Class 9 SELINA Solutions Physics Chapter 6 - Heat and Energy
Heat and Energy Exercise Ex 6(A)
Solution A.1
(d) heat energy
Solution A.2
(a) Heat
Calorie is the unit heat.
Solution A.3
(a) 0.24 cal
1 calorie = 4.186 J
Therefore,
1 J = 1/4.186 = 0.24 cal
Solution A.4
(c) 107 ergs
Solution A.5
(b) Temperature
Solution A.6
(d) all of the above
Solution A.7
(d) Kelvin
The SI unit of temperature is kelvin (K).
Solution A.8
(a) t K = 273 + t° C
Celsius and Kelvin scales are related as t K = 273 + t° C
Solution A.9
(b) kinetic energy
The temperature of a body depends on the average kinetic energy of the molecules.
Solution A.10
(b) 0 K
Solution A.11
(d) 212°F
Solution A.12
(a) C/5 = (F - 32) /9
Celsius and Fahrenheit scales are related as C/5 = (F - 32) /9
Solution A.13
(b) linear expansion
Solution A.14
(c) more, much more
On heating, liquids expand more than solids and gases expand much more than liquids.
Solution A.15
(b) expand
Water shows anomalous behavior between 0 °C and 4 °C. Hence, when it is cooled it expands.
Solution A.16
(b) 4, 0
The change in volume of water when it is cooled from 4 °C to 0 °C is known as anomalous expansion of water.
Solution A.17
(c)4 °C
Water shows anomalous behavior between 0 °C and 4 °C. It has lowest volume at 4 °C. Hence, its density will be maximum at 4 °C.
Solution A.18
(b) insulation
Solution A.19
a.
Solution B.1
Heat is the energy of random motion of molecules constituting the body.
Its S.I. unit is 'joule'.
Solution B.2
Heat will flow from a hot body (body at a higher temperature) to a cold body (body at a lower temperature).
Solution B.3
S.I. unit of heat is 'joule'.
1 joule = 0.24 cal
Solution B.4
Temperature is the parameter which tells the thermal state of a body (i.e. the degree of hotness or coldness).
The S.I. unit of temperature is 'kelvin'.
Solution B.5
On touching a piece of ice, heat flows from our hand (hot body) to the ice (cold body), and hence, it appears cold.
Solution B.6
Brass and iron expand on heating.
Solution B.7
Water contracts on heating from 0![]() to 4
to 4![]() .
.
Silver iodide contracts on heating from 80![]() to 141
to 141![]() .
.
Solution B.8
The expansion of water when it is cooled from 4![]() to 0
to 0![]() is known as the anomalous expansion of water.
is known as the anomalous expansion of water.
Solution B.9
Density of water is maximum at 4![]() . Its value is 1000 kgm-3.
. Its value is 1000 kgm-3.
Solution B.10
(i) Water just in contact with ice is at 0![]() .
.
(ii) Water at the bottom of the pond is at 4![]() .
.
Solution C.1
Heat is a form of energy obtained due to the random motion of molecules in a substance but temperature is a quantity which decided the direction of flow of heat when two bodies at different temperature are placed in contact. Two quantities having the same amount of heat may differ in temperature.
Solution C.2
The expansion of a substance on heating is called thermal expansion.
Solution C.3
The three kinds of thermal expansion are linear expansion, superficial expansion and cubical (or volumetric) expansion.
On heating, gases expand more.
Solution C.4
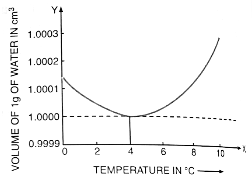
When a given mass of water is heated from 0° C to 4° C, it contracts, i.e. its volume decreases.
On heating from 4° C to 10° C, it expands, i.e. its volume increases.
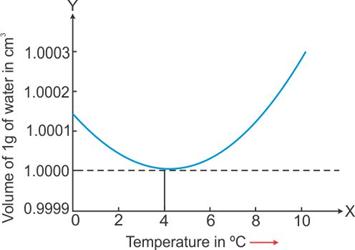
Solution C.5
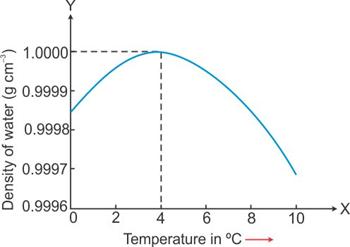
Solution C.6
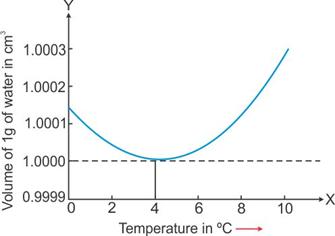
Solution C.7
(a) On winter nights, as the atmospheric pressure starts falling below 4°C, water in the pipe lines expand and exert a great pressure on the pipes, causing them to burst.
