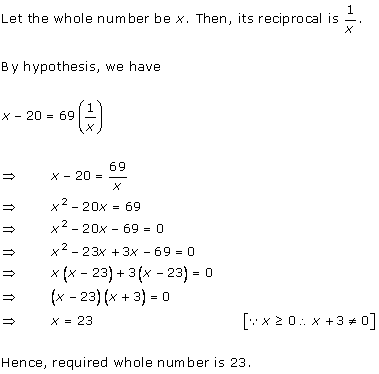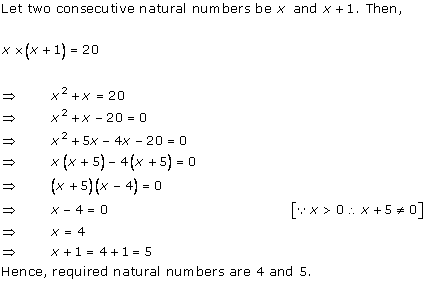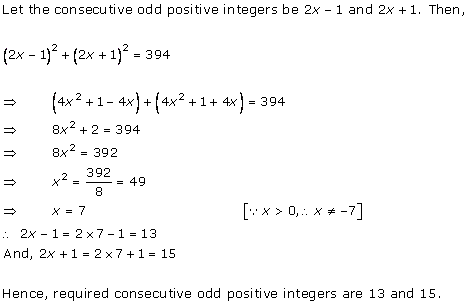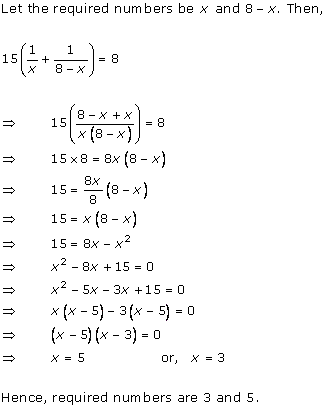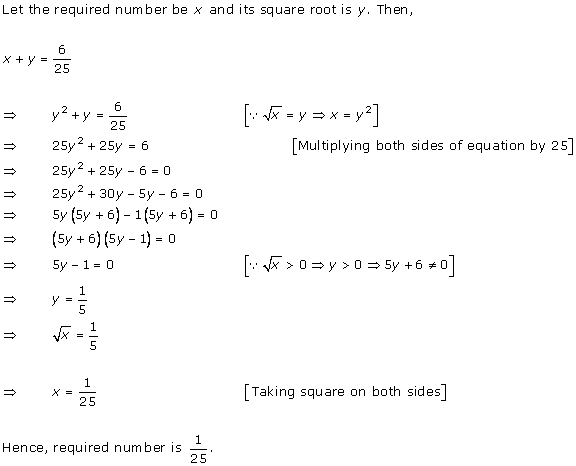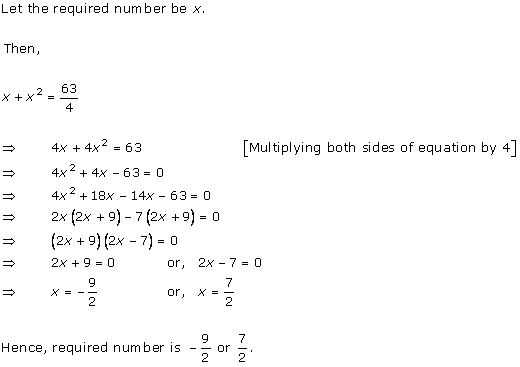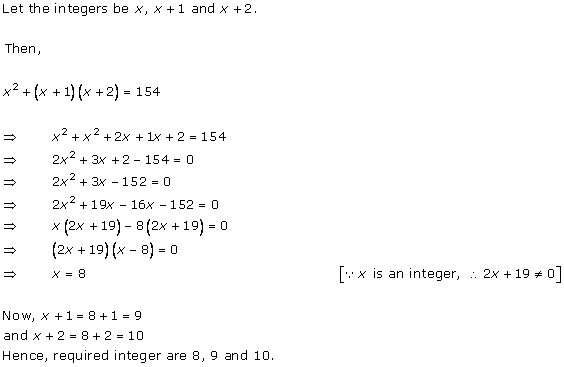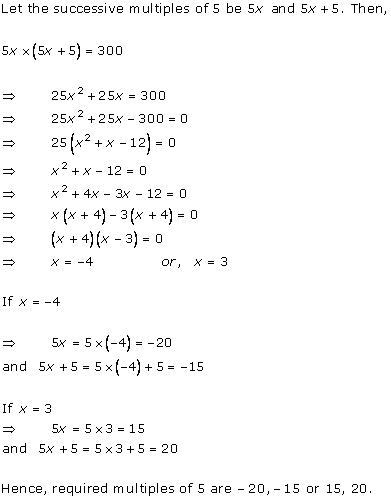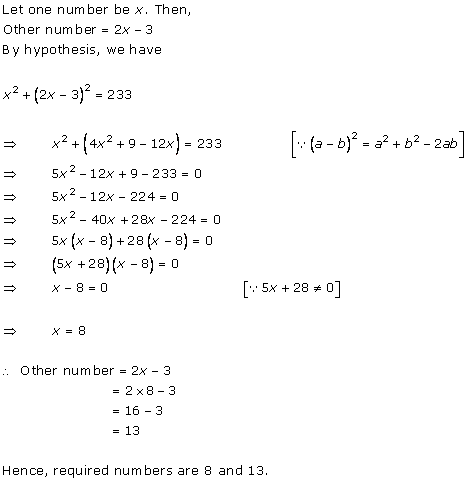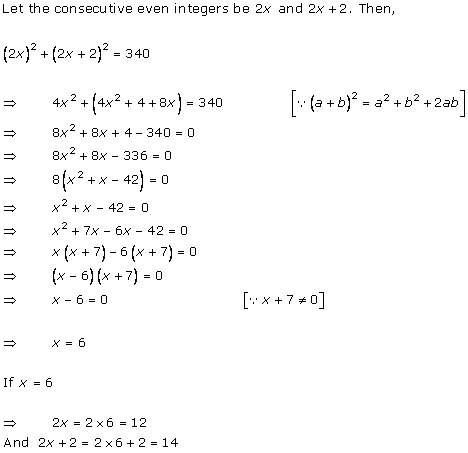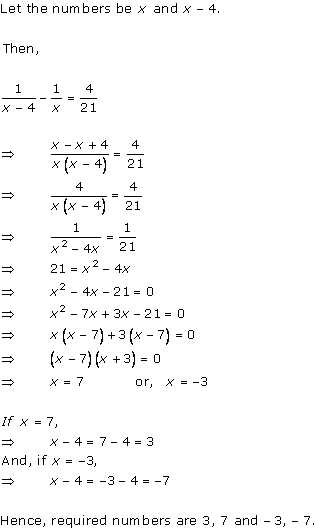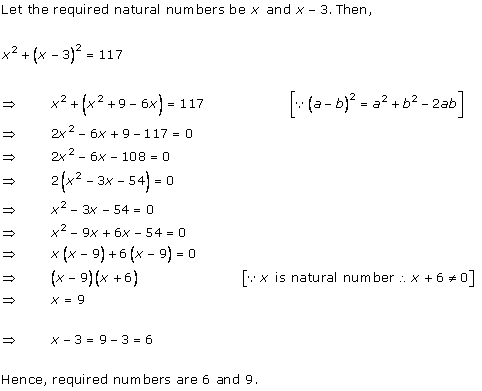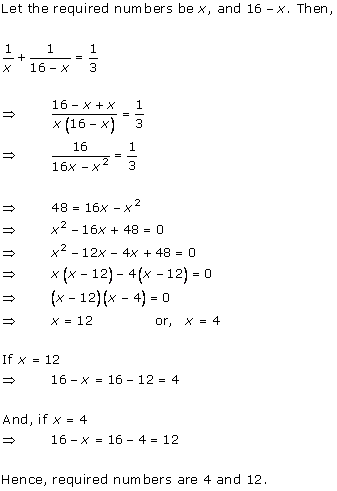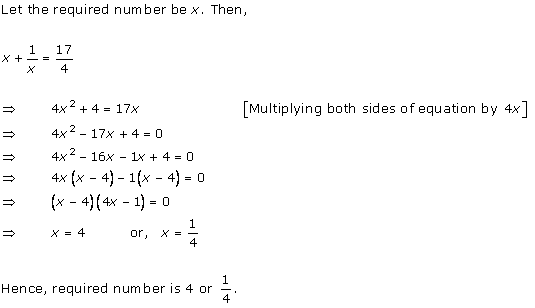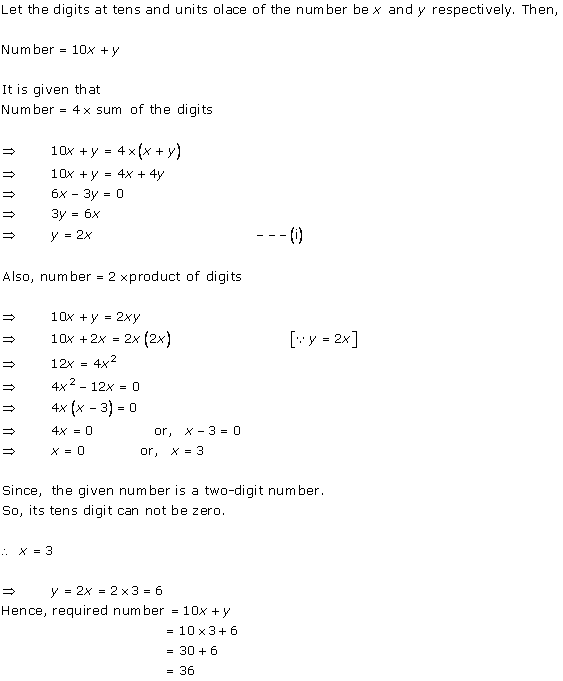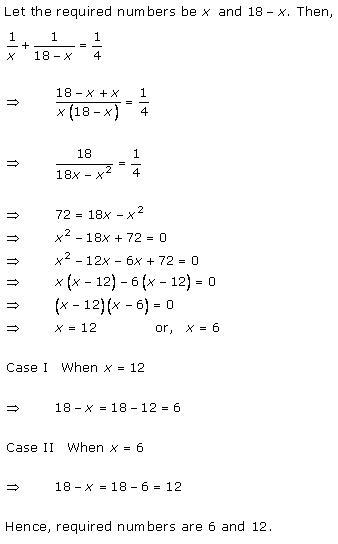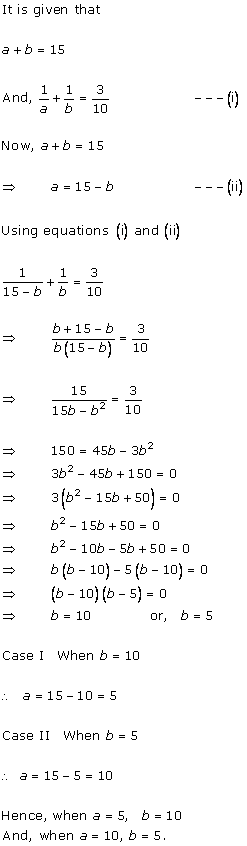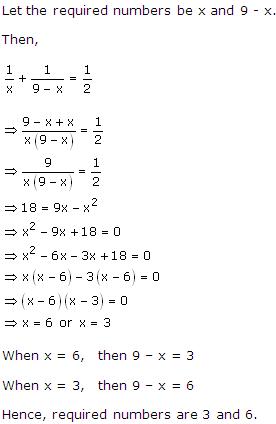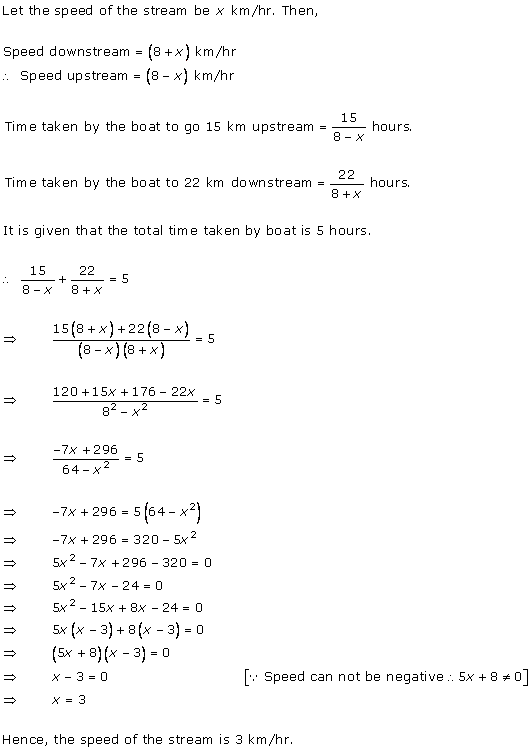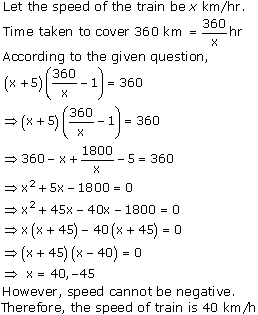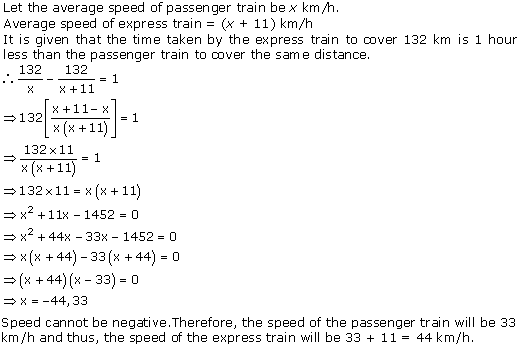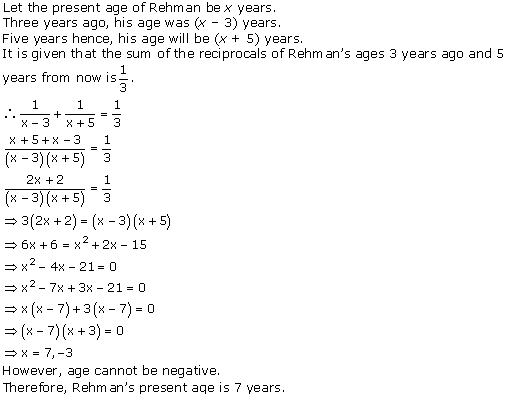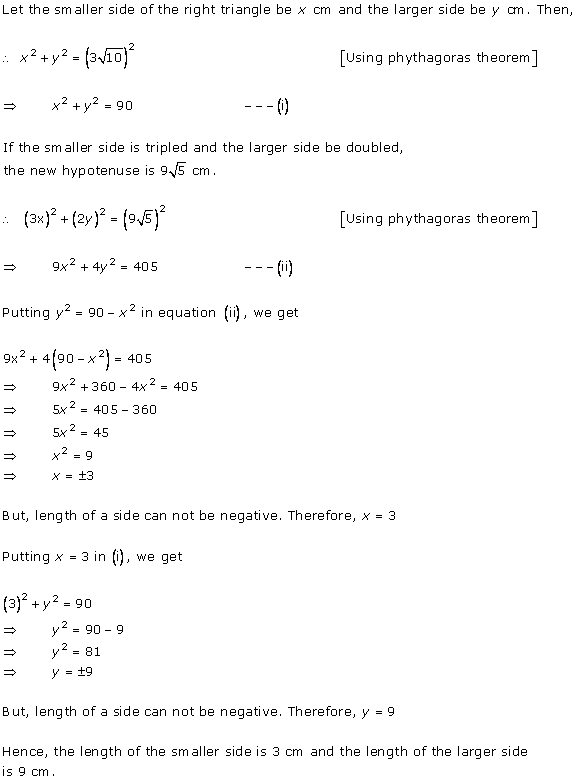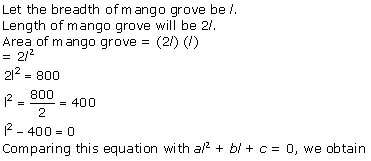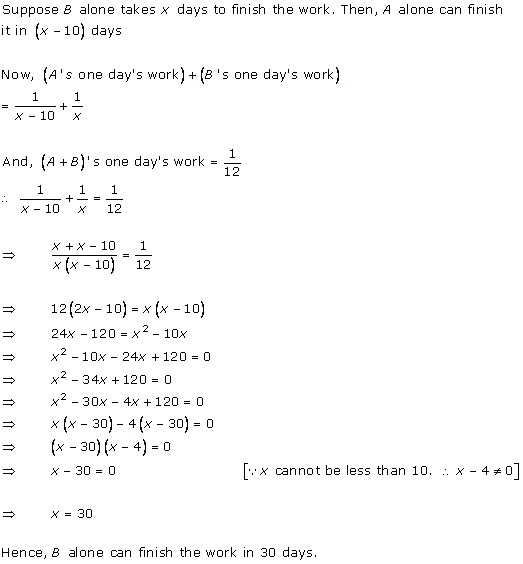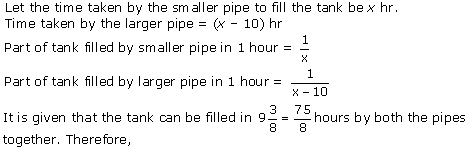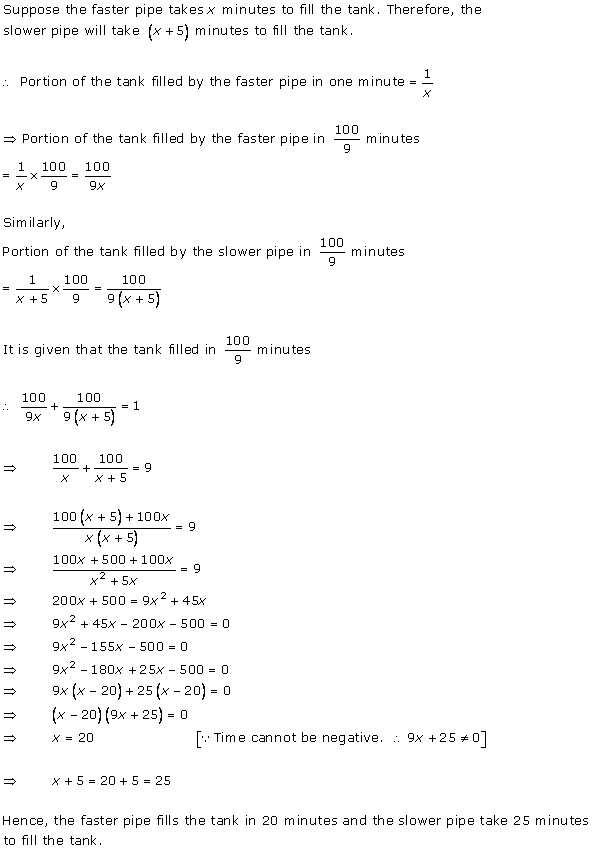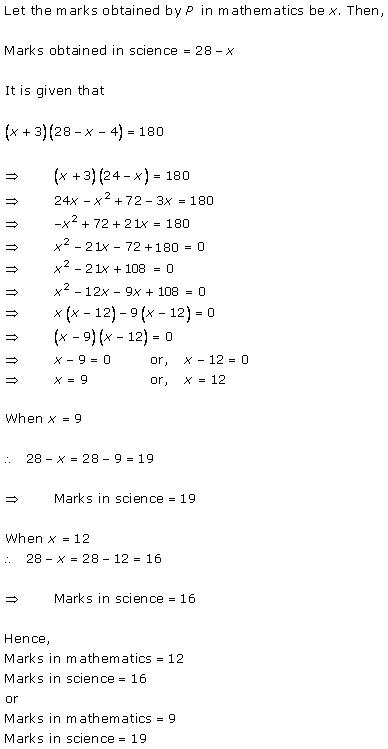Class 10 RD SHARMA Solutions Maths Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations
TopperLearning’s class 10 R.D Sharma solutions in Quadratic Equations are the best when the primary focus is scoring maximum grades. The in-house subject matter experts with years of experience and subjective knowledge have developed the chapter-wise R.D Sharma Maths solutions. Here, multiple illustrative examples and chronologically step-by-step solutions make learning easy. That way, you can aim to score high marks in the upcoming CBSE Class 10 Maths board exam.
The best part is that all the solutions are prepared per the latest syllabus and backed by comprehensive explanations, ensuring proper access to the right answers. Depending on the concept you are stuck on, you can browse through the website and get to know the answer for yourself. Everything related to the chapter on quadratic equations is elaborated correctly, from determining quadratic equations and formulation to applying quadratic equations in real-life situations. As you move further into the solution, you will be able to discover various ways essential to finding the roots or zeros. Besides, simple illustrations of complex rules of the factorisation method are also easily available here.
Moreover, at TopperLearning, you can also avail of R.D Sharma solutions for class 9, class 11 and class 12. More than anything, your confidence and preparedness for the exam will help you fetch great grades. And TopperLearning does make everything easy, with seamless examples and consecutive illustrations. The main aim is to make online education accessible and seamless with free study materials.
As a student of class 10, you can also trust TopperLearing with the best of your knowledge regarding NCERT solutions. The subjects available are Science, Hindi, English and Social Science. Similar solutions are also available for people belonging to ICSE and Maharashtra board.
Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.1
Solution 1 (i)
Solution 1 (ii)
Solution 1 (iii)
Solution 1 (iv)
Solution 1 (v)
Solution 1(vi)
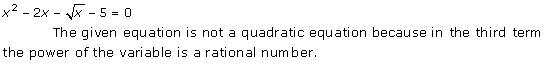
Solution 1 (vii)
Solution 1 (viii)
Solution 1 (ix)
Solution 1 (x)
Solution 1 (xi)
Solution 1 (xii)
Solution 1 (xiii)
Solution 1 (xiv)
Solution 1 (xv)
Solution 2 (i)
Solution 2 (ii)
Solution 2 (iii)
Solution 2 (iv)
Solution 2 (v)
= 2x2 - x + 9 – x2 + 4x + 3
= x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
Here, LHS = x2 - 5x + 6 and RHS = 0
Substituting x = 2 and x = 3
= x2 - 5x + 6
= (2)2 – 5(2) + 6
=10-10
=0
= RHS
= x2 - 5x + 6
= (3)2 – 5(3) + 6
= 9 - 15 + 6
=15 - 15
=0
= RHS
x = 2 and x = 3 both are the solutions of the given quadratic equation.
Solution 2 (vi)
Solution 2 (vii)
Solution 3 (i)
Solution 3 (ii)
Solution 3 (iii)
Solution 3 (iv)
Solution 4
Solution 5
Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.2
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
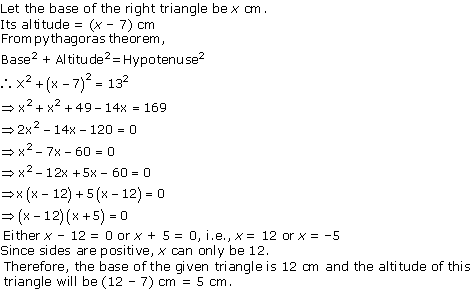
Solution 5
Solution 6
Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.3
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6
Solution 7
Solution 8
Solution 9

