Class 10 SELINA Solutions Chemistry Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding
Chemical Bonding Exercise Intext 1
Solution 1
Atoms lose, gain or share electrons to attain noble gas configuration.
Solution 2
(a) A chemical bond may be defined as the force of attraction between any two atoms, in a molecule, to maintain stability.
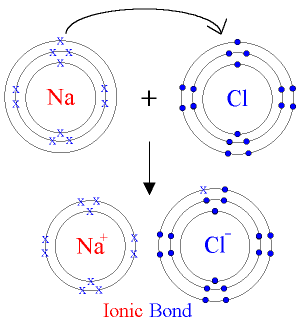
(b) The chemical bond formed between two atoms by transfer of one or more electrons from the atom of a metallic electropositive element to an atom of a non-metallic electronegative element is called as electrovalent bond.
(c) The chemical bond formed due to mutual sharing of electrons between the given pairs of atoms of non-metallic elements is called as a covalent bond.
Solution 3
Conditions for formation of Ionic bond are:
(i) The atom which changes into cation should possess 1, 2 or 3 valency electrons. The other atom which changes into anion should possess 5, 6 or 7 electrons in the valence shell.
(ii) A high difference of electronegativity of the two atoms is necessary for the formation of an Ionic bond.
(iii) There must be an overall decrease in energy i.e., energy must be released.
For this an atom should have low value of Ionisation potential and the other atom should have high value of electron affinity.
(iv) Higher the lattice energy, greater will be the case of forming an ionic compound.
Solution 4
It will form a cation: X3+
(i) X2(SO4)3
(ii) X(NO3)3
(iii) XPO4
(iv) X2(CO3)3
(v) X(OH)3
Solution 5
Atoms combine with other atoms to attain stable octet or noble gas configuration.
Solution 6
(a) X+
(b) X will be a strong reducing agent as it will have the tendency to donate its valence electron.
Solution 7
X and Y form an ionic bond in XY2.
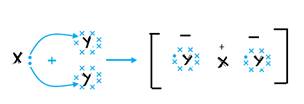 .
.
Solution 8
(a) X has 7 electrons in its outermost shell and Y has only one electron in its outermost shell so Y loses its one electron and X gains that electron to form an ionic bond.
(b) The formula of the compound would be XY.
Solution 9
i. Orbit structure and electron dot diagram of NaCl:
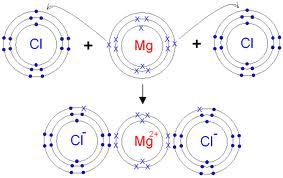
ii. Orbit structure and electron dot diagram of MgCl2:
iii. Orbit structure and electron dot diagram of CaO:
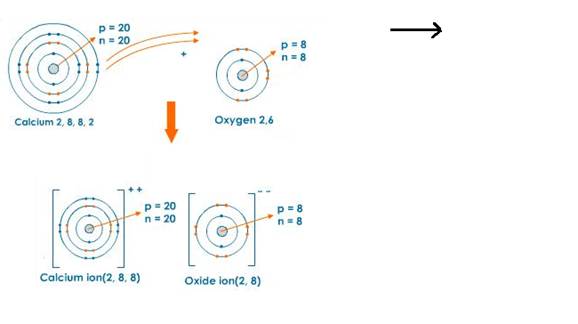
Solution 10
(a) Sodium atom and sodium ion
(i) Sodium atom has one electron in M shell while sodium ion has 8 electrons in L shell.
(ii) Sodium atom is neutral while sodium ion is positively charged.
(iii) Sodium atom is highly reactive while its ion is inert.
iv) Sodium atom is poisonous while sodium ion is non-poisonous.
(b)Chlorine atom and chlorine ion
(i) Chlorine atom has 7 electrons in its M shell while Chloride ion has 8 electrons in the same shell.
(ii) Chlorine atom is neutral while chloride ion is negatively charged.
