Getting To Know Plants Worksheet
Objective Type Questions
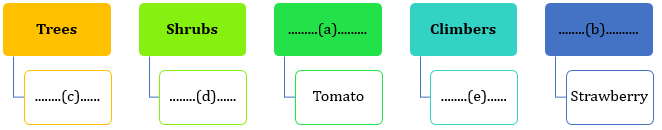
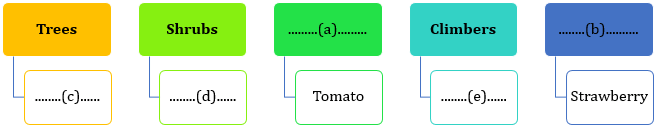
- Complete the chart below by choosing the appropriate terms given in the brackets.
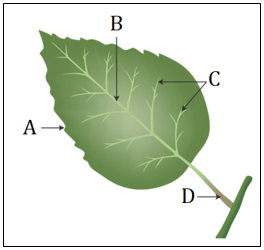
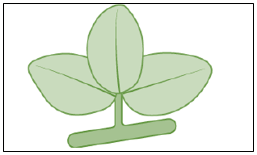
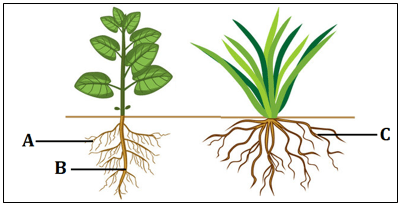
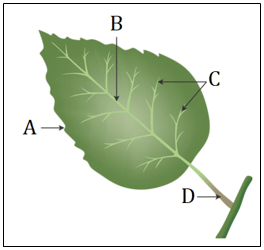
(coconut, bottle gourd, herbs, jasmine, creepers) - The diagram below shows the structure of a leaf. Label the parts A, B, C and D correctly choosing the appropriate terms from those given in the brackets.
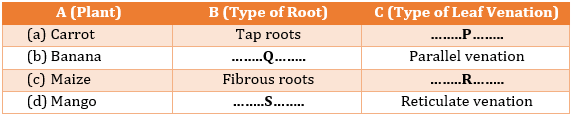
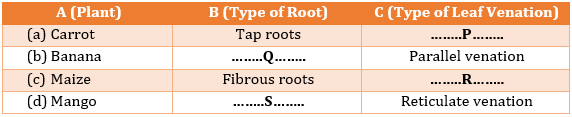
(lamina, veins, midrib, petiole, stipule, node) - Fill in the gaps to complete the table of types of roots and leaf venation found in different plants.
- Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word from those given in the brackets.
(stomata, chlorophyll, glucose, starch, oxygen)
(a) …………………. present in the leaves helps in trapping energy from sunlight.
(b) Minute pores present on the surface of leaves are called ………………….
(c) The simplest food prepared by the leaves during photosynthesis is ………………….
(d) In plants, excess food is stored in the form of …………………. in various plant parts.
(e) Photosynthesis in plants can be written as:
Carbon dioxide + Water → Food + ………………….
Multiple Choice Questions - Vipul went to a garden with his grandmother. He saw several plants there but got confused between an herb and a shrub. Which characteristics of the plant will help Vipul identify the shrubs?
(a) Green stems
(b) Hard and thick stems
(c) Branches developed at the base of the stem
(d) Branches developed in the upper part of the stem - The table shows classification of plants in various categories done by a student after reading their characteristics.
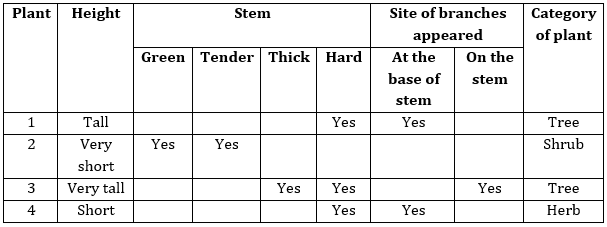
Which plant has been correctly classified by the student?
(a) Plant 1
(b) Plant 2
(c) Plant 3
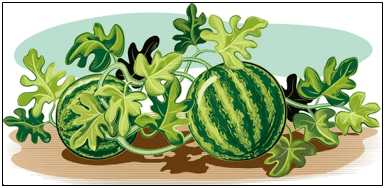
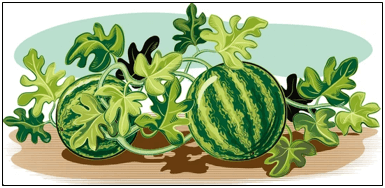
(d) Plant 4 - The image shows a watermelon plant. Richa claimed that it an herb. Is the claim made by Richa, correct?