Solution 10
Solution 11

Solution 12
Solution 13
Solution 14
Solution 15

Solution 16
Solution 17
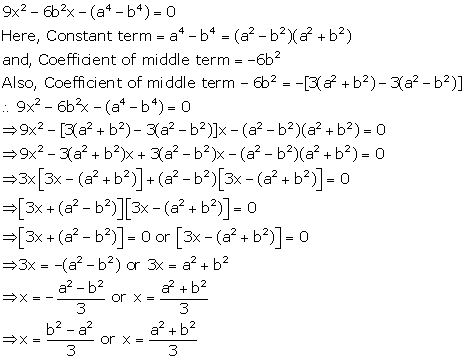
Solution 18
Solution 19
Solution 20
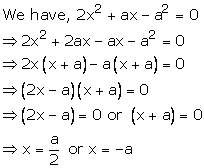
Solution 21

Solution 22
Solution 23
Solution 24
Solution 25
Solution 26
Solution 27
Solution 28
Solution 29

Solution 30

Solution 31

Solution 32

Solution 33

Solution 34
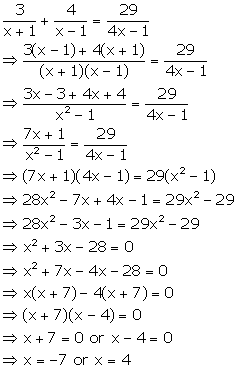
Solution 35
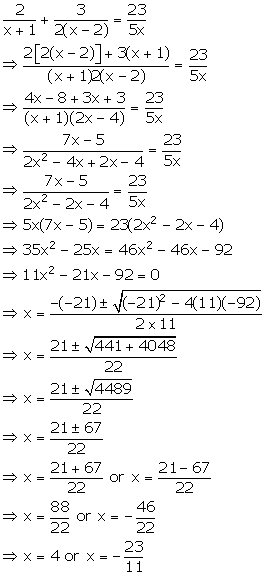
Solution 36