(iii) Chlorine atom is highly reactive while its ion is inert.
iv) Chlorine gas is poisonous while chloride ion is non-poisonous.
Solution 11
Fluoride ion is negatively charged while neon atom is neutral.
Solution 12
(i) Pb → Pb2+ + 2e- (Oxidation)
(ii) Fe2+ - e- → Fe3+ (Oxidation)
(iii) A3+ + e-1→ A2+ (Reduction)
(iv) Cu → Cu2+ + 2e- (Oxidation)
Solution 13
Redox reaction means, in a reaction, one of the reactant atom undergoes reduction by gain of electrons while another reactant atom undergoes oxidation by loss of electrons simultaneously.
Solution 14 (i)
Oxidation means loss of electrons.
Reduction means gain of electrons.
Solution 14 (ii)
Electrovalent bond or ionic bond is formed by losing electrons from one atom and gaining electron by other atom i.e. redox reaction.
Solution 15
- Zn → Zn2+ + 2e- (Oxidation)
Pb2+ + 2e- → Pb (Reduction) - Zn → Zn2+ + 2e- (Oxidation)
Cu2+ + 2e-→ Cu (Reduction) - Cl2 + 2e-→ 2Cl- (Reduction)
2Br-→ Br2 + 2e- (Oxidation) - Sn2+→ Sn4+ + 2e- (Oxidation)
2Hg2+ + 2e-→ Hg2 (Reduction) - Cu+→ Cu2+ + e- (Oxidation)
Cu+ + e- → Cu (Reduction)
Solution 16
2K + Cl2→ 2KCl
i. Oxidation: In the electronic concept, oxidation is a process in which an atom or ion loses electron(s).
K → K+ + e-
ii. Reduction: In the electronic concept, the reduction is a process in which an atom or ion accepts electron(s).
Cl2 + 2e-→ 2Cl-
iii. Oxidising agent
An oxidising agent oxidises other substances either by accepting electrons or by providing oxygen or an electronegative ion, or by removing hydrogen or an electropositive ion.
Cl2 + 2e-→ 2Cl-
iv. Reducing agent
A reducing agent reduces other substances either by providing electrons or by providing hydrogen or an electropositive ion, or by removing oxygen or an electronegative ion.
K → K+ + e-
Chemical Bonding Exercise Intext 2
Solution 1
(i) Both atoms should have four or more electrons in their outermost shells, i.e., non-metals.
(ii) Both the atoms should have high electronegativity.
(iii) Both the atoms should have high electron affinity and high ionisation potential.
(iv) Electronegativity difference between the two atoms should be zero or negligible.
(v) The approach of the atoms towards one another should be accompanied by decrease of energy.
Solution 2
(a) A is a non-metal; B is a metal while C is a chemically inert element.
(b) BA
Solution 3
a.
![]()
b.
c.
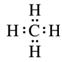
Solution 4
(a) Ionic compounds are formed as a result of the transfer of one or more electrons from the atom of a metallic electropositive element to an atom of a non-metallic electronegative element.
A polar covalent compound is the one in which there is an unequal distribution of electrons between the two atoms.
(b) Ionic compounds, made up of ions, are generally crystalline solids with high melting and boiling points.
They are soluble in water and good conductors of electricity in aqueous solution and molten state.
Covalent compounds, made up of molecules, can exist as soft solids or liquids or gases with low melting and boiling points. They are generally insoluble in water and poor conductors of electricity.
(c) Polar covalent compounds are formed between 2 non-metal atoms that have different electronegativities and therefore have unequal sharing of the bonded electron pair.
Non-polar compounds are formed when two identical non-metals equally share electrons between them.
Solution 5
The crystalline solid is ionic in nature. It has strong electrostatic forces of attraction between its ions, which cannot be separated easily.
Crystalline solids have high melting and boiling points, and a large amount of energy is required to break the strong bonding force between ions.
