Class 9 NCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 8 - Force And Laws Of Motion
Force And Laws Of Motion Exercise 91
Solution 1
Concept Insight: More mass means more inertia.
Solution 2
The velocity of the ball changes four times.
(i) As a football player kicks the football, its speed changes from zero to a certain value. As a result, the velocity of the ball gets changed. In this case, the force is applied by the kick of the player.
(ii) When the ball reaches another player, he kicks the ball towards the goal post. As a result, the direction of the ball and its speed both get changed. Therefore, its velocity also changes. In this case, the force is applied by the kick of the player.
(iii) When the goalkeeper collects the ball, the ball comes to rest, i.e. its speed reduces to zero from a certain value. Thus, the velocity of the ball changes. In this case, the force is applied by the hands of the goalkeeper.
(iv) The goalkeeper then kicks the stationary ball towards his team player, i.e., the speed of the ball increases from zero to a certain value. Hence, its velocity changes once again. In this case, the force is applied by the kick of the goalkeeper.
Concept Insight:- Velocity is a vector quantity. It has both magnitude and direction.
Solution 3
Some leaves of a tree may get detached when we shake its branch vigorously. This is because when the branch of the tree is shaken, it moves to and fro, but due to inertia its leaves tend to remain at rest. Due to this reason, the leaves fall down from the tree.
Solution 4
When a moving bus brakes to a stop, we fall in the forward direction because though the lower part of our body comes to a stop when the bus stops but the upper part of the body continues to be in motion in the forward direction due to its inertia, thus making us fall in the forward direction.
When a bus accelerates from rest, we fall backwards because though the lower part of our body starts moving with the bus but the upper part of the body tries to remain at rest due to its inertia, thus making us fall in the backward direction.
Force And Laws Of Motion Exercise 97
Solution 1
Yes. Even when an object experiences a net zero external unbalanced force, it is possible that the object is travelling with a non-zero velocity. This is possible only when the object has been moving with a constant velocity in a particular direction. Then, there is no net unbalanced force applied on the body. The object will keep moving with the same non-zero velocity.
Solution 2
Inertia of an object tends to resist any change in its state of rest or state of motion. When a carpet is beaten with a stick, then the carpet comes to motion. But, the dust particles try to retain their state of rest. Hence, the dust particles come out of the carpet.
Solution 3
When the bus suddenly accelerates from rest and moves forward, it acquires a state of motion. However, the luggage kept on the roof, owing to its inertia, tends to remain in its state of rest and hence may fall down from the roof of the bus.
Similarly, when the moving bus stops suddenly, then due to its inertia of motion, the luggage kept on the roof of the bus tends to remain in motion and hence may fall down from the roof of the bus.
Hence, it is advised to tie the luggage kept on the roof of a bus with a rope so that it does not fall down when the bus starts or stops suddenly.
Solution 4
(c) There is a force on the ball opposing the motion.
A batsman hits a cricket ball, which then rolls on a level ground. After covering a short distance, the ball comes to rest because there is frictional force on the ball opposing its motion.
Frictional force always acts in the direction opposite to the direction of motion. Hence, this force is responsible for stopping the cricket ball.
Solution 5
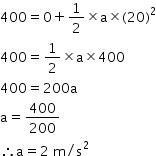
Solution 6
Concept Insight:- The negative sign indicates that acceleration is acting against the motion of the stone.
From Newton's second law of motion:
Force, F = Mass
F = ma
F = 1 × (- 4) = -4 N
Hence, the force of friction between the stone and the ice is -4 N.
Solution 7
From Newton's second law of motion:
Mass of the four wagons behind the first wagon = 4 2000 = 8000 kg
Acceleration of the wagons = 3.5 m/s2
Thus, force of wagon 1 on remaining four wagons behind it = 8000 3.5 = 28000 N
Hence, the force exerted by wagon 1 on wagon 2 is 28000 N.
Solution 8
Force And Laws Of Motion Exercise 98
Solution 9
Solution 10
Force applied, P = 200 N
Force of friction, F = ?
As the wooden cabinet is to move across the floor with a constant velocity, no force (f) is spent in accelerating the cabinet, i.e.,
f = P-F = 0
or, F = P = 200 N
Concept Insight:- For a non-accelerated motion, no net force is required.
Solution 11
When we push a massive truck parked along the roadside, it does not move. The justification given by the student that the two opposite and equal forces cancel each other is totally wrong. This is because force of action and reaction never act on one body. There is no question of their cancellation. The truck does not move because the push applied is far less than the force of friction between the truck and the road.
Concept Insight:- Action and reaction forces act on different objects.
Solution 12
Mass of the hockey ball, m = 200 g = 0.2 kg
Hockey ball travels with velocity, v1 = 10 m/s
Initial momentum = mv1
After being struck by the stick, the hockey ball travels in the opposite direction with velocity, v2 = -5 m/s
Final momentum = mv2
Concept Insight:- Change in momentum = Final momentum - Initial momentum
Change in momentum = mv2 - mv1 = m (v2 - v1) = 0.2 [-5-10] = 0.2 (-15) = -3 kg ms-1
Hence, the change in momentum of the hockey ball is -3 kg ms-1.