Solution 37

Solution 38
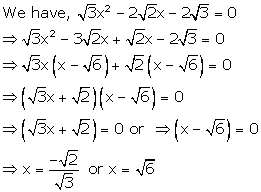
Solution 39
Solution 40
Solution 41
Solution 42
Solution 43
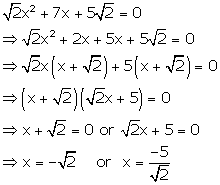
Solution 44
Solution 45
Solution 46
Solution 47
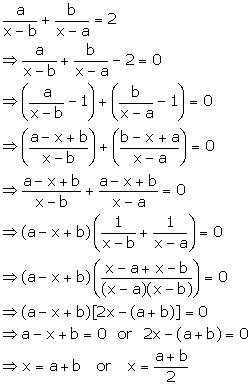
Solution 48
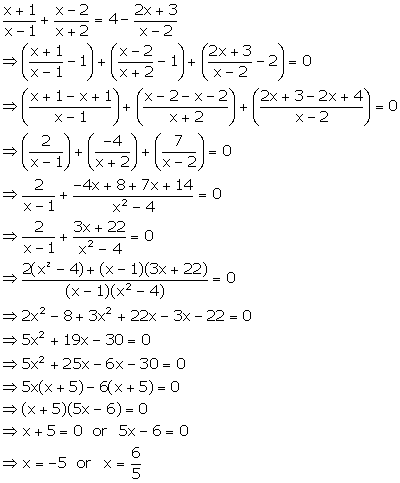
Solution 49
Solution 50
Solution 51
Solution 52
Solution 53
Solution 54
Solution 55
Solution 56
Solution 57
Solution 58

Solution 59

Solution 60

Solution 61
Solution 62
Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.4
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6
Given equation is x2 - 8x + 18 = 0
x2 - 2 × x × 4 + + 42 - 42 + 18 = 0
(x - 4)2 - 16 + 18 = 0
(x - 4)2 = 16 - 18
(x - 4)2 = -2
Taking square root on both the sides, we get
![]()
Therefore, real roots does not exist.
Solution 7
Solution 8
Solution 9
Solution 10
Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.5
Solution 1 (i)
Solution 1 (ii)
Solution 1(iii)
Solution 1 (iv)
Solution 1(v)
Solution 1(vi)
Solution 1 (vii)
x2 + 2 × x × 5 + 52 = 10x - 6
x2 + 10x + 25 = 10x - 6
x2 + 31 = 0
Here, a = 1, b = 0 and c = 31
Therefore, the discriminant is
D = b2 - 4ac
= 0 - 4 × 1 × 31
= -124
Solution 2 (i)
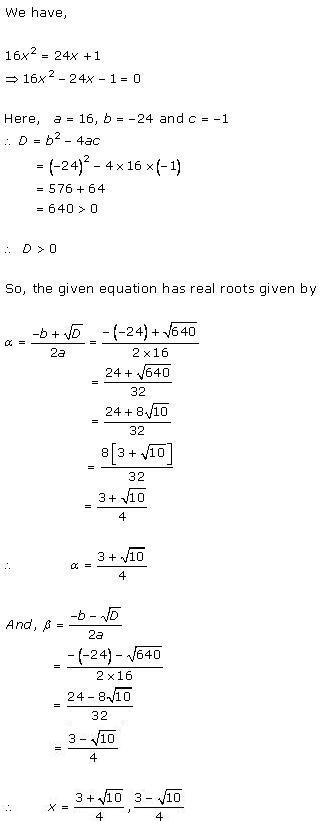
Solution 2 (ii)
Solution 2 (iii)
Solution 2 (iv)
Solution 2 (v)
Solution 2 (vi)
Solution 2 (vii)
Solution 2 (viii)
Solution 2 (ix)
Solution 2(x)
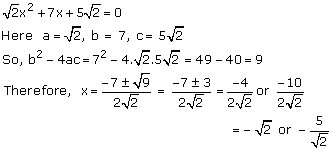
Solution 2(xi)
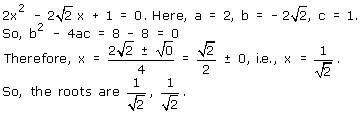
Solution 2(xii)
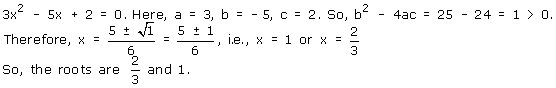
Solution 3(i)
Solution 3(ii)
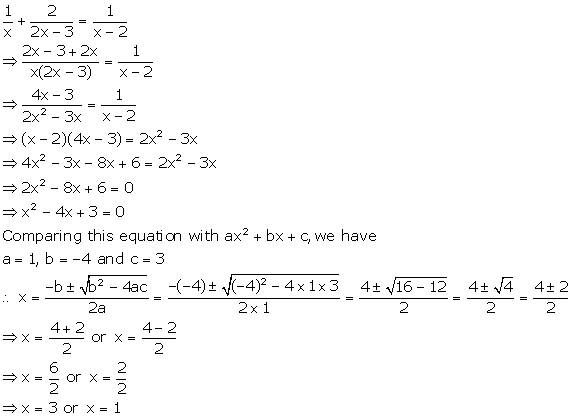
Solution 3(iii)
Solution 3(iv)