Water is a polar compound, so it decreases the electrostatic forces of attraction in the crystalline solid, resulting in free ions in the aqueous solution. Hence, the solid dissolves.
Solution 6
Covalent compounds are said to be polar when shared pair of electrons are unequally distributed between the two atoms. For example in HCl, the high electronegativity of the chlorine atom attracts the shared electron pair towards itself. As a result, it develops a slight negative charge and hydrogen atom develops a slight positive charge. Hence, a polar covalent bond is formed.
![]()
Solution 7
a.
|
Atom |
Electronic configuration |
Nearest noble gas |
To attain stable electronic configuration of a nearest noble gas |
|
Carbon |
126C [2,4] |
Neon [2,8] |
Carbon needs four electrons to complete the octet. |
|
Hydrogen |
11H [1] |
Helium [2] |
Hydrogen needs one electron to complete the duplet. |
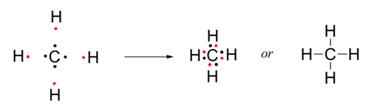
One atom of carbon shares four electron pairs, one with each of the four atoms of hydrogen.
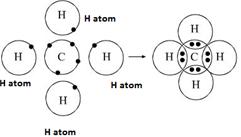
|
|
|
|
Before combination (4 [H] and 1 [C] atom) |
After combination (CH4 - Methane molecule)
|
b. Methane is a covalent compound and is non-polar in nature. This is because the shared pair of electrons is equally distributed between the two atoms. So, no charge separation takes place and the molecule is symmetrical and electrically neutral.
Solution 8
(a) Properties of Electrovalent Compounds:
1. Ionic compounds usually exist in the form of crystalline solids.
2. Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
3. Ionic compounds are generally soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents.
4. They are good conductors of electricity in the fused or in an aqueous solution state.
(b) Properties of Covalent Compounds:
1.The covalent compounds exist as gases or liquids or soft solids.
2. The melting and boiling points of covalent compounds are generally low.
3. Covalent compounds are insoluble in water but dissolve in organic solvents.
4. They are non-conductors of electricity in the solid, molten or aqueous state.
Solution 9
a.
i. Covalent bond
ii. Polar covalent bond
iii. Ionic bond
b.
i. water: Polar covalent bonding takes place in water.
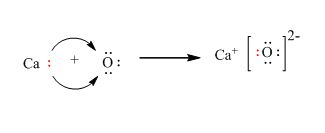
ii. calcium oxide: Electrovalent bonding takes place in calcium oxide.
Solution 10
a. Electrovalent compounds are good conductors of electricity in the fused or aqueous state because electrostatic forces of attraction between ions in the solid state are very strong and these forces weaken in the fused state or in the solution state. Hence, ions become mobile.
b. Electrovalent compounds have a strong force of attraction between the oppositely charged ions, so a large amount of energy is required to break the strong bonding force between ions. So, they have high boiling and melting points.
Covalent compounds have weak forces of attraction between the binding molecules, thus less energy is required to break the force of binding. So, they have low boiling and melting points.
c. As water is a polar compound, it decreases the electrostatic forces of attraction, resulting in free ions in the aqueous solution. Hence, electrovalent compounds dissolve.
Covalent compounds do not dissolve in water but dissolve in organic solvents. Organic solvents are non-polar; hence, these dissolve in non-polar covalent compounds.
d. Electrovalent compounds are usually hard crystals yet brittle because they have strong electrostatic forces of attraction between their ions which cannot be separated easily.
e. Polar covalent compounds conduct electricity because they form ions in their solutions.
f. If the atoms forming a covalent bond have different electro-negativities, the atom with higher electronegativity pulls the shared pair of electron towards itself. Thus, the atom with the higher electronegativity develops a partial negative charge and the atom with the lower electronegativity develops a partial positive charge. This covalent bond with some polarity is called polar covalent bond. Since there is electronegativity difference between O and H present in water molecule, water is polar compound.
