Class 10 SELINA Solutions Maths Chapter 20 - Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume)
The holistic approach of the Indian Certificate of Secondary Education Board makes it a popular choice among students and parents. The ICSE curriculum focuses on both academic excellence and the overall development of students. However, it follows a strict evaluation process to make sure that students are equipped with a strong foundation in various subjects, including Mathematics. Therefore, referring to textbook solutions play a crucial role in the educational journey of ICSE students. They help students understand the right way to answer questions.
The ICSE Class 10 Math Chapter- Cylinder, Cone, and Sphere- Surface Area and Volume contain questions related to these three-dimensional geometric shapes and their surface area and volume calculations. Solving such questions allows students to realise the practical applications of geometric shapes and their measurements. Thus, it fosters a deeper understanding of their significance.
The Selina Solutions of this chapter provide solutions to all the questions covered in the ICSE maths Selina textbook. The structured presentation of solutions makes finding the answers easier and quick. The problems involve real-life scenarios such as calculating the volume of water in a spherical tank, determining the volume of cones used in construction, calculating the capacity of cylindrical tanks, etc.
The following are the benefits of Selina Solutions
- It provides comprehensive explanations and step-by-step solutions.
- The Solutions cover the entire syllabus in an updated and structured manner.
- It promotes self-study and problem-solving skills.
- It offers detailed answers and ample practice opportunitie
- These Solutions enhance the students' understanding, mathematical reasoning, and overall performance.
You can find Selina Solution for all subjects for classes 9 and 10 at TopperLearning. Additionally, we also offer several resource materials such as practice questions, sample papers, video lessons, textbook solutions of different boards, revision notes, and much more. Our Ask a Doubt platform allows students to clarify their doubts through text or uploaded images and browse pre-answered free questions and answers from different boards. Thus, we provide resources and guidance that help students perform exceptionally well in examinations.
Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Exercise Ex. 20(A)
Solution 1

Solution 2
Inner radius of pipe = 2.1 cm
Length of the pipe = 12 m = 1200 cm
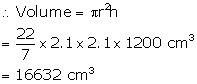
Solution 3
Circumference of cylinder = 8 cm
Therefore, radius = ![]()
Length of the cylinder (h)= 21 cm

(i) If distance covered in one revolution is 8 cm, then distance covered in 9 revolutions = 9 ![]() 8 = 72 cm or distance covered in 1 second = 72 cm.
8 = 72 cm or distance covered in 1 second = 72 cm.
Therefore, distance covered in ![]() seconds =
seconds = ![]()
(ii) Curved surface area = ![]()
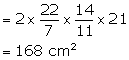
Area covered in one revolution = ![]()
Area covered in 9 revolutions = ![]()
Therefore, area covered in 1 second = ![]()
Hence, area covered in ![]() seconds =
seconds = ![]()
Solution 4
Radius of the well = ![]()
Depth of the well = 28 m
Therefore, volume of earth dug out = ![]()
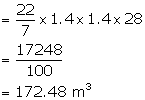
Area of curved surface = ![]()
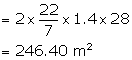
Cost of plastering at the rate of Rs 4.50 per sq m
= Rs 246.40 ![]() 4.50
4.50
= Rs 1108.80
Solution 5
External diameter of hollow cylinder = 20 cm
Therefore, external radius, R = 10 cm
Thickness = 0.25 cm
Hence, internal radius, r = (10 - 0.25) = 9.75 cm
Length of cylinder (h) = 15 cm
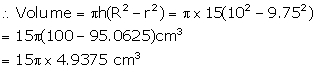
For solid cylinder,
Diameter = 2 cm
Therefore, radius (r) = 1 cm
Let h be the length
then, ![]()
Now, according to given condition:
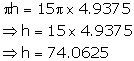
Length of cylinder = 74.06 cm
Solution 6
Diameter of the cylinder = 20 cm
Hence, Radius (r) = 10 cm
Height = h cm
(i) Curved surface area = ![]()
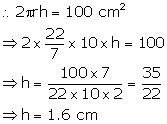
(ii) Volume of the cylinder = ![]()
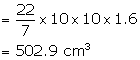
or
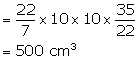
Solution 7

Solution 8
Diameter of cylindrical container = 42 cm
Therefore, radius (r) = 21 cm
Dimensions of rectangular solid = 22cm × 14cm × 10.5cm
Volume of solid =22 × 14 ×10.5 cm3 ...... (i)
Let height of water = h
Therefore, volume of water in the container =πr2h
![]()
From (i) and (ii)
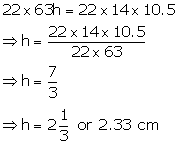
Solution 9
Internal radius of the cylindrical container = 10 cm
Height of water = 7 cm
Therefore, surface area of the wetted surface =
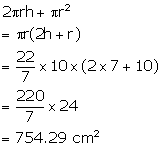
Solution 10
Length of an open pipe = 50 cm
External diameter = 20 cm ⇒ External radius (R) = 10 cm
Internal diameter = 6 cm ⇒ Internal radius (r) = 3 cm
Surface area of pipe open from both sides =
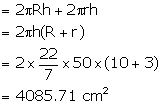
Area of upper and lower part =
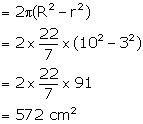
Total surface area =4085.71+572=4657.71 cm2
Solution 11
Ratio between height and radius of a cylinder = 3:1
Volume = ![]() …….(i)
…….(i)
Let radius of the base = r
then height = 3r
![]()
from (i) and (ii)
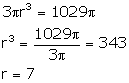
Therefore, radius = 7 cm and height = 3 x 7 = 21 cm
Now, total surface area =
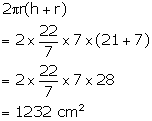
Solution 12