Solution 13
Mass of the bullet, m = 10 g = 0.01 kg
It is given that the bullet is travelling with a velocity of 150 m/s.
Thus, when the bullet enters the block, its velocity = Initial velocity, u = 150 m/s
Final velocity, v = 0 (since the bullet finally comes to rest)
Time taken to come to rest, t = 0.03 s
According to the first equation of motion,
v = u + at
where , a is the acceleration of the bullet
0 = 150 + (a × 0.03)
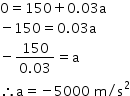
According to the third equation of motion:
v2 = u2 + 2 as
0 = (150)2 + 2×(-5000)×s
0 = 22500 + 2×(-5000)×s
0=22500 - 10000 s
10000 s = 22500
![]()
From Newton's second law of motion:
Concept Insight:- Force, F = Mass Acceleration
Mass of the bullet, m = 0.01 kg
Acceleration of the bullet, a = -5000 m/s2
F = ma = 0.01×(-5000) = -50 N
Hence, the magnitude of force exerted by the wooden block on the bullet is 50 N.
Solution 14
Mass of the object, m1 = 1 kg
Velocity of the object before collision, v1 = 10 m/s
Mass of the stationary wooden block, m2 = 5 kg
Velocity of the wooden block before collision, v2 = 0 m/s
Total momentum before collision = m1v1+m2v2 = (1×10)+(5×0) = 10 kg m s-1
According to the law of conservation of momentum, the total momentum just after the impact will be the same as the total momentum just before the impact.
i.e., the total momentum just after the impact will be 10 kg m s-1.
It is given that after collision, the object and the wooden block stick together.
Total mass of the combined system = m1 + m2
Velocity of the combined system = v
According to the law of conservation of momentum:
Concept Insight:- Total momentum before collision = Total momentum after collision
m1v1+m2v2 = (m1+m2)v
(1×10)+(5×0) = (1+5)v
10+0 = 6v
10 = 6v
![]()
Hence, velocity of the combined object after collision will be 1.67 m/s.
Solution 15
Initial velocity of the object, u = 5 m/s
Final velocity of the object, v = 8 m/s
Mass of the object, m = 100 kg
Time taken by the object to accelerate, t = 6 s
Initial momentum of the object = mu = 100 5 = 500 kg ms-1
Final momentum of the object = mv = 100 8 = 800 kg ms-1
Concept Insight:- Force exerted on the object, F =
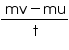
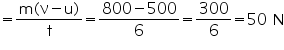
Solution 16
The suggestion made by Kiran that the insect suffered a greater change in momentum as compared to the change in momentum of the motor car is wrong. The suggestion made by Akhtar that the motor car exerted a larger force on the insect because of large velocity of motor car is also wrong. The explanation put forward by Rahul is correct. On collision of insect with motor car, both experience the same force as action and reaction are always equal and opposite. Further, changes in their momenta are also the same. Only the signs of changes in momenta are opposite, i.e., change in momenta of the two occur in opposite directions, though magnitude of change in momentum of each is the same.
Force And Laws Of Motion Exercise 99
Solution 17
Mass of the dumbbell, m = 10 kg
Distance covered by the dumbbell, s = 80 cm = 0.8 m
Acceleration in the downward direction, a = 10 m/s2
Initial velocity of the dumbbell, u = 0
Final velocity of the dumbbell (when it was about to hit the floor) = v
Concept Insight Choose the equation of motion wisely out of the three, to minimize the number of steps in calculations.
According to the third equation of motion:
v2 = u2 + 2as
v2 = 0 + 2 (10) 0.8
v = 4 m/s
Hence, the momentum with which the dumbbell hits the floor = mv = 10×4 = 40 kg m s-1
Momentum transferred to the floor is 40 kg m/s.
Solution A1
(a) A careful observation of the distance-time table shows that
![]()
It is known that
(i) for motion with uniform velocity (zero acceleration)
![]()
(ii) for motion with uniform acceleration
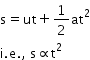
In the present case, ![]() . Therefore, we conclude in this case that acceleration must be increasing uniformly with time.
. Therefore, we conclude in this case that acceleration must be increasing uniformly with time.
(b) As F = ma, therefore, F ![]() a. Hence, the force must also be increasing uniformly with time.
a. Hence, the force must also be increasing uniformly with time.
Solution A2
Here, mass of motorcar, m = 1200 kg
Let each person exert a push F on the motorcar.
Total push of two persons = F + F = 2F
As this push gives a uniform velocity to the motorcar along a level road, it must be a measure of the force of friction (f) between the motorcar and the road,
i.e., f = 2F.
When three person push, total force applied = F + F + F = 3F
Force that produces acceleration (a=0.2 m/s2),
i.e., ma = 3F-f = 3F-2F = F
or, F = ma = 1200 × 0.2 = 240 N
Solution A3

Thus, the force of the nail on the hammer is 2500 N. Negative sign indicates the opposing force.
Solution A4

Change in momentum = mv-mu = m(v-u) = 1200×(5-25)= -24000 kg m/s
Force required , F = ma = 1200×(-5) = -6000 N
Magnitude of force required = 6000 N
Negative sign shows that force is opposing the motion.