Solution 11
a.
i. Y = 9
ii. Z = 12
b. Ionic bond with molecular formula ZY2.
Solution 12
|
MgCl2 - Electrovalent compound |
CCl4 - Covalent compound |
|
They are hard crystalline solids consisting of ions. |
These are gases or liquids or soft solids. |
|
They have high melting and boiling points. |
They have low melting and boiling points. |
|
They conduct electricity in the fused or aqueous state. |
They do not conduct electricity in the solid, molten or aqueous state. |
|
These are soluble in inorganic solvents but insoluble in organic solvents. |
These are insoluble in water but dissolve in organic solvents. |
Solution 13
Potassium chloride is an electrovalent compound and conducts electricity in the molten or aqueous state because the electrostatic forces of attraction weaken in the fused state or in aqueous solution.
Polar covalent compounds like hydrogen chloride ionise in their solutions and can act as an electrolyte. So, both can conduct electricity in their aqueous solutions.
Solution 14(a)
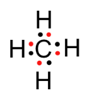

Methane Hydrogen chloride
Methane is a covalent compound and is non-polar in nature. This is because the shared pair of electrons is equally distributed between the two atoms. So, no charge separation takes place and the molecule is symmetrical and electrically neutral.
HCl is a covalent compound formed by sharing one electron between chlorine and hydrogen. Because chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen, the shared pair of electrons shifts towards the chlorine atom. So, a partial negative charge (δ-) develops on chlorine and a partial positive charge (δ+) develops on hydrogen. Hence, the covalent bond is polar in nature.
Solution 14(b)
HCl and NH3
Solution 14(c)
HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl-
NH3 + H2O →NH4+ + OH-
Solution 15
Formula of compound when combined with sulphur - MSFormula of compound when combined with chlorine - MCl2
Solution 16
(a) ![]()
(b) ![]()
(c) If the compound formed between A and B is melted and an electric current is passed through the molten compound, then element A will be obtained at the cathode and B at the anode of the electrolytic cell.
Solution 17
Correct option: (b) Mg
Element M forms a chloride with the formula MCl2 which is solid with a high melting point. M would most likely be in the group in which Magnesium is placed.
Solution 18
|
|
Sodium |
Phosphorus |
Carbon |
|
Formula of chloride |
NaCl |
PCl5 |
CCl4 |
|
Nature of bonding |
Ionic |
Covalent |
Covalent |
|
Physical state of chloride |
Solid |
Solid |
Liquid |
Solution 19
(i) Correct option: C) Covalent
The type of bonding in X molecule would be covalent.
(ii) Correct option: C) Low melting point and low boiling point
X is likely to have a low melting point and low boiling point
(iii) Correct option: D) Not conduct electricity
In the liquid state, X will not conduct electricity
Chemical Bonding Exercise Ex. 2
Solution 1
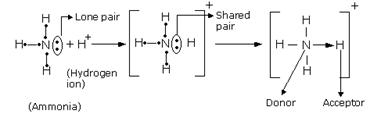
The bond formed between two atoms by sharing a pair of electrons, provided entirely by one of the combining atoms but shared by both is called a coordinate bond. It is represented by an arrow starting from the donor atoms and ending in the acceptor atom.
Conditions:
1. One of the two atoms must have at least one lone pair of electrons.
2. Another atom should be short of at least a lone pair of electrons.
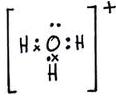
The two lone pair of electrons in the oxygen atom of water is used to form coordinate bond with the hydrogen ion which is short of an electron resulting in the formation of the hydronium ion.
H2O + H+ ![]() H3O+ Over here the hydrogen ion accepts one lone pair of electrons of the oxygen atom of water molecule leading to the formation of a coordinate covalent bond.
H3O+ Over here the hydrogen ion accepts one lone pair of electrons of the oxygen atom of water molecule leading to the formation of a coordinate covalent bond.