Solution 13


Solution 14

Solution 15

Solution 16

Solution 17
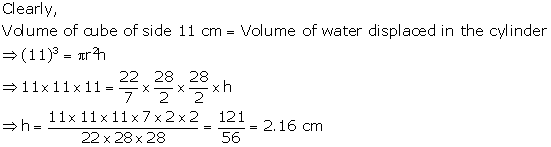
Solution 18

Solution 19
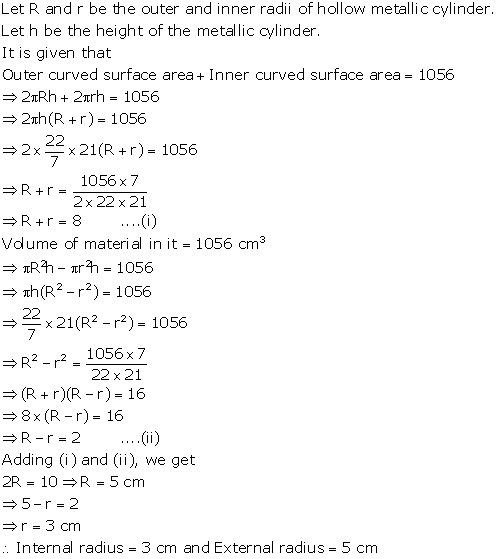
Solution 20
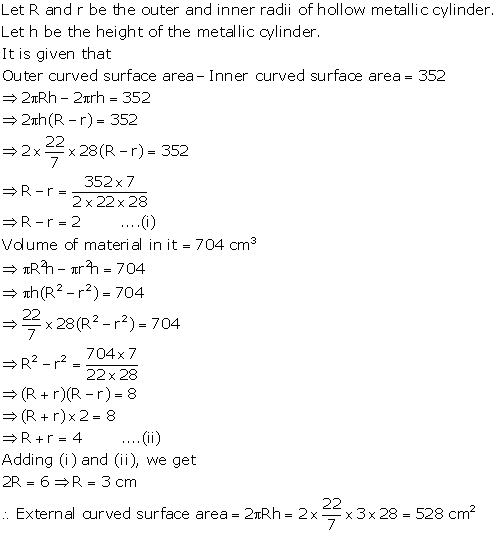
Solution 21

Solution 22

Solution 23

Solution 24

Solution 25
Total surface area of a hollow cylinder = 3575 cm2
Area of the base ring = 357.5 cm2
Height = 14 cm
Let external radius = R and internal radius = r
Let thickness of the cylinder = d = (R-r)
Therefore, Total surface area = ![]()
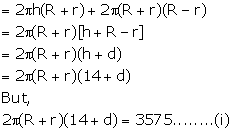
and Area of base =

Dividing (i) by (ii)

Hence, thickness of the cylinder = 3.5 cm
Solution 26

Solution 27

Solution 28

Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Exercise Ex. 20(B)
Solution 1
Slant height (ℓ) = 17 cm
Radius (r) = 8 cm
But,
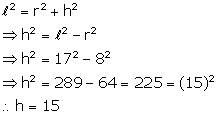
Now, volume of cone = ![]()
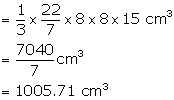
Solution 2
Curved surface area = ![]()
Radius of base (r) = 56 cm
Let slant height = ![]()
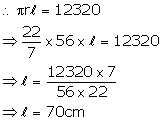
Height of the cone =
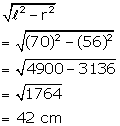
Solution 3
Circumference of the conical tent = 66 m
and height (h) = 12 m
![]()
Therefore, volume of air contained in it = ![]()
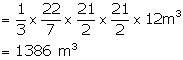
Solution 4
The ratio between radius and height = 5:12
Volume = 5212 cubic cm
Let radius (r) = 5x, height (h) = 12x and slant height = ![]()
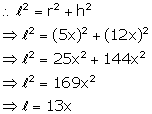
Now Volume = ![]()