(b) In winters, when temperature falls, the surface of water in the tank contracts, becomes denser and sinks to the bottom. A circulation is thus set up until the entire water in the tank reaches its maximum density at 4°C. If the temperature falls further, then the top layer expands and remains on the top till it freezes. Thus, water in a tank starts freezing from the top and not from the bottom.
(c) The anomalous expansion of water helps preserve aquatic life during very cold weather. When temperature falls, the top layer of water in a pond contracts becomes denser and sinks to the bottom. A circulation is thus set up until water in the pond reaches its maximum density at 4°C. If the temperature falls further, then the top layer expands and remains on the top till it freezes. Thus, even though the upper layer are frozen, the water near the bottom is at 4°C and the fishes can survive in it easily.
(d) On heating water above 4![]() , the density of water decreases. As a result, the upthrust acting due to water on hollow glass sphere also decreases, which causes it to sink.
, the density of water decreases. As a result, the upthrust acting due to water on hollow glass sphere also decreases, which causes it to sink.
(e) Inside the freezer, when the temperature of water falls below 4![]() , the water in the bottle starts expanding. If the bottle is completely filled and tightly closed, there is no space for water to expand, and hence, the bottle may burst.
, the water in the bottle starts expanding. If the bottle is completely filled and tightly closed, there is no space for water to expand, and hence, the bottle may burst.
Solution D.1
Hope's experiment to demonstrate that water has maximum density at 4°C:
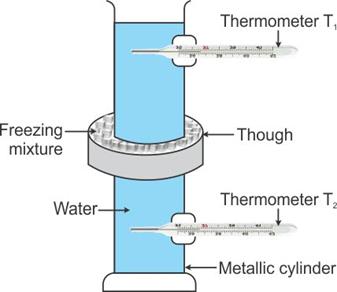
Hope's apparatus consists of a tall metallic cylinder provided with two side openings P and Q, P near the top and Q near the bottom, fitted with thermometers T1 and T2 in them. The central part of the cylinder is surrounded with a cylindrical trough containing a freezing mixture of ice and salt. The cylinder is fitted with pure water at room temperature.
Observations: (i) Initially, both thermometers T1 and T2 are at the same temperature.
(ii) First, the temperature recorded by the lower thermometer T2 starts decreasing and finally it becomes steady at 4°C, while the temperature recorded in the upper thermometer T1 remains almost unchanged during this time.
(iii) Then, the temperature recorded by the lower thermometer T2 remains constant at 4°C and upper thermometer T1 records a continuous fall in temperature up to 0°C and then it becomes steady.
Thus, finally, the temperature recorded by the upper thermometer is 0°C and that by lower thermometer is 4°C.
As the freezing mixture cools water in the central portion of the cylinder, water contracts and its density increases, consequently it sinks to the bottom, thereby causing the reading of the lower thermometer T2 to fall rapidly. The reading of the upper thermometer T1 does not change as the temperature of water in the upper part does not change. This continues till the entire water below the central portion reaches 4°C. On cooling further below 4°C, due to anomalous expansion, water of the central portion expands, so its density decreases and hence it rises up. As a result, reading of the upper thermometer T1 falls rapidly to 0°C and water freezes to form ice at 0°C near the top. This proves that water has maximum density at 4°C.
This anomalous expansion of water helps in preserving the aquatic life during the very cold weather. In winters, when the temperature falls, the top layer of water in a pond contracts, becomes denser and sinks to the bottom. A circulation is thus set up until the entire water in the pond reaches its maximum density at 4°C. If the temperature falls further, then the top layer expands and remains on the top till it freezes. Thus, even though the upper layers are frozen, the water near the bottom is at 4°C and the fishes can survive in it easily.