Solution 3(v)
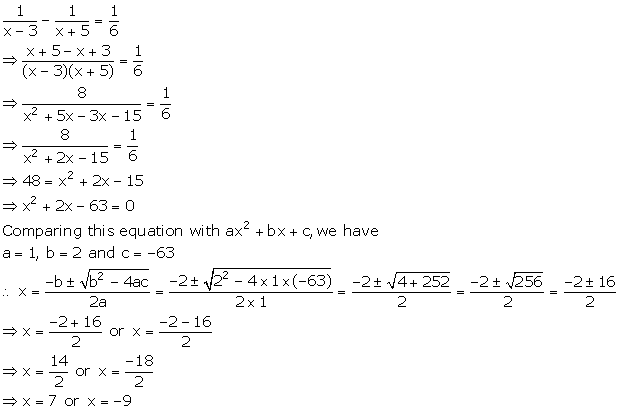
Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.6
Solution 1(i)
Solution 1(ii)
Solution 1(iii)
Solution 1(iv)
Solution 1(v)
Solution 1 (vi)
Given quadratic
equation is ![]()
Here, ![]()
Therefore, we have
![]()
As D = 0, roots of the given equation are real and equal.
Solution 2(i)
Solution 2(ii)
Solution 2(iii)
Solution 2(iv)
Solution 2(v)
Solution 2(vi)
Solution 2(vii)
Solution 2(viii)
Solution 2(ix)
Solution 2(x)
Solution 2(xi)
Solution 2(xii)
Solution 2(xiii)
Solution 2(xiv)
Solution 2(xv)
Solution 2(xvi)
Solution 2(xvii)
Solution 2(xviii)
4x2
- 2 (k + 1)x + (k + 1) = 0
Comparing with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 4, b = -2(k + 1), c = k + 1
According to the question, roots are real and equal.
Hence, b2 - 4ac = 0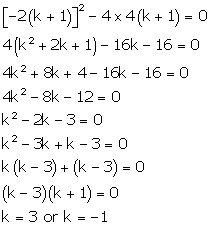
Solution 3(i)
Solution 3(ii)
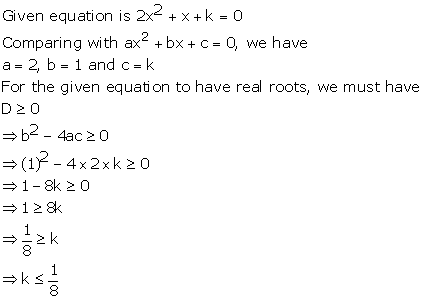
Solution 3(iii)
Solution 3(iv)
Solution 3(v)
Solution 4(i)
Solution 4(ii)
Solution 4(iii)
Solution 4(iv)
x2 + k(2x + k - 1) + 2 = 0
x2 + 2kx + k(k - 1) + 2 = 0
Comparing with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 1, b = 2k, c = k(k - 1) + 2
According to the question, roots are real and equal.
Hence, b2 - 4ac = 0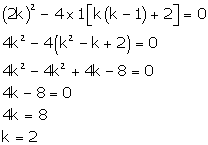
Solution 5(i)
Solution 5(ii)
Solution 5(iii)
Solution 5(iv)

Solution 5(v)

Solution 5(vi)
4x2
+ kx + 3 = 0
Comparing with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 4, b = k, c = 3
According to the question, roots are real and equal.
Hence, b2 - 4ac = 0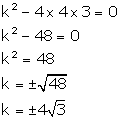
Solution 6 (i)
Solution 6 (ii)
Solution 7
Solution 8
Solution 9(i)

Solution 9 (ii)
Given quadratic equation is x2 + kx + 16 = 0
As it has equal roots, the discriminant will be 0.
Here, a = 1, b = k, c = 16
Therefore, D = k2 - 4(1)(16) = 0
i.e. k2 - 64 = 0
i.e. k = ± 8
When k = 8, the equation becomes x2 + 8x + 16 = 0
or x2 - 8x + 16 = 0
As D = 0, roots of the given equation are real and equal.
Solution 10

Solution 11

Solution 12

Solution 13
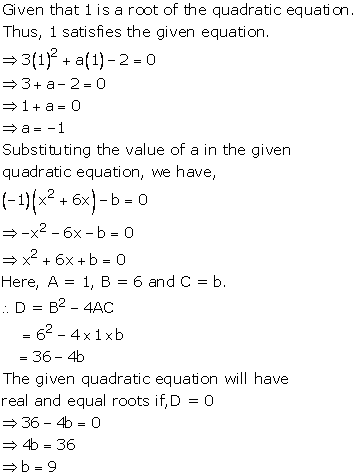
Solution 14

Solution 15(i)
Solution 15(ii)
Solution 15(iii)
Solution 15(iv)
Solution 16(i)
Solution 16(ii)
Solution 16(iii)
Solution 16(iv)
Solution 17
Solution 18
Solution 19
Solution 20
Solution 21
Solution 22
Solution 23
Solution 24
Solution 25
Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.7
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6
Solution 7
Solution 8
Solution 9
Solution 10
Solution 11
Solution 12
Solution 13
Solution 14
Solution 15
Solution 16
Solution 17
Solution 18
Solution 19
Solution 20
Solution 21
Solution 22
Solution 23
Solution 24
Let x be the natural number.
As per the question, we have
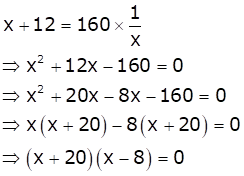
Therefore, x = 8 as x is a natural number.
Hence, the required natural number is 8.
Solution 25
Solution 26
Solution 27
Solution 28
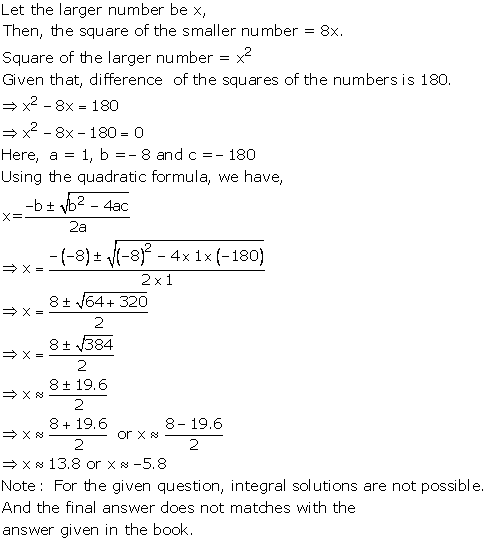
Solution 29
Solution 30
Solution 31
Solution 32
Solution 33
Solution 34

Solution 35
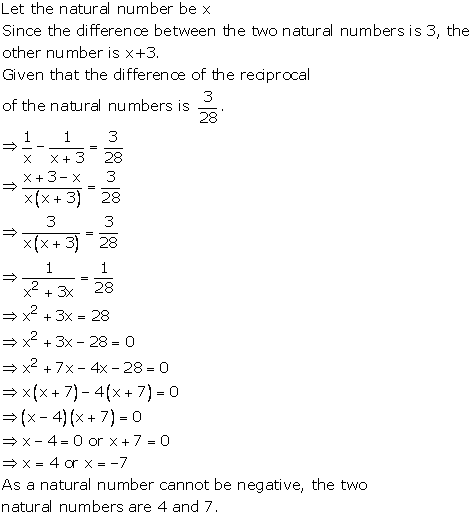
Solution 36

Solution 37

Solution 38

Solution 39

Solution 40
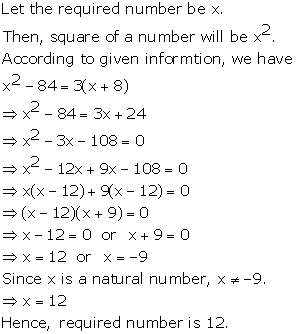
Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.8
Solution 1
Solution 2

Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6

Solution 7
Solution 8
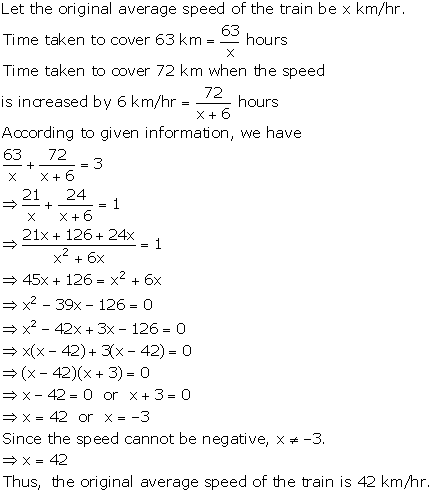
Solution 9
Solution 10
Concept Insight: Use the relation s =d/t to crack this question and remember here distance is constant so speed and time will vary inversely.
Solution 11
Solution 12
Solution 13

Solution 14

Solution 15
Let the
speed of a car be x km/hr.
According to the question, time is ![]() hr.
Distance = Speed × Time
2592 =
hr.
Distance = Speed × Time
2592 = ![]()
![]()
![]() x = 72 km/hr
Hence, the time taken by a car to cover a distance of 2592 km is 36 hrs.
x = 72 km/hr
Hence, the time taken by a car to cover a distance of 2592 km is 36 hrs.
Solution 16
Let x km/hr be the speed of the stream.
Therefore, we have
Downstream speed = (9 + x) km/hr
Upstream speed = (9 - x) km/hr
Distance covered downstream = distance covered upstream
Total time taken =
3 hours 45 minutes = ![]() hours
hours
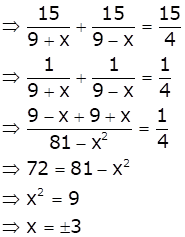
Therefore, x = 3 as the speed can't be negative.
Hence, the speed of the motor boat is 3 km/hr.
Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.9
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6
Solution 7
Solution 8

Solution 9
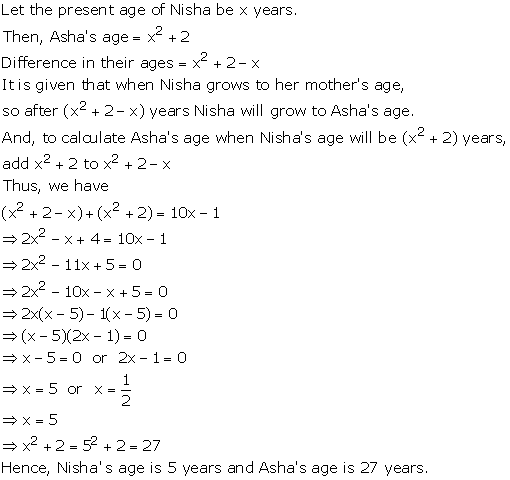
Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.10
Solution 1
Solution 2

Solution 3
Solution 4
Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.11
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6
Solution 7

Solution 8

Solution 9

Solution 10

Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.12
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Let us assume that the larger pipe takes 'x' hours to fill the pool.
So, as per the question, the smaller pipe takes 'x + 10' hours to fill the same pool.

Solution 6
Let the tap with smaller diameter takes x hours to completely fill the tank.
So, the other tap takes (x - 2) hours to fill the tank completely.
Total time taken to
fill the tank ![]() hours
hours
As per the question, we have
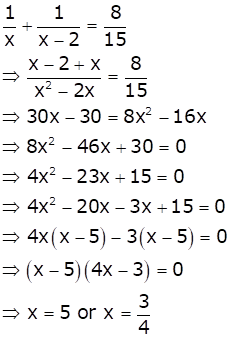
When x = 5, then (x - 2) = 3
When ![]() which can't be
possible as the time becomes negative.
which can't be
possible as the time becomes negative.
Hence, the smaller diameter tap fills in 5 hours and the larger diameter tap fills in 3 hours.
Quadratic Equations Exercise Ex. 4.13
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6
Solution 7
Solution 8
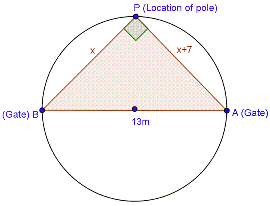

Solution 9
Solution 10
Solution 11
Solution 12
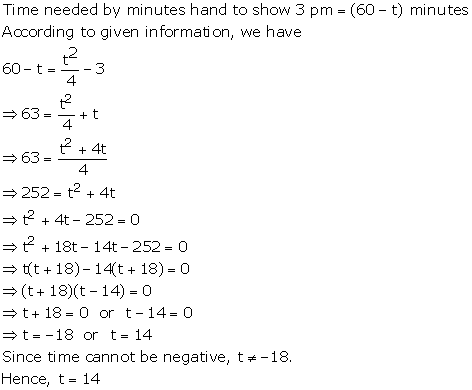
Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.82
Solution 1
We know for the quadratic equation
ax2 + bx + c = 0
condition for roots to be real and distinct is
D = b2 - 4ac > 0 ..........(1)
for the given question
x2 + 4x + k = 0
a = 1, b = 4, c = k
from (1)
16 - 4k > 0
k < 4
So, the correct option is (a).
Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.83
Solution 2
For the equation x2 - ax + 1 = 0 has two distinct roots, condition is
(-a)2 - 4 (1) (1) > 0
a2 - 4 > 0
a2 > 4
|a| > 2
So, the correct option is (c).
Solution 3

Solution 4

Solution 5
For any quadratic equation
ax2 + bx + c = 0
having two distinct roots, condition is
b2 - 4ac > 0
For the equation ax2 + 2x + a = 0 to have two distinct roots,
(2)2 - 4 (a) (a) > 0
4 - 4a2 > 0
4(1 - a2) > 0
1 - a2 > 0 since 4 > 0
that is, a2 - 1 < 0
Hence -1 < a < 1, only integral solution possible is a = 0
So, the correct option is (b).
Solution 6
For any quadratic equation
ax2 + bx + c = 0
having real roots, condition is
b2 - 4ac ≥ 0 .......(1)
According to question
x2 + kx + 64 = 0 have real root if
k2 - 4 × 64 ≥ 0
k2 ≥ 256
|k|≥ 16 ........(2)
Also, x2 - 8x + k = 0 has real roots if
64 - 4k ≥ 0
k ≤ 16 .........(3)
from (2), (3) the only positive solution for k is
k = 16
So, the correct option is (d).
Solution 7