Solution 5
Let radius of cone y = r
Therefore, radius of cone x = 3r
Let volume of cone y = V
then volume of cone x = 2V
Let h1 be the height of x and h2 be the height of y.
Therefore, Volume of cone = ![]()
Volume of cone x = ![]()
Volume of cone y = ![]()
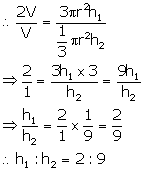
Solution 6
Let radius of each cone = r
Ratio between their slant heights = 5:4
Let slant height of the first cone = 5x
and slant height of second cone = 4x
Therefore, curved surface area of the first cone =
![]()
curved surface area of the second cone = ![]()
Hence, ratio between them = ![]()
Solution 7
Let slant height of the first cone = ![]()
then slant height of the second cone = 2![]()
Radius of the first cone = ![]()
Radius of the second cone = ![]()
Then, curved surface area of first cone = ![]()
curved surface area of second cone = ![]()
According to given condition:
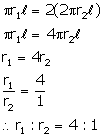
Solution 8
Diameter of the cone = 16.8 m
Therefore, radius (r) = 8.4 m
Height (h) = 3.5 m
(i) Volume of heap of wheat = ![]()
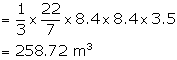
(ii) Slant height (![]() ) =
) = ![]()
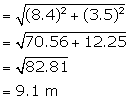
Therefore, cloth required or curved surface area = ![]()
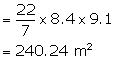
Solution 9
Diameter of the tent = 48 m
Therefore, radius (r) = 24 m
Height (h) = 7 m
Slant height (![]() ) =
) = ![]()
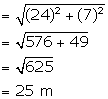
Curved surface area = ![]()
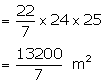
Canvas required for stitching and folding
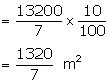
Total canvas required (area)
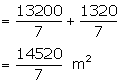
Length of canvas
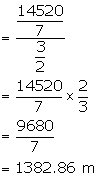
Rate = Rs 24 per meter
Total cost ![]()
Solution 10
Height of solid cone (h) = 8 cm
Radius (r) = 6 cm
Volume of solid cone = ![]()
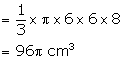
Height of smaller cone = 2 cm
and radius = ![]()
Volume of smaller cone
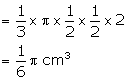
Number of cones so formed
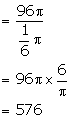
Solution 11
Total surface area of cone = ![]()
slant height (l) = 13 cm
(i) Let r be its radius, then
Total surface area = ![]()
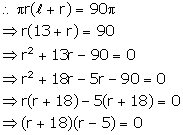
Either r+18 = 0, then r = -18 which is not possible
or r-5=0, then r = 5
Therefore, radius = 5 cm
(ii) Now
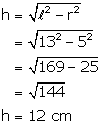
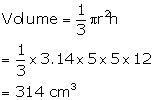
Solution 12

Solution 13
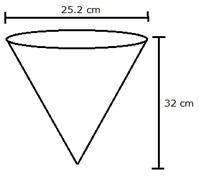
Volume of vessel = volume of water = ![]()
diameter = 25.2 cm, therefore radius = 12.6 cm
height = 32 cm
Volume of water in the vessel = ![]()
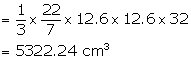
On submerging six equal solid cones into it, one-fourth of the water overflows.
Therefore, volume of the equal solid cones submerged
= Volume of water that overflows
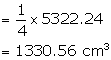
Now, volume of each cone submerged
![]()
Solution 14
(i) Let r be the radius of the base of the conical tent, then area of the base floor = ![]()
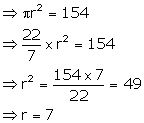
Hence, radius of the base of the conical tent i.e. the floor = 7 m
(ii) Let h be the height of the conical tent, then the volume =
![]()
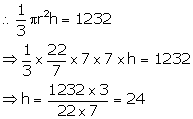
Hence, the height of the tent = 24 m
(iii) Let l be the slant height of the conical tent, then ![]()
![]()
The area of the canvas required to make the tent = ![]()
![]()
Length of the canvas required to cover the conical tent of its width 2 m = ![]()
Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Exercise Ex. 20(C)
Solution 1
Surface area of the sphere = 2464 cm2
Let radius = r, then
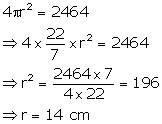
Volume = ![]()
![]()
Solution 2
Volume of the sphere = 38808 cm3
Let radius of sphere = r
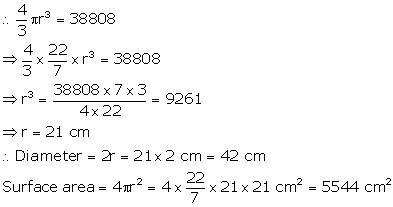
Solution 3
Let the radius of spherical ball = r
![]()
Radius of smaller ball = ![]()
![]()
Therefore, number of smaller balls made out of the given ball =
Solution 4
Diameter of bigger ball = 8 cm
Therefore, Radius of bigger ball = 4 cm
![]()
Radius of small ball = 1 cm
![]()
Number of balls = 
Solution 5
Radius of metallic sphere = 2 mm = ![]()
![]()
Volume of 8 spheres = ![]()
Let radius of new sphere = R
![]()
From (i) and (ii)
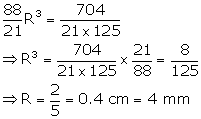
Solution 6
Volume of first sphere = 27 ![]() volume of second sphere
volume of second sphere
Let radius of first sphere =![]()
and radius of second sphere = ![]()
Therefore, volume of first sphere = ![]()
and volume of second sphere = ![]()
(i) Now, according to the question
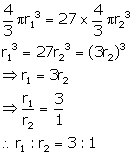
(ii) Surface area of first sphere = ![]()
and surface area of second sphere = ![]()
Ratio in surface area = ![]()
Solution 7
Let r be the radius of the sphere.
Surface area = 4πr2 and volume = ![]()
According to the condition:
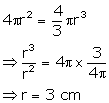
Diameter of sphere = 2 × 3 cm = 6 cm
Solution 8
Diameter of sphere = ![]()
Therefore, radius of sphere = ![]()
Total curved surface area of each hemispheres =
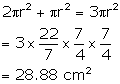
Solution 9
External radius (R) = 14 cm
Internal radius (r) = ![]()
(i) Internal curved surface area =
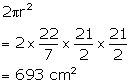
(ii) External curved surface area =
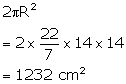
(iii) Total surface area =
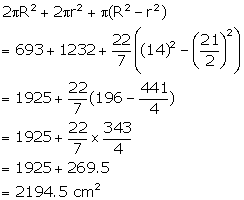
(iv) Volume of material used =