Solution D.2
Heat and Energy Exercise Ex 6(B)
Solution A.1
(a) trees
Solution A.2
(d) 0.02%
Solution A.3
(b) Photosynthesis
Solution A.4
(a) Sun
Solution A.5
(d) Producers
Solution A.6
(b) Consumer
Solution A.7
(b) Carnivores
Solution A.8
(b) plants
Solution A.9
(b) conservation of energy
Solution A.10
(d) None of these
Solution B.1
A unit composed of biotic components (i.e. producers, consumers and decomposers) and abiotic components (i.e. light, heat, rain, and humidity, inorganic and organic substances) is called an ecosystem.
Solution B.2
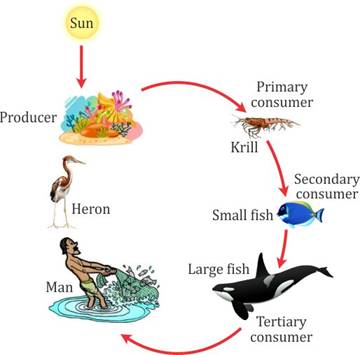
A food chain shows the feeding relationship between different living things in a particular environment or habitat. Often, a plant will begin a food chain because it can make its own food using energy from the Sun. In addition, a food chain represents a series of events in which food and energy are transferred from one organism in an ecosystem to another. Food chains show how energy is passed from the sun to producers, from producers to consumers, and from consumers to decomposers.
Solution B.3
The laws of thermodynamics govern the energy flow in the ecosystem.
According to the first law of thermodynamic, the energy can be transformed from one form to the other form, but it can neither be created nor destroyed.
According to the second law of thermodynamics, when energy is put to work, a part of it is always converted in un-useful form such as heat mainly due to friction and radiation.
Solution B.4
Biotic components: producers, decomposers, consumers such as plants, animals and humans.
Abiotic components: light, heat, rain, humidity, inorganic and organic substances.
Solution B.5
The tertiary consumers obtain their energy from the secondary consumers.
Solution C.1
The source of energy for all ecosystems is the Sun.
Solution C.2
Green plants absorb most of the energy falling on them and by the process of photosynthesis they produce food for the consumers. Plants, being primary producers are of great importance in the ecosystem. They also maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide on earth.
Solution C.3
Producers like plants and some bacteria are capable of producing its own food using the energy of sun but consumers are not capable of producing their own food. They depend on producers for food.
Solution C.4
The role of a decomposer is to break down dead organisms and then feed on them. The nutrients created by the dead organisms are returned to the soil to be later used by the producers. Once these deceased organisms are returned to the soil, they are used as food by bacteria and fungi by transforming the complex organic materials into simpler nutrients. The simpler products can then be used by producers to restart the cycle. These decomposers play an important role in every ecosystem.
Solution C.5
Primary consumers: The primary consumers are those which feeds on producers such as plants and bacteria. Example: Deer, rabbit etc.
Secondary consumers: Secondary consumers are those which feeds on primary consumers and are eaten by tertiary consumers. Examples: tiger, wolf etc.
Tertiary consumers: Tertiary consumers are those which feeds on secondary consumers. Example: Snake, owl etc.
Solution C.6
Some of the energy during the transformation in ecosystem is used in respiration and in decay appears as unuseful energy as it is not transferred further to consumer on next stage. Thus, energy transferred in an ecosystem is not 100 % efficient.
Solution D.1
Solution D.2
Ecosystems maintain themselves by cycling energy and nutrients obtained from external sources. At the first trophic level, primary producers (plants, algae, and some bacteria) use solar energy to produce organic plant material through photosynthesis. Herbivores-animals that feed solely on plants-make up the second trophic level. Predators that eat herbivores comprise the third trophic level; if larger predators are present, they represent still higher trophic levels. Decomposers, which include bacteria, fungi etc. break down wastes and dead organisms and return nutrients to the soil.
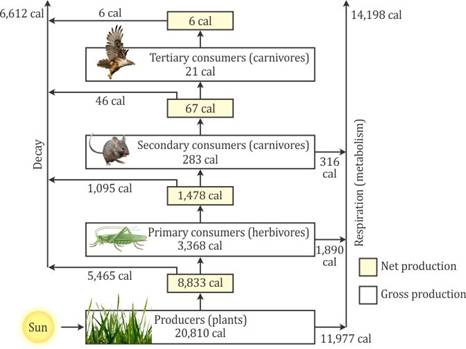
On average about 10 percent of net energy production at one trophic level is passed on to the next level. Processes that reduce the energy transferred between trophic levels include respiration, growth and reproduction, defecation, and non-predatory death.