Solution 8
It is given that 2 is a root of equation x2 + bx + 12 = 0
Hence
(2)2 + b(2) + 12 = 0
4 + 2b + 12 = 0
2b + 16 = 0
b = -8 .........(1)
It is also given that x2 + bx + q = 0 has equal root
so, b2 - 4(q) = 0 ........(2)
from (1) & (2)
(-8)2 - 4q =0
q = 16
So, the correct option is (c).
Solution 9
For any quadratic equation
ax2 + bx + c = 0
Having equal roots, the condition is
b2 - 4ac = 0
For the equation
(a2 + b2) x2 - 2 (ac + bd)x + c2 + d2 = 0
to have equal roots, we have
(-2(ac + bd))2 - 4 (c2 + d2) (a2 + b2) = 0
4 (ac + bd)2 - 4 (a2c2 + b2c2 + d2a2 + b2d2) = 0
(a2c2 + b2d2 + 2abcd) - (a2c2 + b2c2 + a2d2+ b2d2) = 0
2abcd - b2c2 - a2d2 = 0
b2c2 - a2d2 - 2abcd = 0
(bc - ad)2 = 0
bc = ad
So, the correct option is (b).
Solution 10
For any quadratic equation
ax2 + bx + c = 0
having equal roots, condition is
b2 - 4ac = 0
According to question, quadratic equation is
(a2 + b2)x2 - 2b(a + c)x + b2 + c2 = 0
having equal roots, so
(2b(a + c))2 - 4(a2 + b2) (b2 + c2) = 0
4b2 (a + c)2 - 4(a2b2 + a2c2 + b4 + b2c2) = 0
b2(a2 + c2 + 2ac) - (a2b2 + a2c2 + b2c2 + b4) = 0
a2b2 + b2c2 + 2acb2 - a2b2 - a2c2 - b2c2 - b4 = 0
2acb2 - a2c2 - b4 = 0
a2c2 + b4 - 2acb2 = 0
(ac - b2)2 = 0
ac = b2
So, the correct option is (b).
Solution 11
For any quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 having no real roots, condition is
b2 - 4ac < 0
For the equation, x2 - bx + 1 = 0 having no real roots
b2 - 4 < 0
b2 < 4
-2 < b < 2
So, the correct option is (b).
Solution 12

Solution 13
If p, q are the roots of equation x2 - px + q = 0, then p and q satisfies the equation
Hence
(p)2 - p(p) + q = 0
p2 - p2 + q = 0
q = 0
and (q)2 - p(q) + q = 0
q2 - p(q) + q = 0
0 = 0
p can take any value
p = -2 and q = 0
So, the correct option is (c).
Solution 14
For the ax2 + bx + 1 = 0 having real roots condition is
b2 - 4(a) (1) ≥ 0
b2 ≥ 4a
For a = 1
b2 ≥ 4
b ≥ 2
b can take value 2, 3, 4
Here, 3 possible solutions are possible .......(1)
For a = 2
b2 ≥ 8
Here, b can take value 3, 4 ......(2)
Here, 2 solutions are possible
For a = 3
b2 ≥ 12
possible value of b is 4
Hence, only 1 possible solution ......(3)
For a = 4
b2 ≥ 16
possible value of b is 4
Hence, only 1 possible solution .......(4)
from (1), (2), (3), (4)
Total possible solutions are 7
So, the correct option is (b).
Solution 15
Any quadratic equation having roots 0 or 1 are only possible quadratic equation because on squaring 0 or 1, it remains same.
Hence, 2 solutions are possible, one having roots 1 and 1, while the other having roots 0 and 1.
So, the correct option is (c).
Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.84
Solution 16
If any quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c has no real roots then b2 - 4ac < 0 ......(1)
According to the question, the equation is
(a2 + b2) x2 + 2(ac + bd) x + c2 + d2 = 0
from (1)
4(ac + bd)2 - 4(a2 + b2) (c2 + d2) < 0
a2c2 + b2d2 + 2abcd - (a2c2 + a2d2 + b2c2 + b2d2) < 0
a2c2 + b2d2 + 2abcd - a2c2 - a2d2 - b2c2 - b2d2 < 0
2abcd - a2d2 - b2c2 < 0
-(ad - bc)2 < 0
(ad - bc)2 > 0
For this condition to be true ad ≠ bc
So, the correct option is (d).
Solution 17

Solution 18
It is given that x = 1 is root of equation ax2 + ax + 2 = 0
Hence, a(1)2 + a(1) + 2 = 0
2a + 2 = 0
a = -1 ......(1)
It is given that x = 1 is also root of x2 + x + b = 0
Hence, (1)2 + (1) + b = 0
b = -2 ......(2)
from (1) & (2)
ab = (-1) (-2)
ab = 2
So, the correct option is (b).
Solution 19

Solution 20

Solution 21

Solution 22

Solution 23
Given, 2 is a root of equation x2 + ax + 12 = 0
so (2)2 + a(2) + 12 = 0
4 + 2a + 12 = 0
a = -8 .....(1)
Given x2 + ax + q = 0 has equal roots so
a2 - 4q = 0 ......(2)
from (1) & (2)
(-8)2 - 4q = 0
4q = 64
q = 16
So, the correct option is (d).
Solution 24

Solution 25
If a and b are roots of the equation x2 + ax + b = 0
Then, sum of roots = -a
a + b = -a
2a + b = 0 .......(1)
product of roots = b
ab = b
ab - b = 0
b(a - 1) = 0 ........(2)
from (1) and (2)
-2a(a - 1) = 0...(From (1), we have b = -2a)
a(a - 1) = 0
a = 0 or a = 1
if a = 0 ![]() b = 0
b = 0
if a = 1 ![]() b = -2
b = -2
Now a and b can't be zero at same time, so correct solution is
a = 1 and b = -2
a + b = -1
So, the correct option is (d).
Solution 26
Given sum of roots is zero and one root is 2.
So the other root must be -2
so any quadratic equation having root 2 and -2 is
(x - 2) (x - (-2)) = 0
(x - 2) (x + 2) = 0
x2 - 4 = 0
So, the correct option is (b).
Solution 27

Solution 28

Solution 29
x2 + ax + 3 = 0
product of roots = 3
One root is 1. Hence other root is 3.
So, the correct option is (a).
Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.85
Solution 30

Solution 31

Solution 32
Any quadratic equation, ax2 + bx + c = 0 has real and equal roots if b2 - 4ac = 0
For the question, equation is 16x2 + 4kx + 9 = 0,
(4k)2 - 4 × 16 × 9 = 0
16k2 - 36 × 16 = 0
k2 - 36 = 0
k2 = 36
k = ± 6
So, the correct option is (c).