Solution 10
Let the radius of the sphere be 'r1'.
Let the radius of the hemisphere be 'r2'
TSA of sphere = 4∏r12
TSA of hemisphere = 3∏r22
TSA of sphere = TSA of hemi-sphere
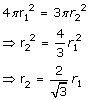
Volume of sphere, V1 = ![]()
Volume of hemisphere, V2 = ![]()
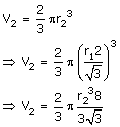
Dividing V1 by V2,
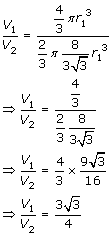
Solution 11
Let radius of the larger sphere be 'R'
Volume of single sphere
= Vol. of sphere 1 + Vol. of sphere 2 + Vol. of sphere 3
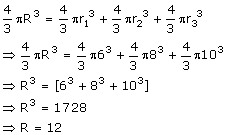
Surface area of the sphere

Solution 12
Let the radius of the sphere be 'r'.
Total surface area the sphere, S ![]()
New surface area of the sphere, S'
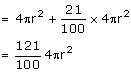
(i) Let the new radius be r1
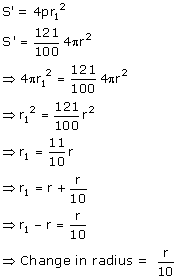
Percentage change in radius
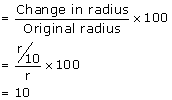
Percentage change in radius = 10%
(ii) Let the volume of the sphere be V
Let the new volume of the sphere be V'.

Percentage change in volume =33.1%
Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Exercise Ex. 20(D)
Solution 1

Solution 2
External diameter = 8 cm
Therefore, radius (R) = 4 cm
Internal diameter = 4 cm
Therefore, radius (r) = 2 cm
Volume of metal used in hollow sphere = ![]()
Diameter of cone = 8 cm
Therefore, radius = 4 cm
Let height of cone = h
![]()
From (i) and (ii)
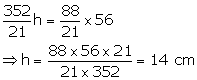
Height of the cone = 14 cm
Solution 3
Internal radius = 3cm
External radius = 5 cm
Volume of spherical shell
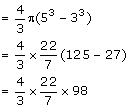
Volume of solid circular cone
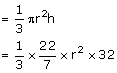
Vol. of Cone = Vol. of sphere
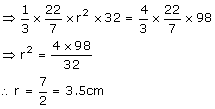
Hence, diameter = 2r = 7 cm
Solution 4
Let the radius of the smaller cone be 'r' cm.
Volume of larger cone
![]()
Volume of smaller cone
![]()
Volume of larger cone=3× Volume of smaller cone
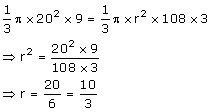

Solution 5
Volume of rectangular block = ![]()
Let r be the radius of sphere
![]()
From (i) and (ii)
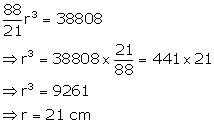
Radius of sphere = 21 cm
Solution 6
Radius of hemispherical bowl = 9 cm
![]()
Diameter each of cylindrical bottle = 3 cm
Radius =  cm, and height = 4 cm
cm, and height = 4 cm
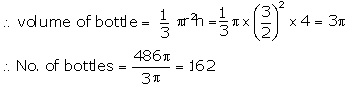
Solution 7
Diameter of the hemispherical bowl = 7.2 cm
Therefore, radius = 3.6 cm
Volume of sauce in hemispherical bowl = ![]()
Radius of the cone = 4.8 cm
Volume of cone = ![]()
Now, volume of sauce in hemispherical bowl = volume of cone

Height of the cone = 4.05 cm
Solution 8
Radius of a solid cone (r) = 5 cm
Height of the cone = 8 cm
⇒Volume of a cone
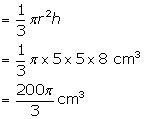
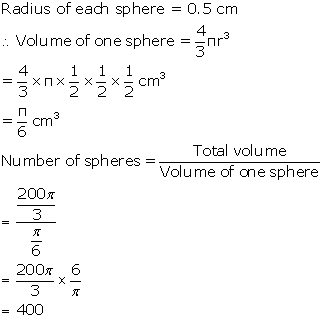
Solution 9
Total area of solid metallic sphere = 1256 cm2
(i)Let radius of the sphere is r then
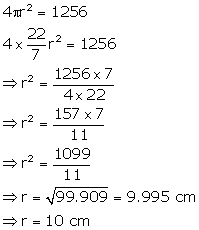
(ii) Volume of sphere = ![]() Volume of right circular cone =
Volume of right circular cone =
![]()
Number of cones
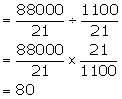
Solution 10
Volume of the whole cone of metal A
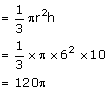
Volume of the cone with metal B
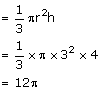
Final Volume of cone with metal A=120 ![]() -12
-12 ![]() =108
=108 ![]()
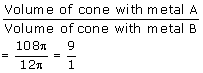
Solution 11
Let the number of small cones be 'n'
Volume of sphere
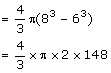
Volume of small spheres
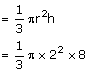
Volume of sphere = n× Volume of small sphere
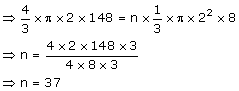
The number of cones = 37
Solution 12

Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Exercise Ex. 20(E)
Solution 1
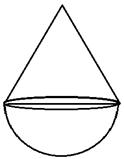
Height of cone = 15 cm
and radius of the base = ![]() cm
cm
Therefore, volume of the solid = volume of the conical part + volume of hemispherical part.
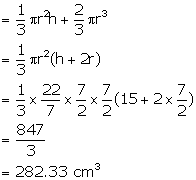
Solution 2
Radius of hemispherical part (r) = 3.5 m = ![]()
Therefore, Volume of hemisphere = ![]()
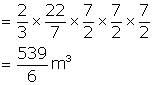
Volume of conical part = ![]() (2/3 of hemisphere)
(2/3 of hemisphere)
Let height of the cone = h
Then,
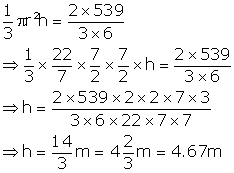
Height of the cone = 4.67 m
Surface area of buoy = ![]()
But ![]()
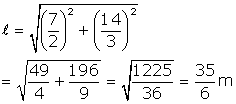
Therefore, Surface area =
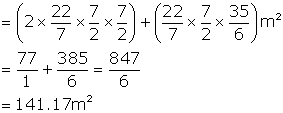
Surface Area = 141.17 m2
Solution 3
(i) Total surface area of cuboid = 2(ℓb + bh + ℓh)
=2(42 × 30 + 30 × 20 + 20 × 42)
=2(1260 + 600 + 840)
=2 × 2700
=5400 cm2
Diameter of the cone = 14 cm
⇒ Radius of the cone = ![]()
Area of circular base![]()
Area of curved surface area of cone![]()
Surface area of remaining part = 5400 + 550 - 154 =5796 cm2
(ii) Dimensions of rectangular solids = (42 × 30 × 20) cm
volume = (42 × 30 × 20) = 25200 cm3
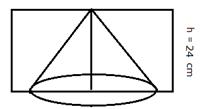
Radius of conical cavity (r) =7 cm
height (h) = 24 cm
Volume of cone = ![]()
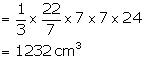
Volume of remaining solid = (25200 - 1232) = 23968 cm3
(iii) Weight of material drilled out
=1232 × 7 g = 8624g = 8.624 kg
Solution 4
The diameter of the largest hemisphere that can be placed on a face of a cube of side 7 cm will be 7 cm.
Therefore, radius = ![]()
Its curved surface area =
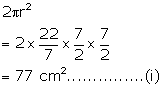
Surface area of the top of the resulting solid = Surface area of the top face of the cube - Area of the base of the hemisphere
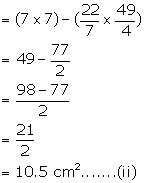
Surface area of the cube = 5 × (side)2 = 5 × 49 = 245 cm2 .........(iii)
Total area of resulting solid = 245 + 10.5 + 77 = 332.5 cm2
Solution 5
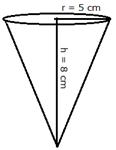
Height of cone = 8 cm
Radius = 5 cm
Volume = ![]()
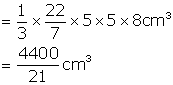
Therefore, volume of water that flowed out =
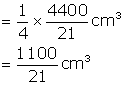
Radius of each ball = 0.5 cm = ![]()
Volume of a ball = ![]()
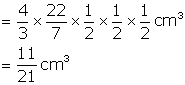
Therefore, No. of balls = ![]()
Hence, number of lead balls = 100
Solution 6
Let r be the radius of the bowl.
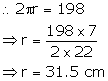
Capacity of the bowl =

Solution 7
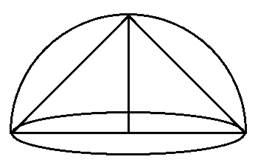
For the volume of cone to be largest, h = r cm
Volume of the cone
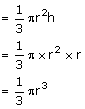
Solution 8
Let the height of the solid cones be 'h'
Volume of solid circular cones
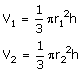
Volume of sphere
![]()
Volume of sphere = Volume of cone 1 + volume of cone 2
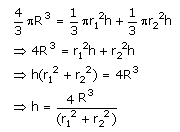
Solution 9
Volume of the solid hemisphere
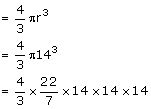
Volume of 1 cone
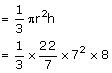
No. of cones formed
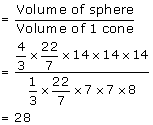
Solution 10
Let the radius of base be 'r' and the height be 'h'
Volume of cone, Vc
![]()
Volume of hemisphere, Vh
![]()
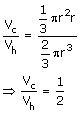
Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Exercise Ex. 20(F)
Solution 1
Height of the cylinder (h) = 10 cm
and radius of the base (r) = 6 cm
Volume of the cylinder = ![]()
Height of the cone = 10 cm
Radius of the base of cone = 6 cm
Volume of the cone = ![]()
Volume of the remaining part
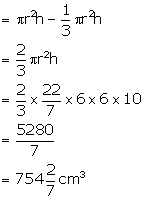
Solution 2
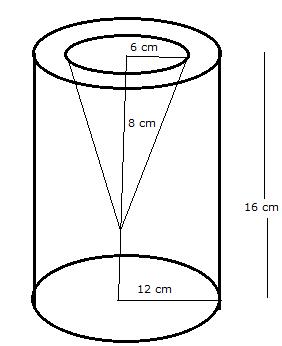
Radius of solid cylinder (R) = 12 cm
and Height (H) = 16 cm
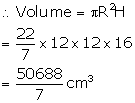
Radius of cone (r) = 6 cm, and height (h) = 8 cm.
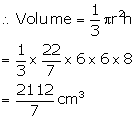
(i) Volume of remaining solid