The low rate of energy transfer between trophic levels makes decomposers generally more important than producers in terms of energy flow. Decomposers process large amounts of organic material and return nutrients to the ecosystem in inorganic forms, which are then taken up again by primary producers.
Solution D.3
The energy flow in ecosystem is linear i.e., it moves in a fixed direction. The solar energy is absorbed by plants and a part of it is converted into food. These plants (or primary producers) are then eaten by the primary consumers, which are consumed by secondary consumers and the secondary by tertiary consumers. This cycle is unidirectional. The dead and decomposed are fed by decomposers, which return the nutrients to the soil. At the end, the energy reaches the degraded state. It does not return to the sun to make the process cyclic, thus energy flow is linear.
Solution D.4
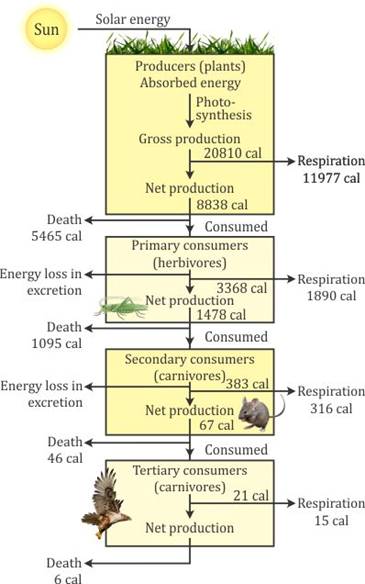
Solution D.5
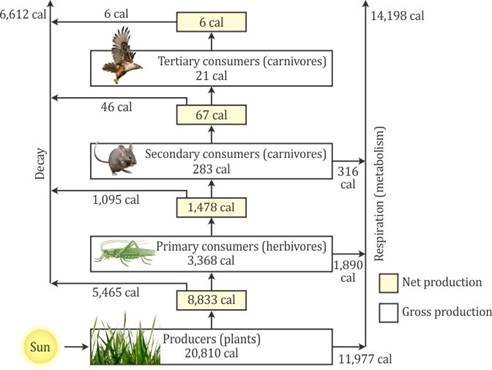
Heat and Energy Exercise Ex 6(C)
Solution A.1
(d) Sun
The ultimate source of energy is the Sun.
Solution A.2
(d) Sun
A renewable source of energy is the Sun.
Solution A.3
(c) renewable
Solution A.4
(d) Kinetic
Solution A.5
(d) both (a) and (b)
The energy obtained from the sun is called solar energy which is a renewable energy.
Solution A.6
(b) 1.34 kW m-2
Solution A.7
(d) (i) and (ii)
Biomass and nuclear fuel are renewable sources of energy.
Solution A.8
(d) Rocks
Solution A.9
(d) methane
The main constituent of biogas is methane.
Solution A.10
(b) C2H5SH
The chemical formula of the strong-smelling substance that is mixed in LPG is C2H5SH.
Solution A.11
(d) fractional distillation
Solution A.12
(a) (i)
The initial cost of solar panels is sufficiently high, but their running costs is almost nil.
Thus, statement (i) is incorrect.
Solution A.13
(d) All of the above
Coal, petroleum and natural gas are non - renewable sources of energy.
Solution B.1
1. A source of energy should be safe and convenient to use.
2. A source of energy should be economical and easy to store and transport.
Solution B.2
Renewable: Wood, Water and Wind
Non-renewable: Coal, Diesel and Oil
Solution B.3
Sun is the main source of energy on Earth.
Solution B.4
i. Light energy into electrical energy
ii. Mechanical energy into electrical energy.
iii. Mechanical energy into electrical energy.
iv. Nuclear energy (or heat energy) into electrical energy.
Solution B.5
The conversion of part of energy into a non-useful form of energy is called degradation of energy.
Solution C.1
The two groups in which various sources of energy are classified are renewable or non-conventional sources of energy and non-renewable or conventional sources of energy.
These sources are classified on the basis of their availability and utility.
Solution C.2
Renewable: The natural sources providing us energy continuously are called renewable sources of energy.
Non-renewable: The sources of energy which have accumulated in nature over a very long period of time and cannot be quickly replaced when exhausted are called non-renewable sources of energy.
Difference:
|
Renewable sources |
Non-renewable sources |
|
They can be utilised continuously. |
They cannot be utilised once exhausted. |
|
Examples: Sun, Wind |
Example: Coal, Petroleum |
Solution C.3
Wood is obtained from trees. Hence, trees need to be cut down for wood to be used as a fuel.