(a) Yes, the plant has green stems, so it is an herb.
(b) Yes, the plant has several branches, so it is an herb.
(c) No, the plant has weak stems and spreads on the ground, so it is a creeper.
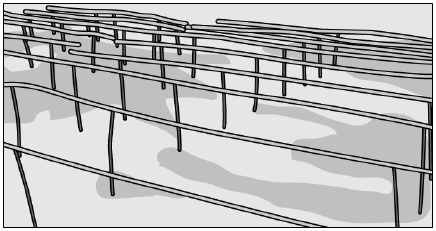
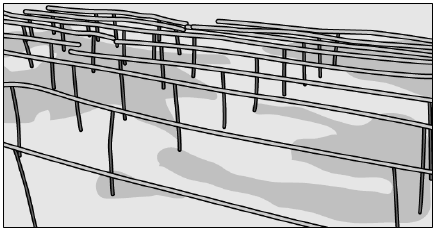
(d) No, the plant has weak stems which are supporting the watermelons on the ground, so it is a climber. - A farmer designed a home vineyard to plant grapevines, as shown in the image.
What could be the reason for the farmer to design it in this way?
(a) To make the yard beautiful as grape flowers will cover all these poles
(b) To manage the space so that some other plants can be grown along the ground
(c) To provide equal space to each grapevine as these require a lot of space to grow
(d) To get good productivity of grapes as grapevines are climbers which need support to climb upwards - When Jayesh pulled out an herb from the soil, he saw some hair-like structures attached to the plant. Which part of the plant could that be?
(a) Root
(b) Stem
(c) Leaf
(d) Flower - Disha wants to collect that part of the plant which contains its reproductive structures. What features would be possessed by that plant part?
(a) Mid-rib
(b) Stomata
(c) Root hairs
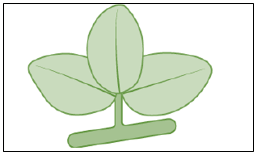
(d) Petals and sepals - Renuka observed some leaves that were attached to a stem, as shown in the image. Which part of the leaf helps them to become attached to the stem?
(a) Lamina
(b) Petiole
(c) Midrib
(d) Veins - A student observed the leaves of different plants as listed below.
In which of these plants, the student might have observed parallel venation?
(a) Banana and Peepal
(b) Mango and Neem
(c) Neem and Grass
(d) Banana and Grass - Mita wants to determine the presence of starch in that part of the plant where photosynthesis takes place. Which plant part and chemical should be chosen by Mita to perform a test to detect the presence of starch?
(a) Leaf; Iodine
(b) Leaf, Caustic soda
(c) Root; Iodine
(d) Root; Caustic soda - Kirti performed an experiment to determine the role of roots in holding the soil particles together. In pot 1, she planted an onion plant but in pot 2, she did not plant anything. It just had soil in it. Kirti watered both these pots for a week. After a week, she placed these pots inclined under tap water. What is likely to be observed by Kirti?
Pot 1 Pot 2 (a) The soil will be washed out with the flow of water The soil will be washed out with the flow of water (b) The soil will not be washed out with the flow of water The soil will not be washed out with the flow of water (c) The soil will not be washed out with the flow of water The soil will be washed out with the flow of water (d) The soil will be washed out with the flow of water The soil will not be washed out with the flow of water - Pankaj has a small plant with a main root and some smaller roots. Identify the type of root system and the type of venation shown by this plant.
(a)Tap root; Parallel venation
(b)Tap root; Reticulate venation
(c)Fibrous root; Parallel venation
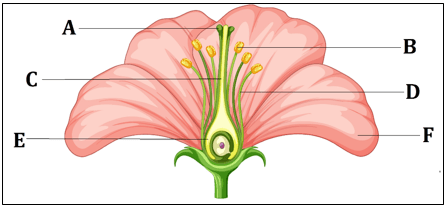
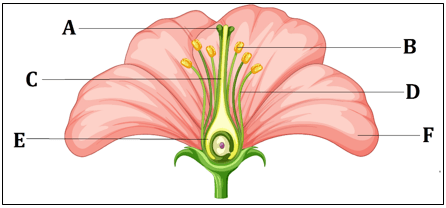
(d)Fibrous root; Reticulate venation - From the given image, identify the parts that form the pistil of a flower.
(a) A, B, C
(b) B, D, F
(c) A, C, E
(d) D, E, F
Subjective Questions - The table below lists some functions of the root and the shoot system of a plant. Categorise them as functions of the root and functions of the stem respectively.
- Sagar took a healthy, well-watered plant and enclosed one of its leafy branches in a polythene bag. After few hours, he observed some water drops on the inner side of the polythene bag.