(ii) Slant height of cone ![]()
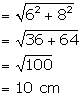
Therefore, total surface area of remaining solid = curved surface area of cylinder + curved surface area of cone + base area of cylinder + area of circular ring on upper side of cylinder
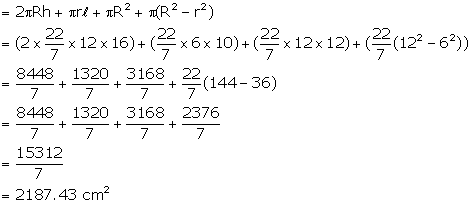
Solution 3
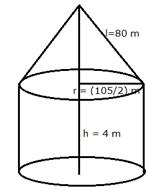
Radius of the cylindrical part of the tent (r) = ![]()
Slant height (![]() ) = 80 m
) = 80 m
Therefore, total curved surface area of the tent = ![]()
Width of canvas used = 1.5 m
Length of canvas = ![]()
Total cost of canvas at the rate of Rs 15 per meter
![]()
Solution 4
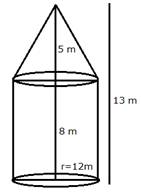
Height of the cylindrical part = H = 8 m
Height of the conical part = h = (13-8)m = 5 m
Diameter = 24 m ![]() radius = r = 12 m
radius = r = 12 m
Slant height of the cone = l
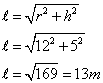
Slant height of cone = 13 m
(i) Total surface area of the tent = ![]()

(ii)Area of canvas used in stitching = total area

Solution 5
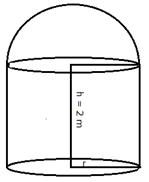
Diameter of cylindrical boiler = 3.5 m
![]()
Height (h) = 2 m
Radius of hemisphere (R) = ![]()
Total volume of the boiler = ![]()
Solution 6
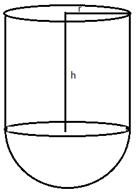
Diameter of the base = 3.5 m
Therefore, radius = ![]()
Height of cylindrical part = ![]()
(i) Capacity (volume) of the vessel = ![]()
(ii)Internal curved surface area = ![]()
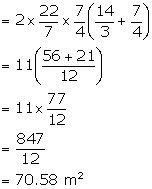
Solution 7
Height of the cone = 24 cm
Height of the cylinder = 36 cm
Radius of the cone = twice the radius of the cylinder = 10 cm
Radius of the cylinder = 5 cm
Slant height of the cone = ![]()
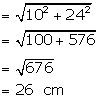
Now, the surface area of the toy = curved area of the conical point + curved area of the cylinder
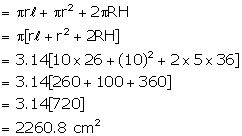
Solution 8
Diameter of cylindrical container = 42 cm
Therefore, radius (r) = 21 cm
Dimensions of rectangular solid = 22cm ![]() 14cm
14cm ![]() 10.5cm
10.5cm
Volume of solid = ![]()
Let height of water = h
Therefore, volume of water in the container = ![]()
![]()
From (i) and (ii)
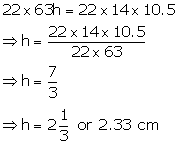
Solution 9
Diameter of spherical marble = 1.4 cm
Therefore, radius = 0.7 cm
Volume of one ball ![]()
Diameter of beaker = 7 cm
Therefore, radius = ![]()
Height of water = 5.6 cm
Volume of water = ![]()
No. of balls dropped
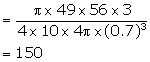
Solution 10
Breadth of the tunnel = 6 m
Height of the tunnel = 8 m
Length of the tunnel = 35 m
Radius of the semi-circle = 3 m
Circumference of the semi-circle = ![]()
Internal surface area of the tunnel
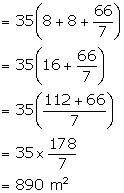
Rate of plastering the tunnel = Rs 2.25 per m2
Therefore, total expenditure ![]()
Solution 11
Length = 21 m
Depth of water = 2.4 m
Breadth = 7 m
Therefore, radius of semicircle = ![]()
Area of cross-section = area of rectangle + Area of semicircle
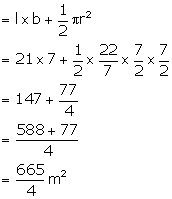
Therefore, Volume of water filled in gallons