Solution 2
A pair of electrons which is not shared with any other atom is known as a lone pair of electrons. It is provided to the other atom for the formation of a coordinate bond.
Solution 3
a. Polar covalent bond
b. Ionic bond
c. O and H are bonded with a single covalent bond and oxygen possesses a single negative charge in the hydroxyl ion.
d. Covalent bond
e. Coordinate bond
f. Electrovalent bond, dative bond (or coordinate bond) and covalent bond
Solution 4
(a)
(i)
(ii)
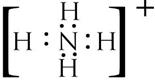
(iii)
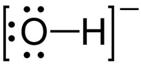
(b)
(i) Ammoniumion and hydronium ion
(ii) Phosphoruspentachloride and diamond
(iii) Hydrogen chloride and water vapour
(iv) Oxygen gas and nitrogen gas
(v) Toluene and Gasoline
(vi) ammonium chloride and sodium hydroxide
(vii) Ammonium chloride and Ammonium hydroxide
Solution 5
a. CaO - 1 calcium atom + 1 oxygen atom
Cl2 - 2 chlorine atoms
H2O - 2 hydrogen atoms + 1 oxygen atom
CCl4 - 1 carbon atom + 4 chlorine atoms
b.
Ca - will donate two electrons
O - will accept two electrons
Cl - will accept one electron, so two Cl atoms will share an electron pair.
C - will accept four electrons by sharing electrons pairs with hydrogen forming covalent bonds.
H - will donate one electron by sharing an electron pair with carbon.
Solution 6
(a) Unequal,polar
(b) Middle, equally
(c) solid
(d) Electrovalent, electrostatic
Solution 7
a.
i. Y is getting reduced.
ii. Y is positive since electrons are getting added to it and hence, it will migrate towards negative electrode that is cathode.
b.
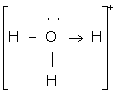
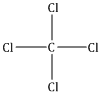
c. It is a non-polar covalent compound and does not dissolve in polar solvents like water.
Solution 8
(a) Solid
(b) No, in the formation of an ionic compound, one element is a metal and the other is a non-metal.
(c) B
(d) A
Solution 9 (a)
Magnesium oxidises and chlorine reduces during the formation of magnesium chloride.
Solution 9 (b)
(i) Covalent bond
(ii) Co-ordinate bond
Solution (2009)
a. Ammonium chloride
b.
A single covalent bond is present.
Solution (2010)
a. Oxidation
b.
i. ionic bond
ii. covalent and oordinate bond
iii. covalent bond
Solution (2011)
a.
i. Sharing
ii. high
iii. nitrogen
b.
c.
HCl is a covalent compound formed by sharing one electron between chlorine and hydrogen. Because chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen, the shared pair of electrons shifts towards the chlorine atom. So, a partial negative charge (δ-) develops on chlorine and a partial positive charge (δ+) develops on hydrogen. Hence, the covalent bond is polar in nature.
Solution (2012)
a.
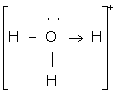
Covalent and coordinate bond
b. E = 19
F = 8
G= 17
Molecular formula: EG
Chemical bond: Ionic bond
Solution (2013)
a. Dative or coordinate bond
b. B Ammonium chloride
c. C Are insoluble in water
d.
|
Carbon tetrachloride |
Sodium chloride |
|
It is insoluble in water but dissolves in organic solvents. |
It is soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents. |
|
It is a non-conductor of electricity due to the absence of ions. |
It does not conduct electricity in the solid state but conducts electricity in the fused or aqueous state. |
Solution (2014)
a. B
b. D
c. Ionisation
d. Their constituent particles are molecules. These exist as gases or liquids or soft solids because they have weak forces of attraction between their molecules.
Solution 2016
(i) Ionic bond is formed by transfer of one electron from element W to element X.
(ii) Covalent bond is formed by sharing of electrons between elements Y and Z.