Also, burning wood releases a lot of smoke which pollutes the atmosphere.
Solution C.4
Renewable:
1. Sun
2. Wind
3. Flowing water
4. Tides
5. Nuclear fuel
Non-renewable:
1. Coal
2. Petroleum
3. Natural gas
Solution C.5
i. Tidal energy: The energy possessed by rising and falling water in tides is known as tidal energy.Dams are constructed across a narrow opening to the sea to harness tidal energy and produce electricity. However, it is not a major source of energy as the rise and fall of seawater during tides is not enough to generate electricity on a large scale.
ii. Ocean energy: Water in the oceans possesses energy in two forms:
a. Ocean thermal energy- The energy available due to the difference in temperature of water at the surface and at deeper levels of ocean is called the ocean thermal energy. This energy is harnessed for producing electricity by a device called ocean thermal energy conversion power plant (OCTEC power plant).
b. Oceanic waves energy- The kinetic energy possessed by fast moving oceanic (or sea) waves is called oceanic waves energy. Though models have been made to generate electricity from oceanic waves, but so far it has not been put to practical use.
iii. Geo thermal energy: The heat energy possessed by the rocks inside the Earth is called geothermal energy.The hot rocks present at the hot spots deep inside the Earth, heat the underground water and turn it into steam. This steam is compressed at high pressure between the rocks. Holes are drilled deep into the Earth up to the hot spots to extract the steam through pipes, which is utilized to rotate the turbines connected to the armature of an electric generator to produce electricity.
Solution C.6
Advantages of using solar panels:
- They do not cause any pollution in the environment.
- Running cost of solar panel is almost zero.
- They last over a long period of time.
- They do not require any maintenance.
- They are suitable for remote and inaccessible places where electricity power lines cannot be laid.
Disadvantages of using solar panels:
- The initial cost of a solar panel is sufficiently high.
- The efficiency of conversion of solar energy to electricity is low.
- A solar panel produces d.c. electricity which cannot be directly used for many household purposes.
Solution C.7
Advantages of using wind energy:
1. It does not cause any kind of pollution.
2. It is an everlasting source.
Limitations of using wind energy:
1. The establishment of a wind farm is expensive.
2. A large area of land is needed for the establishment of a wind farm.
Solution C.8
When a heavy nucleus is bombarded with slow neutrons, it splits into two nearly equal light nuclei with a release of tremendous amount of energy. In this process of nuclear fission, the total sum of masses of products is less than the total sum of masses of reactants. This lost mass gets converted into energy. The energy so released is called nuclear energy.
Principle: The heat energy released due to the controlled chain reaction of nuclear fission of uranium-235 in a nuclear reactor is absorbed by the coolant which then passes through the coils of a heat exchanger containing water. The water in heat exchanger gets heated and converts into steam. The steam is used to rotate the turbine which in turn rotates the armature of a generator in a magnetic field and thus produces electricity.
Solution D.1
The energy obtained from Sun is called solar energy.
A solar power plant is a device in which heat energy of sun is used to generate electricity. It consists of a large number of concave reflectors, at the focus of which there are black painted water pipes. The reflectors concentrate the heat energy of the sun rays on the pipes due to which water inside the pipes starts boiling and produces steam. The steam thus produced is used to rotate a steam turbine which drives a generator producing electricity.
Solution D.2
A solar cell is an electrical device that converts light energy directly into electricity with the help of photovoltaic effect. Solar cells are usually made from semiconductors like silicon and gallium with some impurity added to it. When sunlight is made incident on a solar cell, a potential difference is produced between its surface, due to which a current flows in the circuit connected between the opposite faces of the semiconductor.
Two uses of solar cells are as listed below:
- They do not require maintenance and last over a long period of time at zero running cost.
- They are very useful for remote, inaccessible and isolated places where electric power lines cannot be laid.Solar cell produces d.c. (direct current).
One disadvantage of solar cell is listed below:
(i) The initial cost of a solar panel is sufficiently high.
Solution D.3
Advantages of producing the hydro electricity:
- It does not produce any environmental pollution.
- It is a renewable source of energy.
Disadvantages of producing hydroelectricity:
- Due to the construction of dams over the rivers, plants and animals of that place get destroyed or killed.