Solution 12
Length = 21 cm, Breadth = 7 cm
Radius of semicircle = ![]()
Area of cross section of the water channel = ![]()
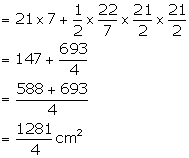
Flow of water in one minute at the rate of 20 cm per second
![]() Length of the water column = 20
Length of the water column = 20 ![]() 60 = 1200 cm
60 = 1200 cm
Therefore, volume of water =
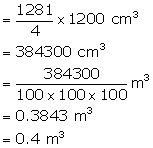
Solution 13
Diameter of the base of the cylinder = 7 cm
Therefore, radius of the cylinder = ![]()
Volume of the cylinder ![]()
Diameter of the base of the cone = ![]()
Therefore, radius of the cone = ![]()
Volume of the cone ![]()
On placing the cone into the cylindrical vessel, the volume of the remaining portion where the water is to be filled
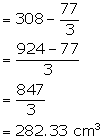
Height of new cone = ![]()
Radius = 2 cm
Therefore, volume of new cone
![]()
Volume of water which comes down = ![]()
Let h be the height of water which is dropped down.
Radius = ![]()
![]()
From (i) and (ii)
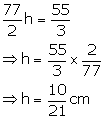
Drop in water level = ![]()
Solution 14
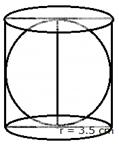
Radius of the base of the cylindrical can = 3.5 cm
(i) When the sphere is in can, then total surface area of the can =
Base area + curved surface area
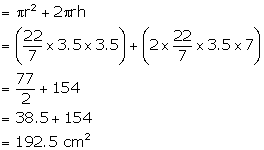
(ii) Let depth of water = x cm
When sphere is not in the can, then volume of the can =
volume of water + volume of sphere
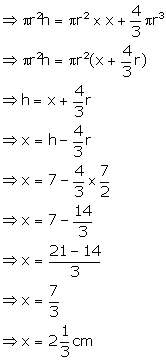
Solution 15
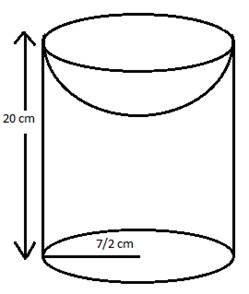
Let the height of the water level be 'h', after the solid is turned upside down.
Volume of water in the cylinder
![]()
Volume of the hemisphere
![]()
Volume of water in the cylinder
= Volume of water level - Volume of the hemisphere
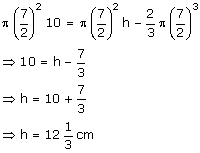
![]()
Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Exercise Ex. 20(G)
Solution 1
Let the number of solid metallic spheres be 'n'
Volume of 1 sphere
![]()
Volume of metallic cone
= ![]()
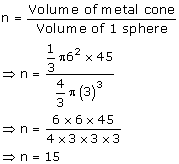
The least number of spheres needed to form the cone is 15
Solution 2
Radius of largest sphere that can be formed inside the cylinder should be equal to the radius of the cylinder.
Radius of the largest sphere = 7 cm
Volume of sphere
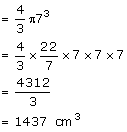
Solution 3
Let the number of cones be 'n'.
Volume of the cylinder = ![]()
Volume of ice-cream cone = Volume of cone + Volume of hemisphere


Hence, number of cones required = 10
Solution 4
Volume of the solid
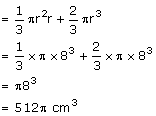
Solution 5
Diameter of a sphere = 6 cm
Radius = 3 cm
![]()
Diameter of cylindrical wire = 0.2 cm
Therefore, radius of wire = ![]()
Let length of wire = h
![]()
From (i) and (ii)
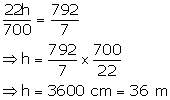
Hence, length of the wire = 36 m
Solution 6
Let edge of the cube = a
volume of the cube = ![]()
The sphere, which exactly fits in the cube, has radius = ![]()
Therefore, volume of sphere = ![]()
Volume of cube : volume of sphere
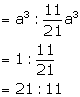
Solution 7
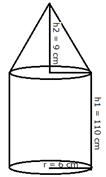
Radius of the base of poles (r) = 6 cm
Height of the cylindrical part (h1) = 110 cm
Height of the conical part (h2) = 9 cm
Total volume of the iron pole = ![]()
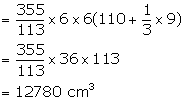
Weight of 1 cm3 = 8 gm
Therefore, total weight = 12780 ![]() 8 = 102240 gm = 102.24 kg
8 = 102240 gm = 102.24 kg
Solution 8
Length of the platform = 22 m
Circumference of semicircle = 11 m
![]()
Therefore, breadth of the rectangular part = ![]()
And length = ![]()
Now area of platform = ![]()
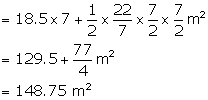
Height of the platform = 1.5 m
![]()
Rate of construction = Rs 4 per m3
Total expenditure = Rs 4 ![]() 223.125 = Rs 892.50
223.125 = Rs 892.50
Solution 9
Side of square = 7 m
Radius of semicircle = ![]()
Length of the tunnel = 80 m
Area of cross section of the front part = ![]()
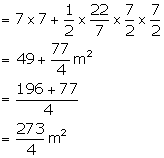
(i) Therefore, volume of the tunnel = area x length
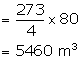
(ii) Circumference of the front of tunnel
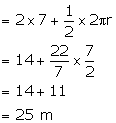
Therefore, surface area of the inner part of the tunnel
= 25 ![]() 80
80
= 2000 m2
(iii) Area of floor = l ![]() b = 7
b = 7 ![]() 80 = 560 m2
80 = 560 m2
Solution 10
Diameter of cylindrical tank = 2.8 m
Therefore, radius = 1.4 m
Height = 4.2 m
Volume of water filled in it = ![]()
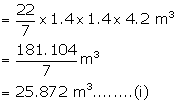
Diameter of pipe = 7 cm
Therefore, radius (r) = ![]()
Let length of water in the pipe = h1
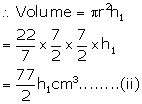
From (i) and (ii)
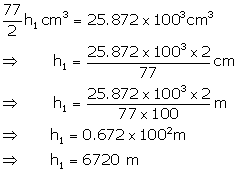
Therefore, time taken at the speed of 4 m per second
![]()
Solution 11
Rate of flow of water = 9 km/hr
Water flow in 1 hour 15 minutes
i.e. in ![]()
Area of cross-section = ![]()
Therefore, volume of water![]()
Dimensions of water tank = 7.5m × 5m × 4m
Area of tank = l × b = 7.5 × 5 = 37.5 m2
Let h be the height of water then,
37.5 × h = 28.125
![]()
Solution 12
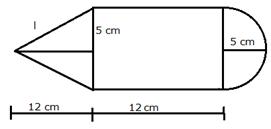
Diameter = 10 cm
Therefore, radius (r) = 5 cm
Height of the cone (h) = 12 cm
Height of the cylinder = 12 cm
![]()
(i) Total surface area of the solid
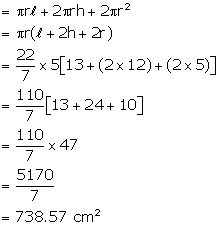
(ii) Total volume of the solid
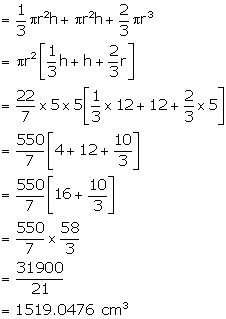
(iii) Total weight of the solid = 1.7 kg
Solution 13
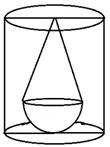
Radius of cylinder = 3 cm
Height of cylinder = 6 cm
Radius of hemisphere = 2 cm
Height of cone = 4 cm
Volume of water in the cylinder when it is full =
![]()
Volume of water displaced = volume of cone + volume of
hemisphere
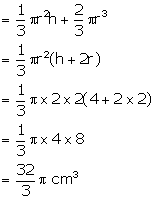
Therefore, volume of water which is left
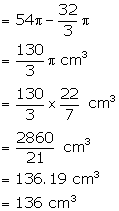
Solution 14
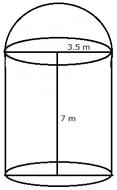
Radius of the cylinder = 3.5 m
Height = 7 m
(i) Total surface area of container excluding the base = Curved
surface area of the cylinder + area of hemisphere
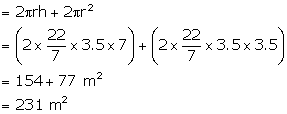
(ii) Volume of the container = ![]()
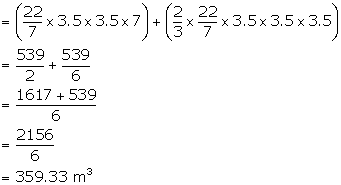
Solution 15
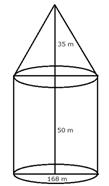
Total height of the tent = 85 m
Diameter of the base = 168 m
Therefore, radius (r) = 84 m
Height of the cylindrical part = 50 m
Then height of the conical part = (85 - 50) = 35 m
Slant height (l) ![]()
Total surface area of the tent = ![]()

