Class 10 NCERT Solutions Chemistry Chapter 4 - Carbon and its Compounds
Carbon and its Compounds Exercise 61
Solution 1
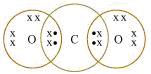
Concept insight: Recall that atomic number of carbon is 6 with electronic configuration 2,4. Atomic number of oxygen is 8 with electronic configuration 2, 6. So, carbon atom will form double covalent bond with 2 oxygen atoms in order to satisfy its octet configuration. O=C=O
Solution 2
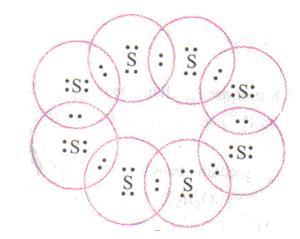
Concept Insight: Remember that atomic number of sulphur is 16 with electronic configuration of 2,8,6. Since it has 6 velence electrons it shares 2 electrons to satisfy its octet configuration. Secondly, in formation of S8 molecule, each sulphur atom shares 1 electron each with 2 adjoining sulphur atoms which results in a ring structure.
Carbon and its Compounds Exercise 68
Solution 1
Three structural isomers are possible for pentane.
(i) CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - CH3
n-Pentane
(ii)
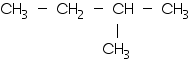
iso-Pentane
(iii)
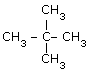
neo-Pentane
Concept Insight: While drawing structures of isomers, students should remember that the molecular formula of isomers does not change and secondly the side chains can not be present on the terminal carbons.
Solution 2
The two features of carbon that give rise to a large number of carbon compounds are as follows:
(i) Catenation - It is the ability of carbon to form bonds with other atoms of carbon.
(ii) Tetravalency - With the valency of four, carbon is capable of bonding with four other atoms.
Concept Insight: The students must learn these features of carbon as this question is often repeated.
Solution 3
Its electron dot structure is given below.
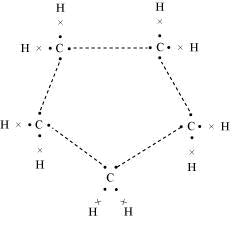
Concept Insight: Recall that the word "cyclo" indicates that it is a cyclic structure. The general formula for cyclic alkanes is CnH2n. First, make a pentagon with a carbon atom present at each vertex and then in order to complete the tetravalency, bond each carbon to two hydrogen atoms.
Carbon and its Compounds Exercise 69
Solution 4

Solution 5
(i) Bromoethane
This compound has 2 carbon atoms so its parent name is ethane and it has also a bromo group; hence its name will be bromoethane.
(ii) Methanal (formaldehyde)
This compound has 1 carbon atom so its parent name is methane and it has also a functional group -CHO (aldehyde) so its name will be methanal.
(iii) Hexyne
This compound has 6 carbon atoms so its parent name is hexane and it has also a triple bond hence its name will be hexyne.
Concept Insight: The students must learn the formulae and prefixes/suffixes of different functional groups.
Carbon and its Compounds Exercise 71
Solution 1
Since the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid involves the addition of oxygen to ethanol, it is an oxidation reaction.
Concept Insight: Recall that oxidation is gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen. In the presence of oxidising agents like alkaline potassium permanganate or acidified potassium dichromate, ethanol (C2H5OH) gains an oxygen atom as well as loses 2 hydrogen atoms and gets converted into ethanoic acid (CH3 COOH).
Solution 2
When ethyne is burnt in air, it gives a sooty flame due to incomplete combustion caused by limited supply of oxygen by air. This is the reason, why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used. However, if ethyne is burnt with oxygen, because of complete combustion, it gives a clean flame with a temperature of about 3000oC. Thus, oxy-acetylene flame is used for welding.
Concept Insight: The key to answer lies in the fact that the high temperature needed for welding can only be provided by complete combustion of ethyne.While if ethyne is burnt in air, which contains only 21% oxygen, it leads to incomplete combustion with much lesser amount of heat.
Carbon and its Compounds Exercise 74
Solution 1
Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide
Alcohols, on the other hand, do not react with sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Concept Insight: Recall that carboxylic acids react with sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate to produce carbon dioxide which is released as brisk efferevescence. When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, lime water turns milky.
Solution 2
Substances which are capable of adding oxygen to the starting material are called oxidising agents.
They provide oxygen for oxidizing other substances.
Concept insight: Remember the definition of oxidizing agents.
Carbon and its Compounds Exercise 76
Solution 1
Concept Insight: Recall that soaps form scum with hard water while detergents can be comfortably used both in hard as well as soft water.
Solution 2
When the soap is added to dirty clothes, which contains grease and oily substances, the greasy and oily dirt particles attach themselves to the hydrocarbon part and ionic part remains attached to the water forming clusters of molecules. In these clusters, the hydrophobic tails are in the interior of the cluster and the ionic ends are on the surface of the cluster. This formation is called a micelle.
When the dirty clothes are agitated in soap or detergent solution, the dirt particles attached to the hydrocarbon part get washed away in water and the clothes get cleaned.
Concept Insight: The cleansing action of soap must be understood and learnt properly as it is an important question from examination point of view.
Carbon and its Compounds Exercise 77
Solution 1
Concept insight: The students often think that since each carbon forms 4 bonds to satisfy its tetravalency the answer is 8, but they should remember that the carbon atoms are bonded to each other by a single bond, therefore the correct answer is 8-1 = 7
Solution 2
Concept Insight: Recall that organic compounds with functional group of ketones(C=O) have suffix "one" in their IUPAC names.
Solution 3
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, then it means that the fuel is not burning completely.
Concept insight: Recall that incomplete combustion of carbon results in formation of unburnt carbon particles called soot.