- The ecological balance in the downstream areas of rivers gets disturbed.
Solution D.4
At present only about 3% of the total electrical power generated in India is obtained from the nuclear power plants.
Tarapur in Maharahtra and Narora in Uttar Pradesh are the places where electricity is produced using nuclear energy.
Solution D.5
Advantages of using nuclear energy:
- A very small amount of nuclear fuel can produce a tremendous amount of energy.
- Once the nuclear fuel is loaded into nuclear power plant, it continues to release energy for several years.
Disadvantages of using nuclear energy:
- It is not a clean source of energy because very harmful nuclear radiations are produced in the process.
- The waste causes environmental pollution.
Solution D.6
Four ways for the judicious use of energy are:
- The fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, natural gas should be used only for the limited purposes when there is no other alternative source of energy available.
- The wastage of energy should be avoided.
- Efforts must be made to make use of energy for community or group purposes.
- The cutting of trees must be banned and more and more new trees must be roped to grow.
Solution D.7
The gradual decrease of useful energy due to friction etc. is called the degradation of energy.
Examples:
- When we cook food over fire, the major part of heat energy from the fuel is radiated out in the atmosphere. This radiated energy is of no use to us.
- When electrical appliances are run by electricity, the major part of electrical energy is wasted in the form of heat energy.
Solution D.8
The kinetic energy of the moving large masses of air is called the wind energy. Wind energy is used in a wind generator to produce electricity by making use of wind mill to drive a wind generator.
At present in India, more than 1025 MW electric power is generated using wind energy.
Heat and Energy Exercise Ex 6(D)
Solution A.1
(c) absorbers
Solution A.2
(d) Carbon dioxide
Solution A.3
Increase in temperature
Solution A.4
(a) -18°C
Without greenhouse effect, the average temperature of Earth's surface would have been -18 °C.
Solution A.5
(d) increase, increase
Solution A.6
(d) the increase in sea levels
The global warming has resulted in the increase in sea levels.
Solution B.1
Greenhouse effect is the process of warming of planet's surface and its lower atmosphere by absorbtion of infrared radiations of longer wavelength emitted out from the surface of planet.
Solution B.2
Carbon-di-oxide, water vapour and methane are greenhouse gases.
Solution B.3
Visible light rays and short infrared radiation pass through the atmosphere of earth.
Solution B.4
Infrared radiations of long wavelength are absorbed by the green house gases.
Solution B.5
In absence of green house gases, the average temperature on earth would be -18![]() .
.
Solution C.1
The concentration of carbon-di-oxide content's of earth's atmosphere has increased due to industrial growth, combustion of fossil fuels and clearing of forests.
Solution C.2
The greenhouses gases have an average warming effect on Earth's surface of about 15.5![]() (or 60
(or 60![]() ).
).
Solution C.3
Global warming means the increase in average effective temperature near the earth's surface due to an increase in the amount of green house gases in its atmosphere.
Solution C.4
With activities industrialization, deforestation, excess burning of fossil fuel, the concentration of green house gases has increased on earth's atmosphere. This increase in the amount of greenhouse gases present in atmosphere has caused the rise in atmospheric temperature.
Solution C.5
The increase in green house gases due to activities like industrialization, deforestation, natural gas exploration, burning of biomass, natural gas exploration, more use of gadgets like refrigerators has caused the increase of green house effect.
Solution C.6
At the poles, due to increase in temperature, the snow and ice will melt which will cause flood in coastal countries. The icebergs of dark land and oceans will melt, so the dark land and oceans will become uncovered and will absorb more heat radiations coming from sun, increasing the green house effect further.
Solution C.7
Due to global warming, the snow and ice around the poles will melt and cause flood in coastal countries.
Solution C.8
Due to melting of polar ice and glaciers, there will be rise in sea level on coastal wet lands. It would raise worldwise sea level, thereby, many big cities in the coastal areas will be covered by sea water.
Solution C.9
Global warming will cause drastic changes in the patterns of wind, rainfall etc. Thus it will result in low agricultural yield.
Solution C.10
- Use of renewable sources of energy to generate electricity in place of generating electricity from the fossil fuels based power plants.
- Controlling population through family planning, welfare reforms and the empowerment of women.
Solution C.11
The tax calculated on the basis of carbon emission from industry, number of employee hour and turnover of the factory is called carbon tax.
This tax shall be paid by industries. This will encourage the industries to use the energy efficient techniques.