Since 20% extra is needed for folds and stitching,
total area of canvas needed
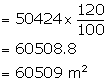
Solution 16
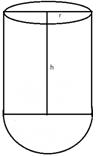
Volume of water filled in the test tube = ![]()
Volume of water filled up to 4 cm = ![]()
Let r be the radius and h be the height of test tube.
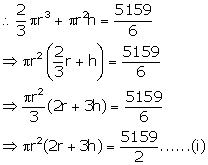
and
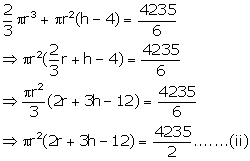
Dividing (i) by (ii)
![]()
Subtracting (ii) from (i)
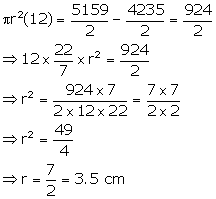
Substituting the value of r in (iii)
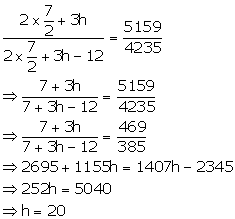
Hence, Height = 20 cm and radius = 3.5 cm
Solution 17
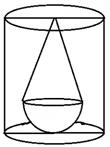
Diameter of hemisphere = 7 cm
Diameter of the base of the cone = 7 cm
Therefore, radius (r) = 3.5 cm
Height (h) = 8 cm
Volume of the solid =
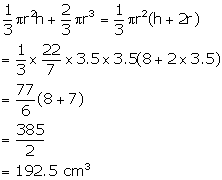
Now, radius of cylindrical vessel (R) = 7 cm
Height (H) = 10 cm
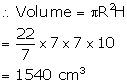
Volume of water required to fill = 1540 - 192.5 = 1347.5 cm3
Solution 18

Solution 19
Let the number of cones melted be n.
Let the radius of sphere be rs = 6 cm
Radius of cone be rc = 2 cm
And, height of the cone be h = 3 cm
Volume of sphere = n (Volume of a metallic cone)
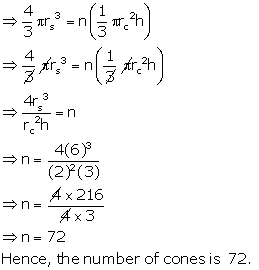
Solution 20
According to the condition in the question,
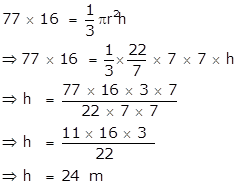
We know that,
l2 = r2 + h2
⇒ l2 = (7)2 + (24)2
⇒ l2 = 49 + 576
⇒ l2 = 625
⇒ l = 25 m
∴ Curved Surface Area = πrl = ![]() × 7× 25 = 550m2
× 7× 25 = 550m2
Therefore the height of the tent is 24m and it curved surface area is 550m2.