Carbon and its Compounds Exercise 78
Solution 4
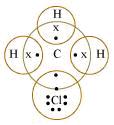
Here, carbon requires 4 electrons to complete its octet, while each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete its duplet. Also, chlorine requires an electron to complete the octet. Therefore, carbon shares one electron with each of the three atoms of hydrogen and one electron with the atom of chlorine. As a result, carbon forms 3 single covalent bonds with hydrogen and one with chlorine to form CH3Cl.
Concept insight: Recall that carbon is tetravalent atom while valency of hydrogen as well as chlorine is 1. Another important point to remember is that a covalent bond is formed by mutual sharing of electrons and therefore equal number of electrons is provided by each atom.
Solution 5
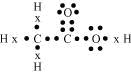
(b) H2S
(c) Propanone
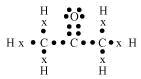
(d) F2
Concept insight: The students must remember that while drawing electron dot structure, it is imperative to depict the non bonded or lone electrons as students often only show bonded pair of electrons. Another commonly committed mistake is that students think that the shared pair of electrons is only contributed by any one atom.
Solution 6
For example, methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc are all part of the alkane homologous series. The general formula of this series is CnH2n+2.
Methane CH4
Ethane CH3CH3
Propane CH3CH2CH3
Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3
It can be noticed that there is a difference of - CH2 unit between each successive compound.
Concept insight: The students should not only learn the definition and features of homologous series but also on the basis of these, they should be able to identify the organic compounds belonging to the same homologous series.
Solution 7

Concept insight: Recall that ethanoic acid like all carboxylic acids react with metal carbonates and hydrogen carbonates to form salt, carbon dioxide and water. But alcohols do not show any reaction with metal carbonates or hydrogen carbonates.
Solution 8
A soap molecule has two parts namely the non polar (hydrocarbon) hydrophobic chain and polar (ionic) hydrophilic head, COO-Na+.
The long hydrocarbon chain being hydrophobic is insoluble in water but soluble in oil and grease. On the other hand, the ionic part of soap being hydrophilic is soluble in water but insoluble in oil and grease.
When soap is added to water, soap molecules arrange them in a cluster to keep the non-polar hydrophobic tail are towards the interior of the cluster and the polar hydrophilic head towards water. Since the dirt present on clothes is organic in nature and insoluble in water, the hydrophobic ends of the clusters attach themselves to the dirt. This cluster formation in which the dirt is entrapped is the micelle.The micelles stay in solution as a colloid and does not come together to precipitate because of ion-ion repulsion.
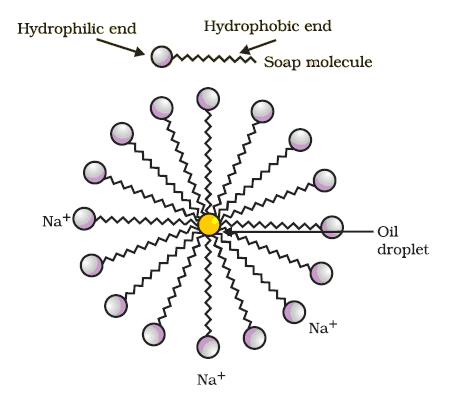
Micelle formation does not occur in alcohol because the alkyl chain of soap becomes soluble in alcohol.
Concept insight: The students must remember that the micelle formation occurs because of the difference in the nature of the two parts of soap towards water. One end (head) of the soap is ionic and therefore soluble in water while the other end (tail) is non-polar and therefore insoluble in water but soluble in organic oil and grease molecules.
Solution 9
Concept insight: Recall that combustion of carbon as well as its compounds is an exothermic reaction and therefore accompanied with the release of heat and light.
Solution 10
Concept insight: The students should remember that calcium and magnesium salts of long chain carboxylic acids are insoluble in water.
Solution 11
Concept insight: Recall that bases turn red litmus blue but have no effect on blue litmus.
Solution 12
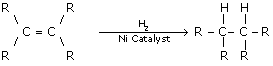
This reaction is applied in the hydrogenation of vegetables oils, which contain long chains of unsaturated carbons.
Concept insight: The key to this answer lies in the fact that an addition reaction, in organic chemistry, is in its simplest terms an organic reaction where two or more molecules combine to form a larger one.
Solution 13
Concept insight: Recall that unsaturated hydrocarbons like alkenes with general formula CnH2n and alkynes Cn H2n-2 undergo addition reactions.
Solution 14
Concept insight: Recall that saturated hydrocarbons burn with a clean blue flame without smoke.
Solution 15
A soap molecule has two parts namely the non polar (hydrocarbon) hydrophobic tail and polar (ionic) hydrophilic head, COO-Na+.
The long hydrocarbon chain being hydrophobic is insoluble in water but soluble in oil and grease. On the other hand, the ionic part of soap being hydrophilic is soluble in water but insoluble in oil and grease.
When soap is added to water, soap molecules arrange them in a cluster to keep the non-polar hydrophobic tail are towards the interior of the cluster and the polar hydrophilic head towards water. Since the dirt present on clothes is organic in nature and insoluble in water, the hydrophobic ends of the clusters attach themselves to the dirt. This cluster formation in which the dirt is entrapped is the micelle.The micelles stay in solution as a colloid and does not come together to precipitate because of ion-ion repulsion.
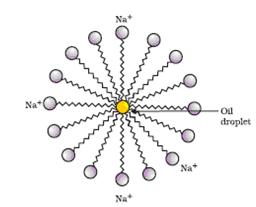
When the dirty clothes are agitated, the dirt particles attached to the hydrocarbon part get washed away in water and the clothes get cleaned.
Concept insight: The students must understand and learn the cleansing action of soap. Do not forget to substantiate your answer with a diagram of micelle. It's an important question from exam point of view.