(a) Which phenomenon is responsible for the formation of water droplets inside the polythene bag?
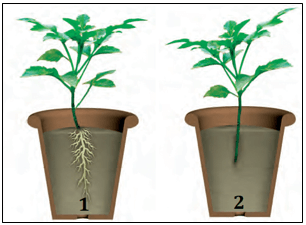
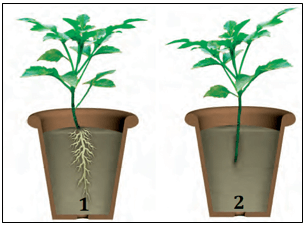
(b) Define this phenomenon. - Hrishi dug out two plants of the same kind with the roots from the soil. He planted one of these plants in pot 1, and cut off the roots of the other plant and planted it in pot 2 as shown below. He watered both these plants for a week and then compared their growth.
(a) Which pot will have a healthy plant, and what could be the reason for this?
(b) Which plant can be easily pulled out? Why?
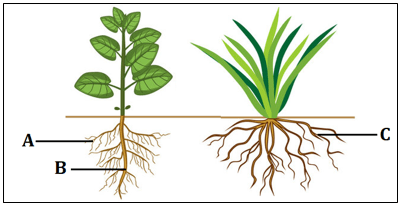
(c) Can you think of one more function of roots apart from the ones discussed in the above questions? - Given below are two types of plants with their root system.
(a) Identify the types of roots – A, B, C.
(b) Define the types of roots – A, B, C.
(c) Give two examples of plants which have root systems B and C.
(d) Which type of root system is seen in the wheat plant?
Case-Based Questions - Ravi conducted an experiment in which he filled a glass with one-third of water. He added a drop of red ink into that glass and then stirred it for few minutes. He took a tender twig and made an oblique cut at the base of its stem and then put it into the water as shown in the figure.
a) What will Ravi observe if this set up is left undisturbed overnight?
(a) Shedding of leaves from the stem
(b) Rise of the colour into the stems
(c) Development of red coloured roots
(d) Development of more branches at the stem
b) When Ravi made a cut at the base of twig stem, he observed a drop of water collected at its end. What could be the reason for the appearance of this drop of water?
(a) Conduction of water through the stem
(b) Transpiration of water through the stem
(c) Formation of dew due to water condensation
(d) Absorption of water by the stem from the surroundings
c) What can be concluded from the experiment performed by Ravi?
(a) To show that roots carry water and minerals in plants
(b) To show that stem carries water and minerals in plants
(c) To show that leaves conduct water and minerals in plants
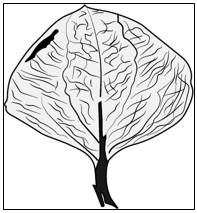
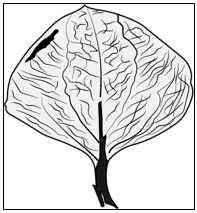
(d) To show that plants can absorb coloured liquids - Prajesh took a leaf from the mango tree and began to draw its impression with the help of a pencil and paper. Below is the sketch of the impression of the mango leaf.
a) What is the technical term for the design made by the veins of the leaf in the sketch?
b) What can you conclude from the design made by the mango leaf?
(a) Parallel; as the obtained design represents net-like veins.
(b) Parallel; as the obtained design represents parallel veins.
(c) Reticulate; as the obtained design represents net-like veins.
(d) Reticulate; as the obtained design represents parallel veins.
c) Which of the following plants can make a design like the mango leaf?
(a) Grass
(b) Bamboo
(c) Maize
(d) Hibiscus
Assertion-Reasoning Questions
Below questions consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below: - Assertion (A): A rose flower consists of five petals.
Reason (R): The sepals of a rose flower are joined together. - Assertion (A): Small, bead-like structures inside the ovary are called ovules.
Reason (R): Anther and filament are parts of a stamen.
Explore more Science Sample papers and Solutions
- Components Of Food Worksheet
- Sorting Materials Into Groups Worksheet
- Separation Of Substances Worksheet
- Body Movements Worksheet
- The Living Organisms – Characteristics and Habitats Worksheet
- Motion And Measurement Of Distances Worksheet
- Light, Shadows And Reflections Worksheet
- Electricity and Circuits Worksheet
- Fun With Magnets Worksheet
- Air Around Us Worksheet
-
Competency Based Questions for CBSE Class 6 Science
-
Sample Papers for CBSE Class 6 Science Term 1 #1
- Sample Papers for CBSE Class 6 Science Term 1 #2
-
Sample Papers for CBSE Class 6 Science Term 2 #1
- Sample Papers for CBSE Class 6 Science Term 2 #2